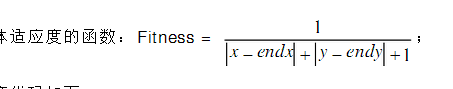遗传算法在走迷宫游戏中的应用
我的数据挖掘算法库:https://github.com/linyiqun/DataMiningAlgorithm
我的算法库:https://github.com/linyiqun/lyq-algorithms-lib
前言
遗传(GA)算法是一个非常有意思的算法,因为他利用了生物进化理论的知识进行问题的求解。算法的核心就是把拥有更好环境适应度的基因遗传给下一代,这就是其中的关键的选择操作,遗传算法整体的阶段分为选择,交叉和变异操作,选择操作和变异操作在其中又是比较重要的步骤。本篇文章不会讲述GA算法的具体细节,之前我曾经写过一篇专门的文章介绍过此算法,链接:http://blog.csdn.net/androidlushangderen/article/details/44041499,里面介绍了一些基本的概念和算法的原理过程,如果你对GA算法掌握的还不错的话,那么对于理解后面遗传算法在走迷宫的应用来说应该不是难事。
算法在迷宫游戏中的应用
先说说走迷宫游戏要解决的问题是什么, 走迷宫游戏说白了就是给定起点,终点,中间设置一堆的障碍,然后要求可达的路径,注意这里指的是可达路径,并没有说一定是最优路径,因为最优路径一定是用步数最少的,这一点还是很不同的。而另一方面,遗传算法也是用来搜索问题最优解的,所以刚刚好可以转移到这个问题上。用一个遗传算法去解决生活中的实际问题最关键的就是如何用遗传算法中的概念表示出来,比如遗传算法中核心的几个概念,基因编码,基因长度的设置,适应度函数的定义,3个概念每个都很重要。好的,目的要求已经慢慢的明确了,下面一个个问题的解决。
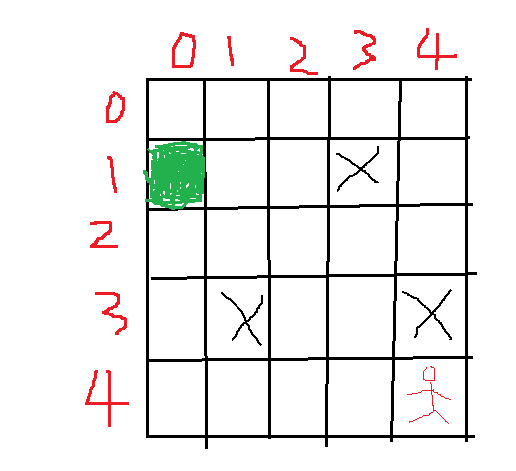
为了能让大家更好的理解,下面举出一个例子,如图所示:
图是自己做的,比较简略,以左边点的形式表示,从图中可以看出,起点位置(4, 4),出口左边为绿色区域位置(1,0),X符号表示的障碍区域,不允许经过,问题就转为搜索出从起点到终点位置的最短路径,因为本身例子构造的不是很复杂,我们按照对角线的方式出发,总共的步数=4-1 + 4-0=7步,只要中间不拐弯,每一步都是靠近目标点方向的移动就是最佳的方式。下面看看如何转化成遗传算法中的概念表示。
个体基因长度
首先是基于长度,因为最后筛选出的是一个个体,就是满足条件的个体,他的基因编码就是问题的最优解,所以就能联想把角色的每一步移动操作看出是一个基因编码,总共7步就需要7个基因值表示,所以基因的长度在本例子中就是7。
基因表示
已经将角色的每一次的移动步骤转化为基因的表示,每次的移动总共有4种可能,上下左右,基因编码是标准的二进制形式,所以可以取值为00代表向上,01向下,10向左,11向右,也就是说,每个基因组用2个编码表示,所以总共的编码数字就是2*7=14个,两两一对。
适应度函数
适应度函数的设置应该是在遗传算法中最重要了吧,以为他的设置好坏直接决定着遗传质量的好坏,基因组表示的移动的操作步骤,给定起点位置,通过基因组的编码组数据,我们可以计算出最终的抵达坐标,这里可以很容易的得出结论,如果最后的抵达坐标越接近出口坐标,就越是我们想要的结果,也就是适应值越高,所以我们可以用下面的公式作为适应度函数:
(x, y)为计算出的适应值的函数值在0到1之间波动,1为最大值,就是抵达的坐标恰好是出口位置的时候,当然适应度函数的表示不是唯一的。
算法的代码实现
算法地图数据的输入mapData.txt:
0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 1
就是上面图示的那个例子.
