Flume NG源码分析(六)应用程序使用的RpcClient设计
上一篇Flume NG源码分析(五)使用ThriftSource通过RPC方式收集日志 介绍了ThriftSource利用Thrfit服务ThriftSourceProtocol来收集日志。这篇说说flume-ng-sdk中提供给应用层序使用的RpcClient的设计和实现。继续使用ThriftRpcClient来作例子。
先看看ThriftSourceProtocol提供的原生的客户端,它是Thrfit通过flume.thrift文件定义的Thrfit服务默认生成。这个原生的Client提供了网络传输和协议编解码等RPC客户端的基本功能。关于Thrift客户端可以参考这篇Thrift源码分析(三)-- IDL和生成代码分析
public static class Client extends org.apache.thrift.TServiceClient implements Iface {
public static class Factory implements org.apache.thrift.TServiceClientFactory<Client> {
public Factory() {}
public Client getClient(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot) {
return new Client(prot);
}
public Client getClient(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol oprot) {
return new Client(iprot, oprot);
}
}
public Client(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot)
{
super(prot, prot);
}
public Client(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot, org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol oprot) {
super(iprot, oprot);
}
public Status append(ThriftFlumeEvent event) throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
send_append(event);
return recv_append();
}
public void send_append(ThriftFlumeEvent event) throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
append_args args = new append_args();
args.setEvent(event);
sendBase("append", args);
}
public Status recv_append() throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
append_result result = new append_result();
receiveBase(result, "append");
if (result.isSetSuccess()) {
return result.success;
}
throw new org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException(org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException.MISSING_RESULT, "append failed: unknown result");
}
public Status appendBatch(List<ThriftFlumeEvent> events) throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
send_appendBatch(events);
return recv_appendBatch();
}
public void send_appendBatch(List<ThriftFlumeEvent> events) throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
appendBatch_args args = new appendBatch_args();
args.setEvents(events);
sendBase("appendBatch", args);
}
public Status recv_appendBatch() throws org.apache.thrift.TException
{
appendBatch_result result = new appendBatch_result();
receiveBase(result, "appendBatch");
if (result.isSetSuccess()) {
return result.success;
}
throw new org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException(org.apache.thrift.TApplicationException.MISSING_RESULT, "appendBatch failed: unknown result");
}
}
来看看Flume NG是如何封装Thrift客户端的。Flume NG支持Avro,Thrfit等多种RPC实现,它的RpcClient层次结构如下
RpcClient接口定义了给应用程序使用的RPC客户端的基本功能
public interface RpcClient {
public int getBatchSize();
public void append(Event event) throws EventDeliveryException;
public void appendBatch(List<Event> events) throws
EventDeliveryException;
public boolean isActive();
public void close() throws FlumeException;
}
AbstractRpcClient抽象类实现了RPCClient接口,提供了getBatchSize的默认实现,并增加了configure接口来支持配置
public abstract class AbstractRpcClient implements RpcClient {
protected int batchSize =
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE;
protected long connectTimeout =
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS;
protected long requestTimeout =
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT_MILLIS;
@Override
public int getBatchSize(){
return batchSize;
}
@Override
public abstract void append(Event event) throws EventDeliveryException;
@Override
public abstract void appendBatch(List<Event> events)
throws EventDeliveryException;
@Override
public abstract boolean isActive();
@Override
public abstract void close() throws FlumeException;
protected abstract void configure(Properties properties)
throws FlumeException;
}
对于一个设计良好的服务框架的客户端来说,有几个基本的特性
1. 服务寻址
2. 连接池管理
3. 客户端实现RPC调用的负载均衡
4. 缓存
5. 容灾处理,失效转移
我们来看看Flume NG是如何设计它的服务客户端的。基本的组件如下:
服务寻址
Flume NG的RPC客户端的服务寻址实现比较简单,只是在Properties配置文件里设置Thrift服务器的IP和端口,然后用这个值来创建TSocket。这里是一个可以扩展点,使服务寻址的能力更强,更灵活
HostInfo host = HostInfo.getHostInfoList(properties).get(0);
hostname = host.getHostName();
port = host.getPortNumber();
// ClientWrapper
public ClientWrapper() throws Exception{
// 使用hostname, port来构建TSocket
transport = new TFastFramedTransport(new TSocket(hostname, port));
transport.open();
client = new ThriftSourceProtocol.Client(new TCompactProtocol
(transport));
// Not a great hash code, but since this class is immutable and there
// is at most one instance of the components of this class,
