Spring入门
Spring入门
基本概述
Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson 在其著作Expert One-On-One J2EE Development and Design中阐述的部分理念和原型衍生而来。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 J2EE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。然而,Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。Spring的核心是控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP)。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
Spring是什么?
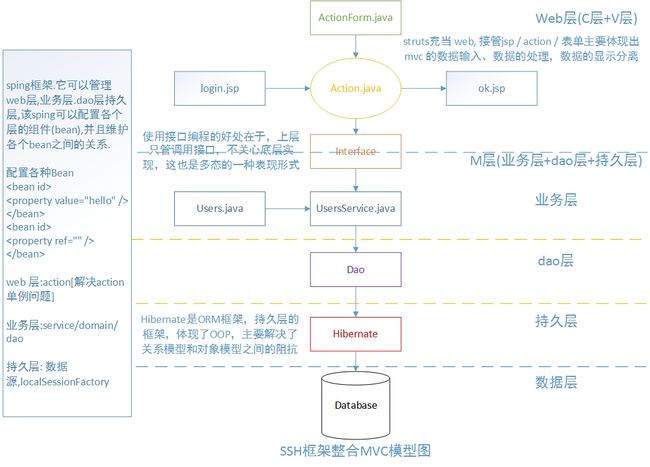
1、Spring是容器框架,用于配置Bean,并维护Bean之间关系的框架。(Struts是web框架,管理jsp、action、actionform)(hibernate是ORM框架,处于持久层)
2、spring中的核心概念是IOC(Inverse of Control控制反转)或者叫做DI(Dependency injection 依赖注入)和AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming 面向切面编程)。
3、spring是用Bean来管理组件的,bean可以是Java中的任意一种对象(javabean,service,action,数据源,dao等)。
SHH框架整合MVC模型图
PS:这可以和前端时间写的Hibernate入门、Struts入门、Web MVC模式实现、Hibernate框架整合这四篇博客里的MVC模式进行比较。
Spring入门案例
1、引入spring开发包(最小配置spring.jar,common-logging.jar)。
2、创建spring核心文件applicationContext.xml(该文件一般放在src目录下,该文件引入xsd文件,可以从案例项目中拷贝)。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> </beans>
3、配置bean。
<!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) -->
<!-- bean元素的作用是,加载spring框架时,spring会自动创建bean对象,放入内存 相当于 UserService userService
= new UserService(); userService.setName("zs"); -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.pc.service.UserService">
<!-- 这里就体现出注入的概念 -->
<property name="name">
<value>zs</value>
</property>
<!-- 在userService中引用user2Service bean-->
<property name="user2Service" ref="user2Service"/>
</bean>
<bean id="user2Service" class="com.pc.service.User2Service">
<property name="name" value="ls"/>
</bean>
4、测试。
// 使用传统方法,调用UserService中的printOK()
// UserService userService = new UserService();
// userService.setName("zs");
// userService.printOK();
// 采用Spring框架来实现上述功能
// 1.得到spring的applicationContext对象(容器对象)
// ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 用工具类获取单态 applicationContext
ApplicationContext applicationContext = ApplicationContextUtil.getApplicationContext();
// 2.获取bean
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.printOK();
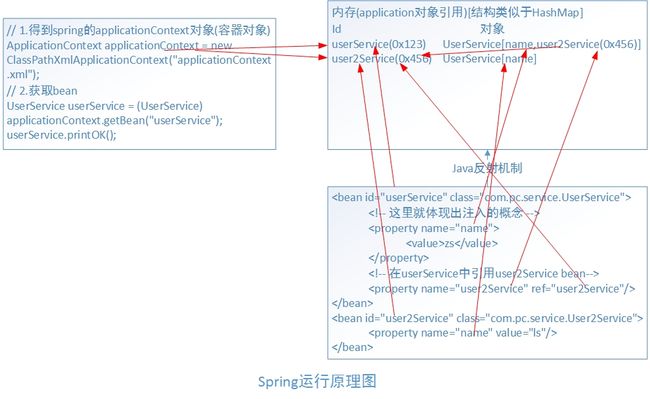
spring运行原理图
总结
1、当ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");执行的时候,spring容器对象被创建,同时applicaionContext.xml中配置 bean就会被创建。
2、UserService us=(UserService) ac.getBean("userService");us.sayHello();可以使用bean。
3、spring实际上是一个容器框架,可以配置各种bean(action/service/domain/dao),并且可以维护bean与bean的关系,当需要使用某个bean的时候,可以使用getBean(id)。
IOC是什么?
ioc(inverse of controll ) 控制反转: 所谓控制反转就是把创建对象(bean),和维护对象(bean)的关系的权利从程序中转移到spring的容器(applicationContext.xml),而程序本身不再维护。
DI是什么?
