.NET NLog 详解(五) - Condition Expression
Sample
<!-- during normal execution only log Info messages -->
<defaultFilter>level >= LogLevel.Info</defaultFilter>
<!-- if there is at least one error, log everything from trace level -->
<when exists="level >= LogLevel.Error" filter="level >= LogLevel.Trace" />实现将字符串转换成表达式进行逻辑判断,然后做出相应的动作。这个过程的实现使用Condition Expression。
从简单的例子开始:
public void BooleanOperatorTest()
{
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "false or false");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "false or true");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "true or false");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "true or true");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "false and false");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "false and true");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "true and false");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "true and true");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "not true");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "not false");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "not not false");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "not not true");
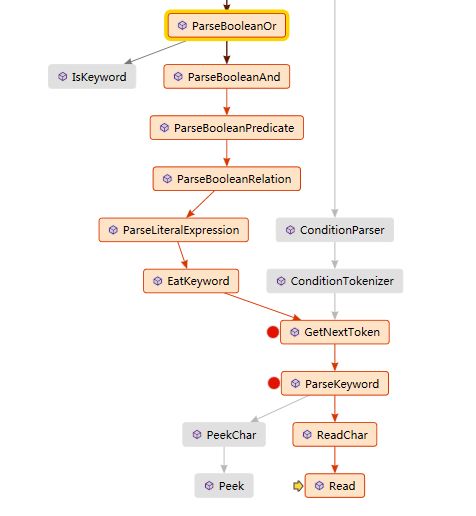
}输入的是字符串false or false,我们希望的结果是得到false,大概的过程是这样的:
CondtionParser
/// <summary>
/// Condition parser. Turns a string representation of condition expression
/// into an expression tree.
/// </summary>
public class ConditionParser第一步就是初始化这个Parser
var parser = new ConditionParser(new SimpleStringReader(expressionText), configurationItemFactories);顺带初始化了tokenizer
private ConditionParser(SimpleStringReader stringReader, ConfigurationItemFactory configurationItemFactory)
{
this.configurationItemFactory = configurationItemFactory;
this.tokenizer = new ConditionTokenizer(stringReader);
}构造函数里直接取到了第一个token false
public ConditionTokenizer(SimpleStringReader stringReader)
{
this.stringReader = stringReader;
this.TokenType = ConditionTokenType.BeginningOfInput;
this.GetNextToken();
}获取的过程也比较的简单,一个接一个的读入char,遇到非指定的字符即停止
private void ParseKeyword(char ch)
{
int i;
this.TokenType = ConditionTokenType.Keyword;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.Append((char)ch);
this.ReadChar();
while ((i = this.PeekChar()) != -1)
{
if ((char)i == '_' || (char)i == '-' || char.IsLetterOrDigit((char)i))
{
sb.Append((char)this.ReadChar());
}
else
{
break;
}
}
this.TokenValue = sb.ToString();
}这里有一系列比较复杂的表达式树生成的过程:
private ConditionExpression ParseBooleanOr()
{
ConditionExpression expression = this.ParseBooleanAnd();
while (this.tokenizer.IsKeyword("or") || this.tokenizer.IsToken(ConditionTokenType.Or))
{
this.tokenizer.GetNextToken();
expression = new ConditionOrExpression(expression, this.ParseBooleanAnd());
}
return expression;
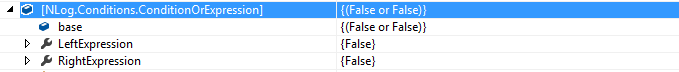
}最后拿到的表达式树是这样的:
左右的表达式为ConditionLiteralExpression。
private ConditionExpression ParseLiteralExpression()
{
//......
if (this.tokenizer.TokenType == ConditionTokenType.Keyword)
{
string keyword = this.tokenizer.EatKeyword();
if (0 == string.Compare(keyword, "level", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return new ConditionLevelExpression();
}
if (0 == string.Compare(keyword, "logger", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return new ConditionLoggerNameExpression();
}
if (0 == string.Compare(keyword, "message", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return new ConditionMessageExpression();
}
if (0 == string.Compare(keyword, "loglevel", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
this.tokenizer.Expect(ConditionTokenType.Dot);
return new ConditionLiteralExpression(LogLevel.FromString(this.tokenizer.EatKeyword()));
}
if (0 == string.Compare(keyword, "true", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return new ConditionLiteralExpression(true);
}再来个例子:
public void ConditionMethodsTest()
{
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "starts-with('foobar','foo')");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "starts-with('foobar','bar')");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "ends-with('foobar','bar')");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "ends-with('foobar','foo')");
AssertEvaluationResult(0, "length('')");
AssertEvaluationResult(4, "length('${level}')");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "equals(1, 2)");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "equals(3.14, 3.14)");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "contains('foobar','ooba')");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "contains('foobar','oobe')");
AssertEvaluationResult(false, "contains('','foo')");
AssertEvaluationResult(true, "contains('foo','')");
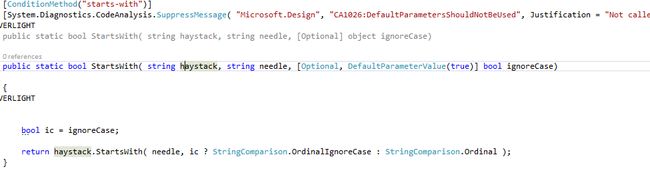
}这里出现了一些条件方法starts-with,ends-with,equals,contains,可以通过这些操作,当log的message包含特定的字符串的时候才写日志
[ConditionMethod("starts-with")]是以属性反射的方式在初始化的时候加载的。
在parse的过程中,多一步判断是否是ConditionMethods并创建实例
private ConditionMethodExpression ParsePredicate(string functionName)
{
try
{
var methodInfo = this.configurationItemFactory.ConditionMethods.CreateInstance(functionName);
return new ConditionMethodExpression(functionName, methodInfo, par);
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
if (exception.MustBeRethrown())
{
throw;
}
throw new ConditionParseException("Cannot resolve function '" + functionName + "'", exception);
}
}那么怎么知道该字符串是否是ConditionMethods呢?这里还是简单从左到右一个个的吃字符。
public string EatKeyword()
{
if (this.TokenType != ConditionTokenType.Keyword)
{
throw new ConditionParseException("Identifier expected");
}
string s = (string)this.TokenValue;
this.GetNextToken();
return s;
}当出现特殊的char时候做出判断。
private static ConditionTokenType[] BuildCharIndexToTokenType()
{
CharToTokenType[] charToTokenType =
{
new CharToTokenType('(', ConditionTokenType.LeftParen),
new CharToTokenType(')', ConditionTokenType.RightParen),
new CharToTokenType('.', ConditionTokenType.Dot),
new CharToTokenType(',', ConditionTokenType.Comma),
new CharToTokenType('!', ConditionTokenType.Not),
new CharToTokenType('-', ConditionTokenType.Minus),
};