Lucene 实例教程(三)之操作索引
作者: 永恒の_☆ 地址: http://blog.csdn.net/chenghui0317/article/details/10366255
一、 前言
前面简单介绍了如何使用Lucene将索引 写入磁盘,并且提供IKAnalyzer中文分词器操作索引和检索索引文件,地址:http://blog.csdn.net/chenghui0317/article/details/10281311
在项目实战中,这还不能完全解决一些比较棘手的问题,比如:
1、之前介绍了如何写入索引,但是没有提供删除索引和修改索引的操作,所以索引文件的累加会产生脏数据或者数据重复。
二、使用Lucene实战
1、使用Lucene操作索引文件
实现的思路如下:
<1> 原先使用的IndexReader操作索引不是很方便,只有执行IndexReader.Close()时,删除操作才会被真正执行,并且这种方式的IndexReader实例方法被改为过期的方法,所以这种方式不可取; <2> 既然写入索引的时候使用的是IndexWriter索引写入器,同样删除和修改也一样使用它来完成;
<4> 删除索引的实现方式:需要先判断一下索引文件是否存在,如果存在使用IndexWriter写入器调用deleteDocument()即可;
<5> 修改索引的实现方式:由于IndexWriter写入器没有直接提供updateDocument(),所以可以先将要修改前的索引删除了然后再写入修改后的索引,实现效果一样;
<6> 最后不要忘记把IndexWriter 关闭了,否则资源一直被占用,浪费内存开销。
具体代码如下:
package com.lucene.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.document.Document;
import org.apache.lucene.document.Field;
import org.apache.lucene.index.CorruptIndexException;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexReader;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriterConfig;
import org.apache.lucene.index.Term;
import org.apache.lucene.queryParser.ParseException;
import org.apache.lucene.queryParser.QueryParser;
import org.apache.lucene.search.Query;
import org.apache.lucene.store.Directory;
import org.apache.lucene.store.LockObtainFailedException;
import org.apache.lucene.store.SimpleFSDirectory;
import org.apache.lucene.util.Version;
import org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzer;
import com.lucene.entity.Article;
/**
* Lucene 检索和操作索引的例子
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class OperateIndexDemo {
public static final String INDEX_DIR_PATH = "indexDir";
/* 创建简单中文分析器 创建索引使用的分词器必须和查询时候使用的分词器一样,否则查询不到想要的结果 */
private Analyzer analyzer = null;
// 索引保存目录
private File indexFile = null;
//目录对象,因为操作索引文件都要用到它,所以定义为全局变量
private Directory directory = null;
//创建IndexWriter索引写入器
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = null;
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = null;
/**
* 初始化方法
* @throws IOException
*/
public void init() throws IOException{
analyzer = new IKAnalyzer(true);
indexFile = new File(INDEX_DIR_PATH);
directory = new SimpleFSDirectory(indexFile);
simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("*****************初始化成功**********************");
}
/**
* 将article对象的属性全部封装成document对象,重构之后方便创建索引
* @param article
* @return
*/
public Document createDocument(Article article){
Document document = new Document();
document.add(new Field("id", article.getId().toString(),Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.NOT_ANALYZED));
document.add(new Field("title", article.getTitle().toString(),Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.ANALYZED));
document.add(new Field("content", article.getContent().toString(),Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.ANALYZED));
return document;
}
/**
* 获得指定格式的时间字符串
* @return
*/
public String getDate(){
return simpleDateFormat.format(new Date());
}
/**
* 为了如实反映操作索引文件之后的效果,每次操作之后查询索引目录下所有的索引内容
* @throws IOException
* @throws CorruptIndexException
*/
public void openIndexFile() throws CorruptIndexException, IOException{
System.out.println("*****************读取索引开始**********************");
IndexReader indexReader = IndexReader.open(directory);
int docLength = indexReader.maxDoc();
for (int i = 0; i < docLength; i++) {
Document doc = indexReader.document(i);
Article article = new Article();
if (doc.get("id") == null) {
System.out.println("id为空");
} else {
article.setId(Integer.parseInt(doc.get("id")));
article.setTitle(doc.get("title"));
article.setContent(doc.get("content"));
}
System.out.println(article);
}
System.out.println("*****************读取索引结束**********************\n");
}
/**
* 创建索引到索引文件中
* @param article
* @throws IOException
* @throws LockObtainFailedException
* @throws CorruptIndexException
*/
public void createIndex(Article article) throws CorruptIndexException, LockObtainFailedException, IOException{
indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_36, analyzer);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