算法的主要实现类GATool.java:
package GA_Maze;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 遗传算法在走迷宫游戏的应用-遗传算法工具类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class GATool {
// 迷宫出入口标记
public static final int MAZE_ENTRANCE_POS = 1;
public static final int MAZE_EXIT_POS = 2;
// 方向对应的编码数组
public static final int[][] MAZE_DIRECTION_CODE = new int[][] { { 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, };
// 坐标点方向改变
public static final int[][] MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE = new int[][] {
{ -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 }, };
// 方向的文字描述
public static final String[] MAZE_DIRECTION_LABEL = new String[] { "上",
"下", "左", "右" };
// 地图数据文件地址
private String filePath;
// 走迷宫的最短步数
private int stepNum;
// 初始个体的数量
private int initSetsNum;
// 迷宫入口位置
private int[] startPos;
// 迷宫出口位置
private int[] endPos;
// 迷宫地图数据
private int[][] mazeData;
// 初始个体集
private ArrayList<int[]> initSets;
// 随机数产生器
private Random random;
public GATool(String filePath, int initSetsNum) {
this.filePath = filePath;
this.initSetsNum = initSetsNum;
readDataFile();
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*/
public void readDataFile() {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
int rowNum = dataArray.size();
mazeData = new int[rowNum][rowNum];
for (int i = 0; i < rowNum; i++) {
String[] data = dataArray.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < data.length; j++) {
mazeData[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(data[j]);
// 赋值入口和出口位置
if (mazeData[i][j] == MAZE_ENTRANCE_POS) {
startPos = new int[2];
startPos[0] = i;
startPos[1] = j;
} else if (mazeData[i][j] == MAZE_EXIT_POS) {
endPos = new int[2];
endPos[0] = i;
endPos[1] = j;
}
}
}
// 计算走出迷宫的最短步数
stepNum = Math.abs(startPos[0] - endPos[0])
+ Math.abs(startPos[1] - endPos[1]);
}
/**
* 产生初始数据集
*/
private void produceInitSet() {
// 方向编码
int directionCode = 0;
random = new Random();
initSets = new ArrayList<>();
// 每个步骤的操作需要用2位数字表示
int[] codeNum;
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
codeNum = new int[stepNum * 2];
for (int j = 0; j < stepNum; j++) {
directionCode = random.nextInt(4);
codeNum[2 * j] = MAZE_DIRECTION_CODE[directionCode][0];
codeNum[2 * j + 1] = MAZE_DIRECTION_CODE[directionCode][1];
}
initSets.add(codeNum);
}
}
/**
* 选择操作,把适值较高的个体优先遗传到下一代
*
* @param initCodes
* 初始个体编码
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<int[]> selectOperate(ArrayList<int[]> initCodes) {
double randomNum = 0;
double sumFitness = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> resultCodes = new ArrayList<>();
double[] adaptiveValue = new double[initSetsNum];
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
adaptiveValue[i] = calFitness(initCodes.get(i));
sumFitness += adaptiveValue[i];
}
// 转成概率的形式,做归一化操作
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
adaptiveValue[i] = adaptiveValue[i] / sumFitness;
}
for (int i = 0; i < initSetsNum; i++) {
randomNum = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
randomNum = randomNum / 100;
//因为1.0是无法判断到的,,总和会无限接近1.0取为0.99做判断
if(randomNum == 1){
randomNum = randomNum - 0.01;
}
sumFitness = 0;
// 确定区间
for (int j = 0; j < initSetsNum; j++) {
if (randomNum > sumFitness
&& randomNum <= sumFitness + adaptiveValue[j]) {
// 采用拷贝的方式避免引用重复
resultCodes.add(initCodes.get(j).clone());
break;
} else {
sumFitness += adaptiveValue[j];
}
}
}
return resultCodes;
}
/**
