单源最短路径:Dijkstra算法
一,Dijkstra算法基本概念
Dijkstra算法使用了广度优先搜索解决非负权有向图的单源最短路径问题,算法最终得到一个最短路径树。该算法常用于路由算法或者作为其他图算法的一个子模块。
该算法的输入包含了一个有权重的有向图 G,以及G中的一个来源顶点 S。我们以 V 表示图 G 中所有顶点的集合。每一个图中的边,都是两个顶点所形成的有序元素对。(u, v) 表示从顶点 u 到 v 有路径相连。我们以 E 表示G中所有边的集合,而边的权重则由权重函数 w: E → [0, ∞] 定义。因此,w(u, v) 就是从顶点 u 到顶点 v 的非负权重(weight)。边的权重可以想像成两个顶点之间的距离。任两点间路径的权重,就是该路径上所有边的权重总和。已知有 V 中有顶点 s 及 t,Dijkstra 算法可以找到 s 到 t的最低权重路径(例如,最短路径)。这个算法也可以在一个图中,找到从一个顶点 s 到任何其他顶点的最短路径。对于不含负权的有向图,Dijkstra算法是目前已知的最快的单源最短路径算法。
1,算法步骤:
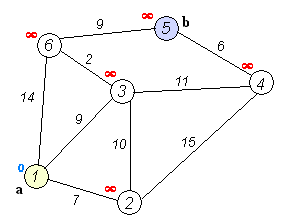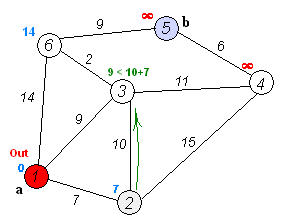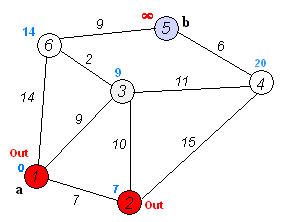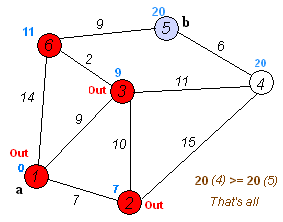
1). 初始时令 S={V0},T={其余顶点},T中顶点对应的距离值,若存在,d(V0,Vi)为弧上的权值,若不存在,d(V0,Vi)为∞。
2). 从T中选取一个其距离值为最小的顶点W且不在S中,加入S。
3). 对其余T中顶点的距离值进行修改:若加进W作中间顶点,从V0到Vi的距离值缩短,则修改此距离值。
4).重复上述步骤2、3,直到S中包含所有顶点,即W=Vi为止。
动画演示如下
二,C++模板实现
1,Graph.h代码如下(无向图):
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
template<class DistType/*边的权值的类型*/>
class Edge//边的定义
{
public:
Edge(int dest, DistType weight)
{
m_nposTable=dest;
m_distWeight=weight;
m_pnext=NULL;
}
~Edge()
{
}
public:
int m_nposTable;//该边的目的顶点在顶点集中的位置
DistType m_distWeight;//边的权重值
Edge<DistType> *m_pnext;//下一条边(注意不是下一个顶点,因为m_nposTable已经知道了这个顶点的位置)
};
//声明
template<class NameType/*顶点集名字类型*/, class DistType/*距离的数据类型*/> class Graph;
template<class NameType/*顶点集名字类型*/, class DistType/*距离的数据类型*/>
class Vertex//顶点的定义
{
public:
Vertex()
{
padjEdge=NULL;
m_vertexName=0;
}
~Vertex()
{
Edge<DistType> *pmove = padjEdge;
while (pmove)
{
padjEdge = pmove->m_pnext;
delete pmove;
pmove = padjEdge;
}
}
private:
friend class Graph<NameType,DistType>;//允许Graph类任意访问
NameType m_vertexName;//顶点中的数据内容
Edge<DistType> *padjEdge;//顶点的邻边
};
template<class NameType/*顶点集名字类型*/, class DistType/*距离的数据类型*/>
class Graph
{
public:
Graph(int size = m_nDefaultSize/*图顶点集的规模*/)
{
m_pVertexTable = new Vertex<NameType, DistType>[size]; //为顶点集分配内存
if (m_pVertexTable == NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
m_numVertexs=0;
m_nmaxSize=size;
m_nnumEdges=0;
}
~Graph()
{
Edge<DistType> *pmove;
for (int i=0; i < this->m_numVertexs; i++)
{
pmove = this->m_pVertexTable[i].padjEdge;
if (pmove){
this->m_pVertexTable[i].padjEdge = pmove->m_pnext;
delete pmove;
pmove = this->m_pVertexTable[i].padjEdge;
}
}
delete[] m_pVertexTable;
}
int GetNumEdges()
{//获得边的数目
return m_nnumEdges/2;
}
int GetNumVertexs()
{//获得顶点数目
return m_numVertexs;
}
bool IsGraphFull() const
{ //图满的?
