组合模式(Composite)
一、组合模式介绍
组合模式:将对象组合成树形结构以表示:部分--整体 的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
java中的组合是指:在A类里定义一个B类的引用,A拥有了B,叫组合。只是单纯的组合而已,而不是一种设计模式。
组合和组合模式不是一回事!
基本上见到的树形结构都使用到了组合模式。
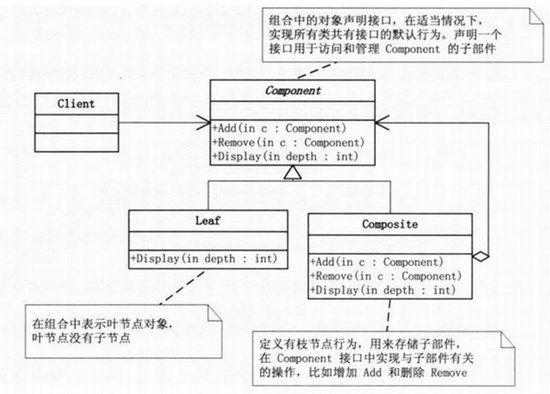
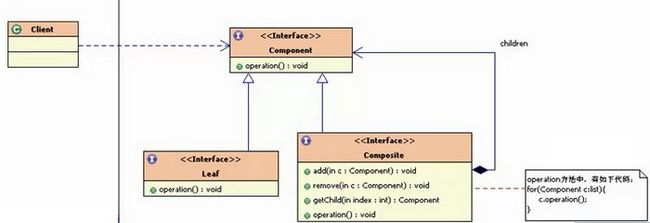
组合模式结构图:
组合模式中有几个核心的部分:
Leaf(叶子):表示该节点下面没有其他子节点了,就称为叶子
Compostie(容器构件):容器构件,该节点下还有其他子节点,理解为一个容器,里面包含了其他子节点。就叫做容器构件
Component(抽象构件):抽象构件中定义了叶子和容器构件的共同点。比如,有公共的添加删除叶子功能,有显示节点功能。
例如:Windows中的文件管理
二、组合模式代码实现
首先,定义一个抽象的Component。提供一系列的公共接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//Component(抽象构件):抽象构件中定义了叶子和容器构件的共同点。比如,有公共的添加删除叶子功能,有显示节点功能。
public
abstract
class
Component {
protected
String name;
public
Component(String name) {
super
();
this
.name = name;
}
public
abstract
void
add(Component c);
public
abstract
void
remove(Component c);
public
abstract
void
display(
int
depth);
}
|
然后定义具体的叶子节点,和容器节点
定义叶子节点,由于叶子节点中没有子节点了,所以不需要add和remove的具体实现
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
//表示该节点下面没有其他子节点了,就称为叶子
public
class
Leaf
extends
Component {
public
Leaf(String name) {
super
(name);
}
@Override
public
void
add(Component c) {
System.out.println(
"leaf no add"
);
}
@Override
public
void
remove(Component c) {
System.out.println(
"leaf no remove"
);
}
@Override
public
void
display(
int
depth) {
StringBuffer sb =
new
StringBuffer(
"-"
);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <= depth; i++) {
sb.append(
"-"
);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString()+name);
}
}
|
再定义一个容器节点
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.List;
//容器构件,该节点下还有其他子节点,理解为一个容器,里面包含了其他子节点。就叫做容器构件
public
class
Composite
extends
Component{
private
List<Component> children =
new
ArrayList<Component>();
public
Composite(String name) {
super
(name);
}
@Override
public
void
add(Component c) {
children.add(c);
}
@Override
public
void
remove(Component c) {
children.remove(c);
}
@Override
public
void
display(
int
depth) {
StringBuffer sb =
new
StringBuffer(
"-"
);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <= depth; i++) {
sb.append(
"-"
);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString()+name);
for
(Component com : children) {
com.display(depth +
2
);
}
}
}
|
最后客户端测试代码:添加一个树形结构
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
Composite root =
new
Composite(
"root"
);
root.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf A"
));
root.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf B"
));
Composite comp =
new
Composite(
"Composite X"
);
comp.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf XA"
));
comp.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf XB"
));
root.add(comp);
Composite comp2 =
new
Composite(
"Composite XY"
);
comp2.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf XYA"
));
comp2.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf XYB"
));
comp.add(comp2);
root.add(
new
Leaf(
"Leaf C"
));
Leaf leaf =
new
Leaf(
"Leaf D"
);
root.add(leaf);
// root.remove(leaf);//这里可以删除某节点
root.display(
1
);
}
|
打印结果如下:
---root
-----Leaf A
-----Leaf B
-----Composite X
-------Leaf XA
-------Leaf XB
-------Composite XY
---------Leaf XYA
---------Leaf XYB
-----Leaf C
-----Leaf D
三、总结
开发中应用场景:
操作系统中的资源管理器
GUI中的容器层次图
XML文件解析
OA系统中,组织结构的处理
Junit单元测试框架
Java23种设计模式学习笔记【目录总贴】
参考资料:
大话设计模式(带目录完整版).pdf
HEAD_FIRST设计模式(中文版).pdf
尚学堂_高淇_java300集最全视频教程_【GOF23设计模式】