* 交叉运算
*
* @param selectedCodes
* 上步骤的选择后的编码
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<int[]> crossOperate(ArrayList<int[]> selectedCodes) {
int randomNum = 0;
// 交叉点
int crossPoint = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> resultCodes = new ArrayList<>();
// 随机编码队列,进行随机交叉配对
ArrayList<int[]> randomCodeSeqs = new ArrayList<>();
// 进行随机排序
while (selectedCodes.size() > 0) {
randomNum = random.nextInt(selectedCodes.size());
randomCodeSeqs.add(selectedCodes.get(randomNum));
selectedCodes.remove(randomNum);
}
int temp = 0;
int[] array1;
int[] array2;
// 进行两两交叉运算
for (int i = 1; i < randomCodeSeqs.size(); i++) {
if (i % 2 == 1) {
array1 = randomCodeSeqs.get(i - 1);
array2 = randomCodeSeqs.get(i);
crossPoint = random.nextInt(stepNum - 1) + 1;
// 进行交叉点位置后的编码调换
for (int j = 0; j < 2 * stepNum; j++) {
if (j >= 2 * crossPoint) {
temp = array1[j];
array1[j] = array2[j];
array2[j] = temp;
}
}
// 加入到交叉运算结果中
resultCodes.add(array1);
resultCodes.add(array2);
}
}
return resultCodes;
}
/**
* 变异操作
*
* @param crossCodes
* 交叉运算后的结果
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<int[]> variationOperate(ArrayList<int[]> crossCodes) {
// 变异点
int variationPoint = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> resultCodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] array : crossCodes) {
variationPoint = random.nextInt(stepNum);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i += 2) {
// 变异点进行变异
if (i % 2 == 0 && i / 2 == variationPoint) {
array[i] = (array[i] == 0 ? 1 : 0);
array[i + 1] = (array[i + 1] == 0 ? 1 : 0);
break;
}
}
resultCodes.add(array);
}
return resultCodes;
}
/**
* 根据编码计算适值
*
* @param code
* 当前的编码
* @return
*/
public double calFitness(int[] code) {
double fintness = 0;
// 由编码计算所得的终点横坐标
int endX = 0;
// 由编码计算所得的终点纵坐标
int endY = 0;
// 基于片段所代表的行走方向
int direction = 0;
// 临时坐标点横坐标
int tempX = 0;
// 临时坐标点纵坐标
int tempY = 0;
endX = startPos[0];
endY = startPos[1];
for (int i = 0; i < stepNum; i++) {
direction = binaryArrayToNum(new int[] { code[2 * i],
code[2 * i + 1] });
// 根据方向改变数组做坐标点的改变
tempX = endX + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][0];
tempY = endY + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][1];
// 判断坐标点是否越界
if (tempX >= 0 && tempX < mazeData.length && tempY >= 0
&& tempY < mazeData[0].length) {
// 判断坐标点是否走到阻碍块
if (mazeData[tempX][tempY] != -1) {
endX = tempX;
endY = tempY;
}
}
}
// 根据适值函数进行适值的计算
fintness = 1.0 / (Math.abs(endX - endPos[0])
+ Math.abs(endY - endPos[1]) + 1);
return fintness;
}
/**
* 根据当前编码判断是否已经找到出口位置
*
* @param code
* 经过若干次遗传的编码
* @return
*/
private boolean ifArriveEndPos(int[] code) {
boolean isArrived = false;
// 由编码计算所得的终点横坐标
int endX = 0;
// 由编码计算所得的终点纵坐标
int endY = 0;
// 基于片段所代表的行走方向
int direction = 0;
// 临时坐标点横坐标
int tempX = 0;
// 临时坐标点纵坐标
int tempY = 0;
endX = startPos[0];
endY = startPos[1];
for (int i = 0; i < stepNum; i++) {
direction = binaryArrayToNum(new int[] { code[2 * i],
code[2 * i + 1] });
// 根据方向改变数组做坐标点的改变
tempX = endX + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][0];
tempY = endY + MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][1];
// 判断坐标点是否越界
if (tempX >= 0 && tempX < mazeData.length && tempY >= 0
&& tempY < mazeData[0].length) {
// 判断坐标点是否走到阻碍块
if (mazeData[tempX][tempY] != -1) {
endX = tempX;
endY = tempY;
}
}
}
if (endX == endPos[0] && endY == endPos[1]) {
isArrived = true;
}
return isArrived;
}
/**
* 二进制数组转化为数字