return m_nmaxSize == m_numVertexs;
}
//在顶点集中位置为v1和v2的顶点之间插入边
bool InsertEdge(int v1, int v2, DistType weight=m_Infinity);
//插入顶点名字为vertex的顶点
bool InsertVertex(const NameType vertex);
//打印图
void PrintGraph();
//顶点v到其他各个顶点的最短路径(包括自身)
void Dijkstra(int v, DistType *shotestpath);
//获取顶点集中位置为v1和v2的顶点之间边的权重值
DistType GetWeight(int v1, int v2);
//获得在顶点集中的位置为v的顶点的名字
NameType GetVertexValue(int v);
//用该顶点的名字来寻找其在顶点集中的位置
int GetVertexPosTable(const NameType vertex);
private:
Vertex<NameType, DistType> *m_pVertexTable; //顶点集
int m_numVertexs;//图中当前的顶点数量
int m_nmaxSize;//图允许的最大顶点数
static const int m_nDefaultSize = 10; //默认的最大顶点集数目
static const DistType m_Infinity = 65536; //边的默认权值(可以看成是无穷大)
int m_nnumEdges;//图中边的数目
};
//返回顶点vertexname在m_pVertexTable(顶点集)中的位置
//如果不在顶点集中就返回-1
template<class NameType, class DistType>
int Graph<NameType, DistType>::GetVertexPosTable(const NameType vertexname)
{
for (int i=0; i < this->m_numVertexs; i++)
{
if (vertexname == m_pVertexTable[i].m_vertexName)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//打印图中的各个顶点及其链接的边的权重
template<class NameType, class DistType>
void Graph<NameType, DistType>::PrintGraph()
{
Edge<DistType> *pmove;
for (int i=0; i<this->m_numVertexs; i++)
{
cout << this->m_pVertexTable[i].m_vertexName << "->";
pmove = this->m_pVertexTable[i].padjEdge;
while (pmove)
{
cout << pmove->m_distWeight << "->" << this->m_pVertexTable[pmove->m_nposTable].m_vertexName << "->";
pmove = pmove->m_pnext;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
}
//获得在顶点集中的位置为v的顶点的名字
template<class NameType, class DistType>
NameType Graph<NameType, DistType>::GetVertexValue(int v)
{
if (v<0 || v>=this->m_numVertexs)
{
cerr << "查找的顶点位置参数有误,请检查!" <<endl;
exit(1);
}
return m_pVertexTable[v].m_vertexName;
}
//返回顶点v1和v2之间的边权值,
//如果没有直接相连(即不是一条边直接相连)则返回无穷大
template<class NameType, class DistType>
DistType Graph<NameType, DistType>::GetWeight(int v1, int v2)
{
if (v1>=0 && v1<this->m_numVertexs && v2>=0 && v2<this->m_numVertexs)
{
if (v1 == v2)
{
return 0;
}
Edge<DistType> *pmove = m_pVertexTable[v1].padjEdge;
while (pmove)
{
if (pmove->m_nposTable == v2)
{
return pmove->m_distWeight;
}
pmove = pmove->m_pnext;
}
}else
{
return m_Infinity;
}
}
//顶点依次插入到分配好的顶点集中
template<class NameType, class DistType>
bool Graph<NameType, DistType>::InsertVertex(const NameType vertexname)
{
if (IsGraphFull())
{
cerr<<"图已经满,请勿再插入顶点!"<<endl;
return false;
}else
{
this->m_pVertexTable[this->m_numVertexs].m_vertexName = vertexname;
this->m_numVertexs++;
}
return true;
}
//在顶点集位置为v1和v2的顶点之间插入权值为weght的边(务必保持输入的准确性,否则.....)