di(dependency injection) 依赖注入: 实际上di和ioc是同一个概念,spring设计者认为di更准确表示spring核心技术。
Spring的接口编程
spring开发提倡接口编程,配合di技术可以层与层的解耦。
案例:字母大小写转换
思路:
1、创建一个接口ChangeLetter
package com.pc.inter;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 字母转换接口
* @description 可以将字母转换的接口
*
*/
public interface ChangeLetter {
// 提供一个字母大小写转换的方法
public String change();
}
2、两个类UpperLetter和LowerLetter实现接口
package com.pc.inter;
import com.pc.inter.ChangeLetter;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 小写转大写
* @description
*
*/
public class UpperLetter implements ChangeLetter {
private String str;
@Override
public String change() {
// 把小写字母->大写
return str.toUpperCase();
}
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
}
package com.pc.inter;
import com.pc.inter.ChangeLetter;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 大写转小写
* @description
*
*/
public class LowerLetter implements ChangeLetter{
private String str;
@Override
// 大写转小写
public String change() {
return str.toLowerCase();
}
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
}
3、对象配置到Spring容器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) --> <!-- <bean id="changeLetter" class="com.pc.inter.UpperLetter"> <property name="str"> <value>abcdefg</value> </property> </bean> --> <bean id="changeLetter" class="com.pc.inter.LowerLetter"> <property name="str" value="GFEDCBA"/> </bean> </beans>
4、使用
package com.pc.inter;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
*
* @author Switch
* @function 测试Spring接口编程类
* @description
*
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/inter/beans.xml");
// 获取,不用接口
// UpperLetter upperLetter = (UpperLetter) applicationContext.getBean("changeLetter");
// System.out.println(upperLetter.change());
// 使用接口访问bean
ChangeLetter changeLetter = (ChangeLetter) applicationContext.getBean("changeLetter");
System.out.println(changeLetter.change());
}
}
PS:通过上述案例,可以发现Spring的DI特性配合接口编程,可以减少上层对下层实现的依赖,也就是说在WEB开发中,可以减少WEB层和业务层的耦合度。
ApplicationContext和Bean工厂
应用上下文(ApplicationContext)
建立在Bean工厂的基础之上,提供系统架构服务。
基本语法:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“上下文XML”);
应用上下文的功能
1.提供文本信息解析工具,包括对国际化支持。
2.提供载入文件资源的通用方法,如图片。
3.可以向注册为监听器的bean发送事件。
Bean工厂
最简单的容器,提供基础的依赖注入支持,创建各种类型的Bean。
基本语法:
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource(“上下文XML”));
beanFactory.getBean(“bean”);
PS:bean工厂只是把bean的定义信息载进来,用的时候才会进行实例化。
案例:
package com.pc.ioc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 从ApplicationContext中取bean
// 当实例化beans.xml时,该文件中配置的bean被实例化
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/ioc/beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
// 使用BeanFactory获取bean,只是实例化该容器,那么容器的bean不被实例化
// 只有去使用getBean获取某个bean时,才会实时创建
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("com/pc/ioc/beans.xml"));
Student student2 = (Student) beanFactory.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student2.getName());
}
小结
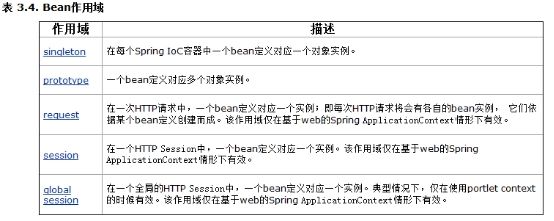
1、如果使用ApplicationContext,则配置的bean如果是singleton不管用不用,都被实例化(好处就是可以预先加载,缺点就是耗内存),如果bean的scope=”prototype|request|session| globalSession”,并不会预加载,而是交给程序去维护。
2、如果是 BeanFactory ,则获取beanfactory时候,配置的bean不会被马上实例化,使用的时候,才被实例(好处节约内存,缺点就是速度)。
3、规定: 一般没有特殊要求,应当使用ApplicatioContext完成。
Bean的scope的细节
配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <!-- 在容器文件中配置bean(service/dao/domain/action/数据源) --> <!-- 配置成singleton,会预先加载,其他配置不会 --> <!-- singleton,prototype适用于所有Java应用,request,session,globalSession只适用于Web应用 --> <!-- <bean id="student" class="com.pc.ioc.Student" scope="singleton"> --> <bean id="student" class="com.pc.ioc.Student" scope="prototype"> <property name="name" value="zs" /> </bean> </beans>
测试案例
// 使用singleton的scope时候,两个对象是相同的
// 使用prototype的scope时候,两个对象是不同的
// web开发,才能使用request,session,global-session
Student student3 = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
Student student4 = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student3 + " " + student4);
三种获取ApplicationContext对象引用的方法
1、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext -> 从类路径加载
2、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext -> 从文件路径加载
3、XmlWebApplicationContext -> 从Web系统中加载
案例:
// 通过类路径加载
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/pc/ioc/beans.xml");
// 通过文件路径加载
ApplicationContext applicationContext2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("XML上下文绝对路径");
Student student5 = (Student) applicationContext2.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student5.getName());
// 通过Web路径加载
ApplicationContext applicationContext3 = new XmlWebApplicationContext();