*
* @param binaryArray
* 待转化二进制数组
*/
private int binaryArrayToNum(int[] binaryArray) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = binaryArray.length - 1, k = 0; i >= 0; i--, k++) {
if (binaryArray[i] == 1) {
result += Math.pow(2, k);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 进行遗传算法走出迷宫
*/
public void goOutMaze() {
// 迭代遗传次数
int loopCount = 0;
boolean canExit = false;
// 结果路径
int[] resultCode = null;
ArrayList<int[]> initCodes;
ArrayList<int[]> selectedCodes;
ArrayList<int[]> crossedCodes;
ArrayList<int[]> variationCodes;
// 产生初始数据集
produceInitSet();
initCodes = initSets;
while (true) {
for (int[] array : initCodes) {
// 遗传迭代的终止条件为是否找到出口位置
if (ifArriveEndPos(array)) {
resultCode = array;
canExit = true;
break;
}
}
if (canExit) {
break;
}
selectedCodes = selectOperate(initCodes);
crossedCodes = crossOperate(selectedCodes);
variationCodes = variationOperate(crossedCodes);
initCodes = variationCodes;
loopCount++;
//如果遗传次数超过100次,则退出
if(loopCount >= 100){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("总共遗传进化了" + loopCount + "次");
printFindedRoute(resultCode);
}
/**
* 输出找到的路径
*
* @param code
*/
private void printFindedRoute(int[] code) {
if(code == null){
System.out.println("在有限的遗传进化次数内,没有找到最优路径");
return;
}
int tempX = startPos[0];
int tempY = startPos[1];
int direction = 0;
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
"起始点位置({0},{1}), 出口点位置({2}, {3})", tempX, tempY, endPos[0],
endPos[1]));
System.out.print("搜索到的结果编码:");
for(int value: code){
System.out.print("" + value);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0, k = 1; i < code.length; i += 2, k++) {
direction = binaryArrayToNum(new int[] { code[i], code[i + 1] });
tempX += MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][0];
tempY += MAZE_DIRECTION_CHANGE[direction][1];
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
"第{0}步,编码为{1}{2},向{3}移动,移动后到达({4},{5})", k, code[i], code[i+1],
MAZE_DIRECTION_LABEL[direction], tempX, tempY));
}
}
}
算法的调用类Client.java:
package GA_Maze;
/**
* 遗传算法在走迷宫游戏的应用
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//迷宫地图文件数据地址
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\lyq\\Desktop\\icon\\mapData.txt";
//初始个体数量
int initSetsNum = 4;
GATool tool = new GATool(filePath, initSetsNum);
tool.goOutMaze();
}
}
算法的输出:
我测了很多次的数据,因为有可能会一时半会搜索不出来,我设置了最大遗传次数100次。
总共遗传进化了2次 起始点位置(4,4), 出口点位置(1, 0) 搜索到的结果编码:10100000100010 第1步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(4,3) 第2步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(4,2) 第3步,编码为00,向上移动,移动后到达(3,2) 第4步,编码为00,向上移动,移动后到达(2,2) 第5步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(2,1) 第6步,编码为00,向上移动,移动后到达(1,1) 第7步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(1,0) 总共遗传进化了8次 起始点位置(4,4), 出口点位置(1, 0) 搜索到的结果编码:10001000101000 第1步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(4,3) 第2步,编码为00,向上移动,移动后到达(3,3) 第3步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(3,2) 第4步,编码为00,向上移动,移动后到达(2,2) 第5步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(2,1) 第6步,编码为10,向左移动,移动后到达(2,0) 第7步,编码为00,向上移动,移动后到达(1,0) 总共遗传进化了100次 在有限的遗传进化次数内,没有找到最优路径
算法小结
遗传算法在走迷宫中的应用总体而言还是非常有意思的如果你去认真的体会的话,至少让我更加深入的理解了GA算法,如果博友向要亲自实现这算法,我给几点建议,第一是迷宫难度的和初始个体数量的设置,为什么要注意这2点呢,一个是这关系到遗传迭代的次数,在一段时间内有的时候遗传算法是找不出来的,如果找不出来,PC机的CPU会持续高速的计算,所以不要让遗传进行无限制的进行,最好做点次数限制,也可能是我的本本配置太烂了。。在算法的调试中修复了一个之前没发现的bug,就是选择阶段的时候对于随机数的判断少考虑了一种情形,当随机数取到1.0的时候,其实是不能判断到的,因为概念和只会无限接近1,就不知道被划分到哪个区域中了。