gradle项目中资源文件的相对路径打包处理技巧
开发java application时,不管是用ant/maven/gradle中的哪种方式来构建,通常最后都会打包成一个可执行的jar包程序,而程序运行所需的一些资源文件(配置文件),比如jdbc.properties, log4j2.xml,spring-xxx.xml这些,可以一起打包到jar中,程序运行时用类似classpath*:xxx.xml的去加载,大多数情况下,这样就能工作得很好了。
但是,如果有一天,需要修正配置,比如:一个应用上线初期,为了调试方便,可能会把log的日志级别设置低一些,比如:INFO级别,运行一段时间稳定以后,只需要记录WARN或ERROR级别的日志,这时候就需要修改log4j2.xml之类的配置文件,如果把配置文件打包在jar文件内部,改起来就比较麻烦,要把重新打包部署,要么在线上,先用jar命令将jar包解压,改好后,再打包回去,比较繁琐。
面对这种需求,更好的方式是把配置文件放在jar文件的外部相对目录下,程序启动时去加载相对目录下的配置文件,这样改起来,就方便多了,下面演示如何实现:(以gradle项目为例)
主要涉及以下几点:
1、如何不将配置文件打包到jar文件内
既然配置文件放在外部目录了,jar文件内部就没必要再重复包含这些文件了,可以修改build.gradle文件,参考下面这样:
processResources {
exclude { "**/*.*" }
}
相当于覆盖了默认的processResouces task,这样gradle打包时,资源目录下的任何文件都将排除。
2、log4j2的配置加载处理
log4j2加载配置文件时,默认情况下会找classpath下的log4j2.xml文件,除非手动给它指定配置文件的位置,分析它的源码,可以找到下面这段:org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.ConfigurationFactory.Factory#getConfiguration(java.lang.String, java.net.URI)
1 public Configuration getConfiguration(final String name, final URI configLocation) { 2 3 if (configLocation == null) { 4 final String configLocationStr = this.substitutor.replace(PropertiesUtil.getProperties() 5 .getStringProperty(CONFIGURATION_FILE_PROPERTY)); 6 if (configLocationStr != null) { 7 ConfigurationSource source = null; 8 try { 9 source = getInputFromUri(NetUtils.toURI(configLocationStr)); 10 } catch (final Exception ex) { 11 // Ignore the error and try as a String. 12 LOGGER.catching(Level.DEBUG, ex); 13 } 14 if (source == null) { 15 final ClassLoader loader = LoaderUtil.getThreadContextClassLoader(); 16 source = getInputFromString(configLocationStr, loader); 17 } 18 if (source != null) { 19 for (final ConfigurationFactory factory : getFactories()) { 20 final String[] types = factory.getSupportedTypes(); 21 if (types != null) { 22 for (final String type : types) { 23 if (type.equals("*") || configLocationStr.endsWith(type)) { 24 final Configuration config = factory.getConfiguration(source); 25 if (config != null) { 26 return config; 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 } else { 34 for (final ConfigurationFactory factory : getFactories()) { 35 final String[] types = factory.getSupportedTypes(); 36 if (types != null) { 37 for (final String type : types) { 38 if (type.equals("*")) { 39 final Configuration config = factory.getConfiguration(name, configLocation); 40 if (config != null) { 41 return config; 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 } else { 49 // configLocation != null 50 final String configLocationStr = configLocation.toString(); 51 for (final ConfigurationFactory factory : getFactories()) { 52 final String[] types = factory.getSupportedTypes(); 53 if (types != null) { 54 for (final String type : types) { 55 if (type.equals("*") || configLocationStr.endsWith(type)) { 56 final Configuration config = factory.getConfiguration(name, configLocation); 57 if (config != null) { 58 return config; 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 66 Configuration config = getConfiguration(true, name); 67 if (config == null) { 68 config = getConfiguration(true, null); 69 if (config == null) { 70 config = getConfiguration(false, name); 71 if (config == null) { 72 config = getConfiguration(false, null); 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 if (config != null) { 77 return config; 78 } 79 LOGGER.error("No log4j2 configuration file found. Using default configuration: logging only errors to the console."); 80 return new DefaultConfiguration(); 81 }
其中常量CONFIGURATION_FILE_PROPERTY的定义为:
public static final String CONFIGURATION_FILE_PROPERTY = "log4j.configurationFile";