indexWriter.addDocument(createDocument(article));
indexWriter.close();
System.out.println("[ " + getDate() + " ] Lucene写入索引到 [" + indexFile.getAbsolutePath() + "] 成功。");
}
/**
* 根据文件中的id删除对应的索引文件
* @param contentId
* @throws IOException
* @throws ParseException
*/
public void deleteIndex(String contentId) throws IOException, ParseException{
//判断索引文件目录内容是否有索引,有返回true ,没有返回false
if(IndexReader.indexExists(directory)){
indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_36, analyzer);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
//封装term去检索字段名为id ,具体值为contentId的记录,如果存在就会删除,否则什么都不做
indexWriter.deleteDocuments(new Term("id",contentId));
/*
QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_36, "id", analyzer);
Query query = queryParser.parse(contentId);
indexWriter.deleteDocuments(query);
*/
indexWriter.close();
System.out.println("[ " + getDate() + " ] Lucene删除索引到 [" + indexFile.getAbsolutePath() + "] 成功。");
}else{
throw new IOException("[ " + getDate() + " ] Lucene删除索引失败,在 " + indexFile.getAbsolutePath() + "目录中没有找到索引文件。" );
}
}
/**
* 由于实际的内容修改,所以索引文件也要跟着修改 ,具体实现方式就是先删除索引,然后重新添加
* @param article
* @throws IOException
* @throws ParseException
*/
public void updateIndex(Article article) throws IOException, ParseException{
deleteIndex(article.getId().toString());
createIndex(article);
}
/**
* 销毁当前的操作类的实现,主要关闭资源的连接
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public void destory() throws IOException{
analyzer.close();
directory.close();
System.out.println("*****************销毁成功**********************");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
OperateIndexDemo luceneInstance = new OperateIndexDemo();
try {
luceneInstance.init();//初始化
Article article = new Article(1,"标题不是很长","内容也不长。但是句号很长。。。。。。。。。。");
luceneInstance.createIndex(article);
luceneInstance.openIndexFile();
luceneInstance.deleteIndex("1");
luceneInstance.openIndexFile();
//article = new Article(1,"修改之后的标题","内容变短了");
//luceneInstance.updateIndex(article);
//luceneInstance.openIndexFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
luceneInstance.destory();//销毁
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
上面的代码 做了一些重构和优化,每一个方法都只做一件事情,分工非常明确。
init() ------> 用于实例化全局的变量;
createDocument(Article article) ------> 用于将article对象的属性全部封装成document对象,重构之后方便创建索引;
openIndexFile() ------> 为了如实反映操作索引文件之后的效果,每次操作之后查询索引目录下所有的索引内容;
createIndex(Article article) ------> 用于将索引写入磁盘中;
deleteIndex(String contentId) ------> 用于将索引文件的索引删除;
updateIndex(Article article) ------> 用于修改索引文件中的索引;
destory() ------> 用于释放资源 关闭目录连接。
<1>首先,调用createDocument(Article article) ,具体效果如下:
根据提示,然后看到索引文件目录,表明 索引已经写入成功了。
另外需要说明的是:
1、每次操作的 IndexWriterConfig的实例不能被使用两次以上,否则如下错误:
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.lucene.util.SetOnce$AlreadySetException: The object cannot be set twice!
所以只能实例化后用一次,即使是同一类型的操作也不行。
2、整个应用程序的执行周期是:(1)实例化; (2)初始化; (3)具体操作; (4)销毁。
如果directory已经关闭还继续操作directory目录对象,就会报如下错误:
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.lucene.store.AlreadyClosedException: this Directory is closed
<2>接下里看看deleteIndex(String contentId)这个方法,先要判断索引文件内是否有索引文件,如果有 则会去索引目录下找对应的索引,有则会删除,没有则什么都不做。
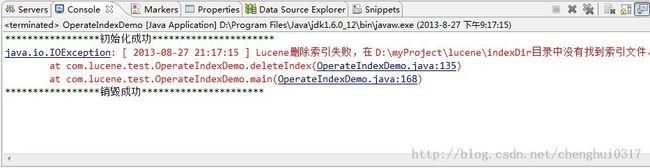
具体可以实践一下,先把索引文件在索引目录中全部删除,然后执行deleteIndex(String contentId)方法,具体效果如下:
然后重新写入索引之后,并且删除是指定添加的article 的id ,再执行以下,具体效果如下:
删除之后再查询索引文件,发现已经没有对应的记录了,表明索引删除成功。另外如果删除的时候指定一个不存在的id,可以看到Lucene什么都不会做。
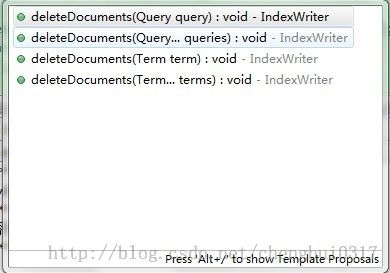
另外,根据eclipse的方法提示如下:
该方法支持Term 和Query的重载,并且参数个数没有上限,所以IndexWriter提供的deleteDocuments方法既支持单个索引的删除也支持多个索引的删除,只需要满足条件即可。
现在把indexWriter.deleteDocuments(new Term("id",contentId));注释掉,替换取消下面注释的代码,然后在运行一下删除操作,具体效果和上面的一样,所以两种传参显示删除索引的方法都可以显示删除索引。 并且使用Term 的实例删除一般用于单个索引的删除,使用Query的实例删除一般用于单个以上的索引删除。
<3>最后看看updateIndex(Article article),该方法最简单,直接调用createIndex(Article article) 和 deleteIndex(String contentId) ,为什么IndexWriter没有提供update方法,可能是因为索引写入到索引文件之后就不允许破坏其存储结构,也许数据表记录的修改操作也是一样,先删除再新增。
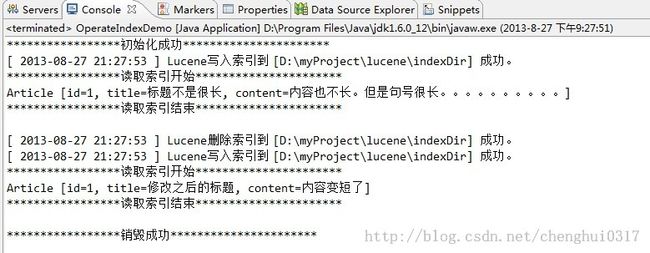
执行该方法的具体效果图如下:
根据图中最后打开索引的结果显示 索引已经被修改成功了。
OK,操作索引的基本功能已经全部实现了。 纸上读来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。