// this works fine [If the objects are equal, hash code is the same]
hashCode = random.nextInt();
}
连接池管理
private class ClientWrapper {
public final ThriftSourceProtocol.Client client;
public final TFastFramedTransport transport;
private final int hashCode;
public ClientWrapper() throws Exception{
transport = new TFastFramedTransport(new TSocket(hostname, port));
transport.open();
client = new ThriftSourceProtocol.Client(new TCompactProtocol
(transport));
// Not a great hash code, but since this class is immutable and there
// is at most one instance of the components of this class,
// this works fine [If the objects are equal, hash code is the same]
hashCode = random.nextInt();
}
}
ConnectionPoolManager实现了一个简单的连接池管理类,提供了checkOut和checkIn两个方法来借出和归还连接对象ClientWrapper。使用ReentrantLock和它的条件队列Condition来实现管程的功能,自管理同步操作。当availableClients为空,并且已经达到连接池的最大值时,checkOut操作会阻塞。当checkIn归还连接对象时,唤醒在checkOut上阻塞的线程。
private class ConnectionPoolManager {
private final Queue<ClientWrapper> availableClients;
private final Set<ClientWrapper> checkedOutClients;
private final int maxPoolSize;
private int currentPoolSize;
private final Lock poolLock;
private final Condition availableClientsCondition;
public ConnectionPoolManager(int poolSize) {
this.maxPoolSize = poolSize;
availableClients = new LinkedList<ClientWrapper>();
checkedOutClients = new HashSet<ClientWrapper>();
poolLock = new ReentrantLock();
availableClientsCondition = poolLock.newCondition();
currentPoolSize = 0;
}
public ClientWrapper checkout() throws Exception {
ClientWrapper ret = null;
poolLock.lock();
try {
if (availableClients.isEmpty() && currentPoolSize < maxPoolSize) {
ret = new ClientWrapper();
currentPoolSize++;
checkedOutClients.add(ret);
return ret;
}
while (availableClients.isEmpty()) {
availableClientsCondition.await();
}
ret = availableClients.poll();
checkedOutClients.add(ret);
} finally {
poolLock.unlock();
}
return ret;
}
public void checkIn(ClientWrapper client) {
poolLock.lock();
try {
availableClients.add(client);
checkedOutClients.remove(client);
availableClientsCondition.signal();
} finally {
poolLock.unlock();
}
}
public void destroy(ClientWrapper client) {
poolLock.lock();
try {
checkedOutClients.remove(client);
currentPoolSize--;
} finally {
poolLock.unlock();
}
client.transport.close();
}
public void closeAll() {
poolLock.lock();
try {
for (ClientWrapper c : availableClients) {
c.transport.close();
currentPoolSize--;
}
/*
* Be cruel and close even the checked out clients. The threads writing
* using these will now get an exception.
*/
for (ClientWrapper c : checkedOutClients) {
c.transport.close();
currentPoolSize--;
}
} finally {
poolLock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
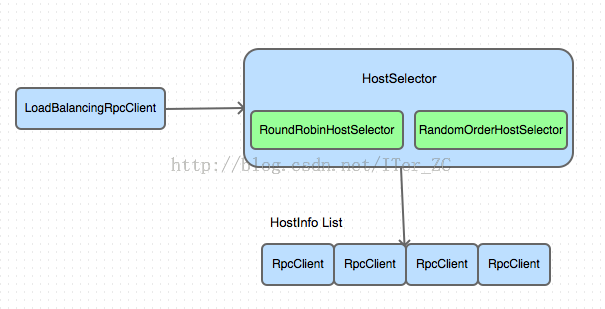
客户端负载均衡
LoadBalancingRpcClient继承了AbstractRpcClient类,提供了RPC客户端的负载均衡。这是一个装饰器模式的实现。
HostSelector接口定义了负载均衡的接口,它是对HostInfo进行负载均衡,再由HostInfo找到对应的RpcClient对象。
public interface HostSelector {
void setHosts(List<HostInfo> hosts);
Iterator<HostInfo> createHostIterator();
void informFailure(HostInfo failedHost);
}
HostSelector有两个默认的实现
RoundRobinHostSelector是轮询方式的负载均衡实现
RandomOrderHostSelector是随机方式的负载均衡实现
看下RoundRobinHostSelector的实现,它的逻辑主要在OrderSelector这个类中实现
private static class RoundRobinHostSelector implements HostSelector {
private OrderSelector<HostInfo> selector;
RoundRobinHostSelector(boolean backoff, long maxBackoff){
selector = new RoundRobinOrderSelector<HostInfo>(backoff);
if(maxBackoff != 0){
selector.setMaxTimeOut(maxBackoff);
}
}
@Override
public synchronized Iterator<HostInfo> createHostIterator() {
return selector.createIterator();
}
@Override
public synchronized void setHosts(List<HostInfo> hosts) {
selector.setObjects(hosts);
}
public synchronized void informFailure(HostInfo failedHost){
selector.informFailure(failedHost);
}
}
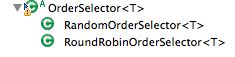
OrderSelector是一个支持回退backoff算法的顺序选择容器,它的类层次结构如下
父类OrderSelector是抽象类,定义了回退算法,子类RoundRobinOrderSelector和RandomOrderSelector实现了创建迭代器的算法。
RoundRobinOrderSelector的代码如下
1. getIndexList()返回状态正常的对象列表
2. nextHead索引指向当前位置,作为轮询的起点
public class RoundRobinOrderSelector<T> extends OrderSelector<T> {
private int nextHead = 0;
public RoundRobinOrderSelector(boolean shouldBackOff) {
super(shouldBackOff);
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> createIterator() {
List<Integer> activeIndices = getIndexList();
int size = activeIndices.size();
// possible that the size has shrunk so gotta adjust nextHead for that
if (nextHead >= size) {
nextHead = 0;
}
int begin = nextHead++;
if (nextHead == activeIndices.size()) {