template<class NameType, class DistType>
bool Graph<NameType, DistType>::InsertEdge(int v1, int v2, DistType weight)
{
if (v1 < 0 && v1 > this->m_numVertexs && v2 < 0 && v2 > this->m_numVertexs)
{
cerr<<"边的位置参数错误,请检查! "<<endl;
return false;
}
else
{
Edge<DistType> *pmove = m_pVertexTable[v1].padjEdge;
if (pmove == NULL)//如果顶点v1没有邻边
{ //建立顶点v1的第一个邻边(该邻边指明了目的顶点)
m_pVertexTable[v1].padjEdge = new Edge<DistType>(v2, weight);
m_nnumEdges++;//图中边的数目
return true;
}else//如果有邻边
{
while (pmove->m_pnext)
{
pmove = pmove->m_pnext;
}
pmove->m_pnext = new Edge<DistType>(v2, weight);
m_nnumEdges++;//图中边的数目
return true;
}
}
}
//Dijkstra单源最短路径算法
template<class NameType, class DistType>
void Graph<NameType, DistType>::Dijkstra(int v, DistType *shPath)
{
int num =GetNumVertexs();
int *visited = new int[num];
for (int i=0; i < num; i++)
{//初始化
visited[i] = 0;//未访问
shPath[i] = this->GetWeight(v, i);//顶点v(当前中间点)到各个相邻顶点的边权值,其他情况返回无穷大
}
visited[v] = 1;//第v个顶点初始化为被访问,并以他为中点点开始找最短路径
for (int i = 1; i < num; i++)
{
DistType min = this->m_Infinity;
int u=0;
//寻找新的中间点u,依据就是数组中权值最小的那个点的位置(且没被访问过)
for (int j=0; j < num; j++)
{
if (!visited[j])
{
if (shPath[j]<min)
{
min = shPath[j];//获得当前shPath数组中的最小边权重
u = j;//用u来记录获取最小值时的顶点位置,即新的中间点
}
}
}
visited[u] = 1;//已经确定的最短路径
//以u为中间点寻找顶点v到顶点w的最短路径
for (int w=0; w < num; w++)
{
DistType weight = this->GetWeight(u, w);//顶点u(当前中间点)到各个相邻顶点的边权值,其他情况返回无穷大
if (!visited[w] && weight != this->m_Infinity )
{
if ( shPath[u]+weight < shPath[w] )
{
shPath[w] = shPath[u] + weight;//更新顶点v到w的最短路径值
}
}
}
}
delete[] visited;
}
2,主测试代码如下:
