【数据压缩】LZ77算法原理及实现
1. 引言
LZ77算法是采用字典做数据压缩的算法,由以色列的两位大神Abraham Lempel与Jacob Ziv于1977年在《A Universal Algorithm for Sequential Data Compression》中提出。
基于统计的数据压缩编码,比如Huffman编码,需要得到先验知识——信源的字符频率,然后进行压缩。但是在大多数情况下,这种先验知识是没有预先获得的。因此,设计一种更为通用的数据压缩编码显得尤为重要。LZ77数据压缩算法应运而生,其核心思想:利用数据的重复结构信息来进行数据压缩。举个简单的例子,比如
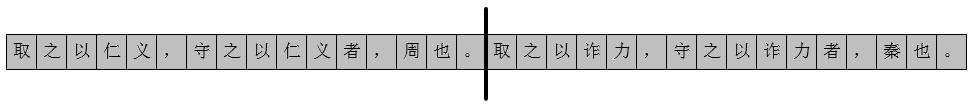
取之以仁义,守之以仁义者,周也。取之以诈力,守之以诈力者,秦也。
取之以、仁义、,、者、守之以、也、诈力、。均重复出现过,只需指出其之前出现的位置,便可表示这些词。为了指明出现位置,我们定义一个相对位置,如图
相对位置之后的消息串为取之以诈力,守之以诈力者,秦也。,若能匹配相对位置之前的消息串,则编码为以其匹配的消息串的起始与末端index;若未能匹配上,则以原字符编码。相对位置之后的消息串可编码为:[(1-3),(诈力),(6),(7-9),(诈力),(12),(6),(秦),(15-16)],如图所示:
上面的例子展示如何利用索引值来表示词,以达到数据压缩的目的。LZ77算法的核心思想亦是如此,其具体的压缩过程不过比上述例子稍显复杂而已。
2. 原理
本文讲主要讨论LZ77算法如何做压缩及解压缩,关于LZ77算法的唯一可译、无损压缩(即解压可以不丢失地还原信息)的性质,其数学证明参看原论文[1]。
滑动窗口
至于如何描述重复结构信息,LZ77算法给出了更为确切的数学解释。首先,定义字符串\(S\)的长度为\(l(s)\),其中\(S(1,j),\ 1\le j \le l(s)\)为\(S\)的前缀。对于\(S(1,j)\)且\(i\le j\),\(L(i)\)为满足下列条件的\(l\)(\(l \le l(S)-j\))的最大值:
\[ S(i,i+l-1)=S(j+1,j+l)\]
我们称字符串\(S(j+1,j+l)\)匹配了字符串\(S(i,i+l-1)\),且匹配字符串的长度为\(l\)。如图所示,存在两类情况,

接着,我们定义\(p\)为最长匹配时的\(i\),即
\[L(p) = \mathop {\max }\limits_{1 \le i \le j} \lbrace L(i)\rbrace \]
则\(S(j+1,j+L(p)\)可以由\(S(1,j)\)所生成,可以看作是\(S(1,j)\)的再生扩展(reproducible extension)。比如,\(S=00101011\)且\(j=3\),则\(L(1)=1\)因为\(S(j+1,j+1)=S(1,1)\),\(S(j+1,j+2)\ne S(1,2)\)。同样地,\(L(2)=4\),\(L(3)=0\)。因此,\(p=2\)且\(S(1,j)\)的再生扩展为\(S(j+1,j+4)\)。
在LZ77算法中,用了滑动窗口(Sliding Window)字典存储历史字符(即之前出现过的字符),Lookahead Buffer存储待压缩的字符,Cursor作为两者之间的分隔,如图所示
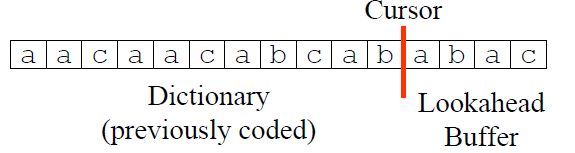
并且字典与Lookahead Buffer的长度是固定的。
压缩
用\((p,l,c)\)表示Lookahead Buffer中字符串的最长匹配结果,其中
- \(p\)表示最长匹配时,字典中字符开始时的位置(相对于Cursor位置,与上小节中定义的\(p\)有所区别),
- \(l\)为最长匹配字符串的长度,
- \(c\)指Lookahead Buffer最长匹配结束时的下一字符
压缩的过程,就是重复输出\((p,l,c)\),并将Cursor移动至\(l+1\),伪代码如下:
Repeat:
Output (p,l,c),
Cursor --> l+1
Until to the end of string压缩示例如图所示:
解压缩
为了能保证正确解码,解压缩时的滑动窗口长度与压缩时一样。在解压缩,遇到\((p,l,c)\)大致分为三类情况:
- \(p==0\)且\(l==0\),即初始情况,直接解码\(c\);
- \(p>=l\),解码为字典
dict[p:p+l+1]; - \(p<l\),即出现循环编码,需要从左至右循环拼接,伪代码如下:
for(i = p, k = 0; k < length; i++, k++)
out[cursor+k] = dict[i%cursor]比如,dict=abcd,编码为(2,9,e),则解压缩为output=abcdcdcdcdcdce。
3. 实现
用bitarray编码实现请参看A Python LZ77-Compressor,下面给出简单的python实现。
# coding=utf-8
class LZ77:
"""
A simplified implementation of LZ77 algorithm
"""
def __init__(self, window_size):
self.window_size = window_size
self.buffer_size = 4
def longest_match(self, data, cursor):
"""
find the longest match between in dictionary and lookahead-buffer
"""
end_buffer = min(cursor + self.buffer_size, len(data))
p = -1
l = -1
c = ''
for j in range(cursor+1, end_buffer+1):
start_index = max(0, cursor - self.window_size + 1)
substring = data[cursor + 1:j + 1]
for i in range(start_index, cursor+1):
repetition = len(substring) / (cursor - i + 1)
last = len(substring) % (cursor - i + 1)
matchedstring = data[i:cursor + 1] * repetition + data[i:i + last]
if matchedstring == substring and len(substring) > l:
p = cursor - i + 1
l = len(substring)
c = data[j+1]
# unmatched string between the two
if p == -1 and l == -1:
return 0, 0, data[cursor + 1]
return p, l, c
def compress(self, message):
"""
compress message
:return: tuples (p, l, c)
"""
i = -1
out = []
# the cursor move until it reaches the end of message
while i < len(message)-1:
(p, l, c) = self.longest_match(message, i)
out.append((p, l, c))
i += (l+1)
return out
def decompress(self, compressed):
"""
decompress the compressed message
:param compressed: tuples (p, l, c)
:return: decompressed message
"""
cursor = -1
out = ''
for (p, l, c) in compressed:
# the initialization
if p == 0 and l == 0:
out += c
elif p >= l:
out += (out[cursor-p+1:cursor+1] + c)
# the repetition of dictionary
elif p < l:
repetition = l / p
last = l % p
out += (out[cursor-p+1:cursor+1] * repetition + out[cursor-p+1:last] + c)
cursor += (l + 1)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
compressor = LZ77(6)
origin = list('aacaacabcabaaac')
pack = compressor.compress(origin)
unpack = compressor.decompress(pack)
print pack
print unpack
print unpack == 'aacaacabcabaaac'4. 参考资料
[1] Jacob Ziv and Abraham Lempel, A Universal Algorithm for Sequential Data Compression.
[2] guyb, 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World.