nextHead = 0;
}
int[] indexOrder = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
indexOrder[i] = activeIndices.get((begin + i) % size);
}
return new SpecificOrderIterator<T>(indexOrder, getObjects());
}
}
对于LoadBalanceRpcClient来说,它的配置文件里,同一个RPC服务的服务器列表至少有两个服务端信息才能使用负载均衡。在配置文件中还配置了回退算法和负载均衡算法相关的配置
protected void configure(Properties properties) throws FlumeException {
clientMap = new HashMap<String, RpcClient>();
configurationProperties = new Properties();
configurationProperties.putAll(properties);
hosts = HostInfo.getHostInfoList(properties);
if (hosts.size() < 2) {
throw new FlumeException("At least two hosts are required to use the "
+ "load balancing RPC client.");
}
String lbTypeName = properties.getProperty(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_HOST_SELECTOR,
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.HOST_SELECTOR_ROUND_ROBIN);
boolean backoff = Boolean.valueOf(properties.getProperty(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_BACKOFF,
String.valueOf(false)));
String maxBackoffStr = properties.getProperty(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_MAX_BACKOFF);
long maxBackoff = 0;
if(maxBackoffStr != null) {
maxBackoff = Long.parseLong(maxBackoffStr);
}
if (lbTypeName.equalsIgnoreCase(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.HOST_SELECTOR_ROUND_ROBIN)) {
selector = new RoundRobinHostSelector(backoff, maxBackoff);
} else if (lbTypeName.equalsIgnoreCase(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.HOST_SELECTOR_RANDOM)) {
selector = new RandomOrderHostSelector(backoff, maxBackoff);
} else {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends HostSelector> klass = (Class<? extends HostSelector>)
Class.forName(lbTypeName);
selector = klass.newInstance();
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new FlumeException("Unable to instantiate host selector: "
+ lbTypeName, ex);
}
}
selector.setHosts(hosts);
isOpen = true;
}
客户端负载均衡的主要组件如下
客户端缓存
客户端缓存比较简单,使用了一个Map结构,保存了HostInfo和对应的RPCClient对象,这样可以复用RPCClient对象,这是一个重对象,包含了一个连接池的实例。
clientMap = new HashMap<String, RpcClient>();
private synchronized RpcClient getClient(HostInfo info)
throws FlumeException, EventDeliveryException {
throwIfClosed();
String name = info.getReferenceName();
RpcClient client = clientMap.get(name);
if (client == null) {
client = createClient(name);
clientMap.put(name, client);
} else if (!client.isActive()) {
try {
client.close();
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close client for " + info, ex);
}
client = createClient(name);
clientMap.put(name, client);
}
return client;
}
客户端容灾处理
FailoverRpcClient也维护了一个HostInfo列表,由HostInfo再找到对应的RpcClient。还维护了一个最大的重试次数maxTries
private synchronized void configureHosts(Properties properties)
throws FlumeException {
if(isActive){
logger.error("This client was already configured, " +
"cannot reconfigure.");
throw new FlumeException("This client was already configured, " +
"cannot reconfigure.");
}
hosts = HostInfo.getHostInfoList(properties);
String tries = properties.getProperty(
RpcClientConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_MAX_ATTEMPTS);
if (tries == null || tries.isEmpty()){
maxTries = hosts.size();
} else {
try {
maxTries = Integer.parseInt(tries);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
maxTries = hosts.size();
}
}
......
}
看一下它的append方法,实现了重试机制来做失效转移
public void append(Event event) throws EventDeliveryException {
//Why a local variable rather than just calling getClient()?
//If we get an EventDeliveryException, we need to call close on
//that specific client, getClient in this case, will get us
//the next client - leaving a resource leak.
RpcClient localClient = null;
synchronized (this) {
if (!isActive) {
logger.error("Attempting to append to an already closed client.");
throw new EventDeliveryException(
"Attempting to append to an already closed client.");
}
}
// Sit in an infinite loop and try to append!
int tries = 0;
while (tries < maxTries) {
try {
tries++;
localClient = getClient();
localClient.append(event);
return;
} catch (EventDeliveryException e) {
// Could not send event through this client, try to pick another client.
logger.warn("Client failed. Exception follows: ", e);
localClient.close();
localClient = null;
} catch (Exception e2) {
logger.error("Failed to send event: ", e2);
throw new EventDeliveryException(
"Failed to send event. Exception follows: ", e2);
}
}
logger.error("Tried many times, could not send event."
throw new EventDeliveryException("Failed to send the event!");
}