// ConsoleAppMyGraph.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Graph.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Graph<char *, int> graph(7);
char *vertex[7] = {"【地大】", "【武大】", "【华科】", "【交大】", "【北大】", "【清华】", "【复旦】"};//顶点集
for (int i=0; i<7; i++)
{
graph.InsertVertex(vertex[i]);
}
cout<<"一,图的初始化(邻结表存储):======================================"<<endl;
graph.PrintGraph();
cout<<"图中顶点的数目:"<<graph.GetNumVertexs()<<endl;
cout <<endl;
int edge[][3] = {{0, 1, 43}/*地大到武大的距离*/, {0, 2, 12}, {1, 2, 38}, {2, 3 ,1325},
{3, 6, 55}, {4, 5, 34}, {4, 6, 248},{0,3,400},{2,6,314},{3,4,66},{2,4,37}}; //分配距离
for (int i=0; i<11; i++)
{
graph.InsertEdge(edge[i][0], edge[i][1], edge[i][2]);
graph.InsertEdge(edge[i][1], edge[i][0], edge[i][2]);
}
cout<<"二,添加边后的图(无向图):=================================="<<endl;
graph.PrintGraph();
cout<<"图中边的数目(实际上是所示边数的两倍,因为是双向的):"<<graph.GetNumEdges()<<endl;
cout <<endl;
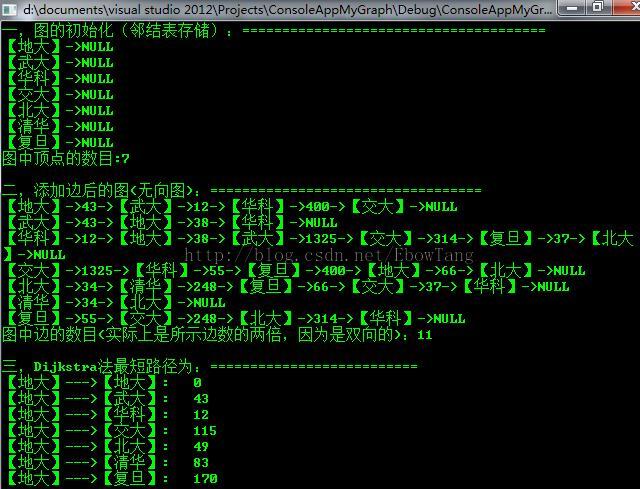
cout<<"三,Dijkstra法最短路径为:=========================="<<endl;
int shortestPath[7];//存储Dijkstra算法最短路径值
graph.Dijkstra(0, shortestPath);
for (int i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout << graph.GetVertexValue(0) << "--->" << graph.GetVertexValue(i)
<< ": " << shortestPath[i] <<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
system("color 0A");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3,测试结果如下:
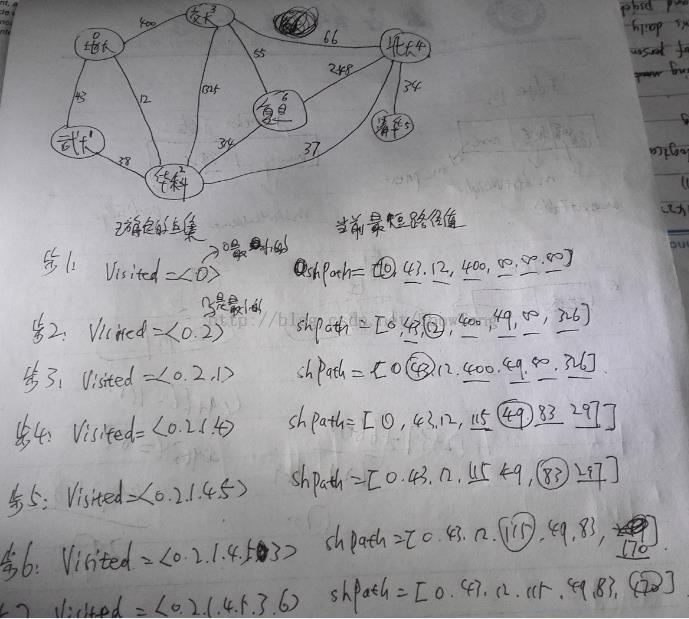
4,其中的计算过程如下:
参考资源:
【1】《算法导论》
【2】《维基百科》
【3】《百度百科》
【4】https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm【5】http://blog.csdn.net/todd911/article/details/9347053
注:
本文部分文字学习并copy自网络,代码转载并改写于网络资源.
如果侵犯了您的版权,请联系本人[email protected],本人将及时编辑掉!