从这段代码可以看出,只要在第一次调用log4j2的getLogger之前设置系统属性,将其指到配置文件所在的位置即可。
3、其它一些配置文件(比如spring配置)的相对路径加载
这个比较容易,spring本身就支持从文件目录加载配置的能力。
综合以上分析,可以封装一个工具类:
1 import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; 2 import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; 3 4 import java.io.File; 5 6 7 public class ApplicationContextUtil { 8 9 private static ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; 10 11 private static ApplicationContextUtil instance = null; 12 13 public static ApplicationContextUtil getInstance() { 14 if (instance == null) { 15 synchronized (ApplicationContextUtil.class) { 16 if (instance == null) { 17 instance = new ApplicationContextUtil(); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 return instance; 22 } 23 24 public ConfigurableApplicationContext getContext() { 25 return context; 26 } 27 28 private ApplicationContextUtil() { 29 30 } 31 32 33 static { 34 35 //加载log4j2.xml 36 String configLocation = "resources/log4j2.xml"; 37 File configFile = new File(configLocation); 38 if (!configFile.exists()) { 39 System.err.println("log4j2 config file:" + configFile.getAbsolutePath() + " not exist"); 40 System.exit(0); 41 } 42 System.out.println("log4j2 config file:" + configFile.getAbsolutePath()); 43 44 try { 45 //注:这一句必须放在整个应用第一次LoggerFactory.getLogger(XXX.class)前执行 46 System.setProperty("log4j.configurationFile", configFile.getAbsolutePath()); 47 } catch (Exception e) { 48 System.err.println("log4j2 initialize error:" + e.getLocalizedMessage()); 49 System.exit(0); 50 } 51 52 //加载spring配置文件 53 configLocation = "resources/spring-context.xml"; 54 configFile = new File(configLocation); 55 56 if (!configFile.exists()) { 57 System.err.println("spring config file:" + configFile.getAbsolutePath() + " not exist"); 58 System.exit(0); 59 } 60 61 System.out.println("spring config file:" + configFile.getAbsolutePath()); 62 63 if (context == null) { 64 context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(configLocation); 65 System.out.println("spring load success!"); 66 } 67 68 } 69 70 71 }
注:这里约定了配置文件放在相对目录resources下,而且log4j2的配置文件名为log4j2.xml,spring的入口配置文件为spring-context.xml(如果不想按这个约定来,可参考这段代码自行修改)
有了这个工具类,mainclass入口程序上可以这么用:
1 import org.slf4j.Logger; 2 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 5 /** 6 * Created by yangjunming on 12/15/15. 7 * author: [email protected] 8 */ 9 public class App { 10 11 private static ApplicationContext context; 12 private static Logger logger; 13 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 17 context = ApplicationContextUtil.getInstance().getContext(); 18 logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(App.class); 19 20 System.out.println("start ..."); 21 22 logger.debug("debug message"); 23 24 logger.info("info message"); 25 26 logger.warn("warn message"); 27 28 logger.error("error message"); 29 30 System.out.println(context.getBean(SampleObject.class)); 31 32 } 33 }
再次友情提醒:logger的实例化,一定要放在ApplicationContextUtil.getInstance().getContext();之后,否则logger在第一次初始化时,仍然尝试会到classpath下去找log4j2.xml文件,实例化之后,后面再设置系统属性就没用了。
4、gradle 打包的处理
代码写完了,还有最后一个工作没做,既然配置文件不打包到jar里了,那就得复制到jar包的相对目录resources下,可以修改build.gradle脚本,让计算机处理处理,在代替手动复制配置文件。
task pack(type: Copy, dependsOn: [clean, installDist]) {
sourceSets.main.resources.srcDirs.each {
from it
into "$buildDir/install/$rootProject.name/bin/resources"
}
}
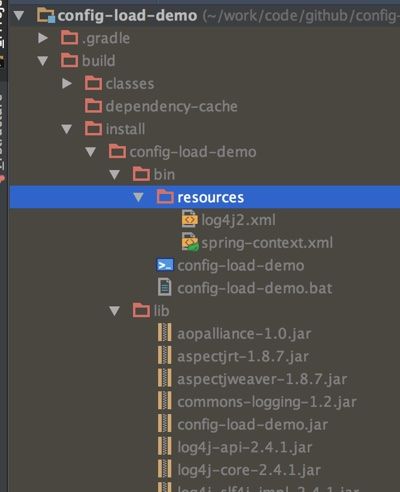
增加这个task后,直接用gradle pack 就可以实现打包,并自动复制配置文件到相对目录resources目录下了,参考下图:
最后国际惯例,给个示例源码:https://github.com/yjmyzz/config-load-demo
gradle pack 后,可进入build/install/config-load-demo/bin 目录,运行./config-load-demo (windows下运行config-load-demo.bat) 查看效果,然后尝试修改resources/log4j2.xml里的日志级别,再次运行,观察变化 。