使用HttpURLConnection发送get和post请求
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/forwardyzk/article/details/45364463
我们在开发的使用,直接使用的开源框架,例如:Xutil,Volley开源框架直接访问网络,但是我们也需要知道其中的一些知识,了解一下怎样访问网络的。下面我们模拟以下客户端和服务端,看看post和get请求。
首先我们开发一下客户端:
1.首先自定义线程,开启get请求。
public class GetThread extends Thread {
private String name;
private String age;
private TextView show_content;
private String url = "";
private Handler handler = new Handler();
public GetThread(String url, TextView show_content) {
this.show_content = show_content;
this.url = url;
}
public GetThread(String url, String name, String age, TextView show_content) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.show_content = show_content;
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
getRun();
}
private void getRun() {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(url)) {
throw new NullPointerException("please ensure url is not equals null ");
}
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
try {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(name) && !TextUtils.isEmpty(age)) {
url = url + "?name=" + URLEncoder.encode(name, "utf-8") + "&age=" + URLEncoder.encode(age, "utf-8");
}
URL httpUrl = new URL(url);
HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) httpUrl.openConnection();
httpURLConnection.setReadTimeout(5000);
httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("GET");
//设置请求头header
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("test-header","get-header-value");
//获取内容
InputStream inputStream = httpURLConnection.getInputStream();
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
final StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuffer.append(line);
}
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
show_content.setText(stringBuffer.toString());
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
if (bufferedReader != null) {
try {
bufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
对于Get请求,请求参数是拼接在Url上的。例如:http://xxxx?name=zhangsan&age=20
httpURLConnection.setReadTimeout(5000);设置超时时间
httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("GET");设置请求方法
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("test-header","get-header-value");设置请求头header
获取从服务器传回来的内容
InputStream inputStream = httpURLConnection.getInputStream();
讲InputStream 转换成BufferedReader,便于操作流
将流中的数据存入到了StringBuffer中,最后设置给展示内容的TextView上。
最后要记得关闭流。
2.自定义PostThread线程,开启Post请求
public class PostThread extends Thread {
private String name;
private String age;
private TextView show_content;
private String url = "";
private Handler handler = new Handler();
public PostThread(String url, TextView show_content) {
this.show_content = show_content;
this.url = url;
}
public PostThread(String url, String name, String age, TextView show_content) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.show_content = show_content;
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
getRun();
}
private void getRun() {
// Properties p=System.getProperties();
// p.list(System.out);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(url)) {
throw new NullPointerException("please ensure url is not equals null ");
}
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
try {
URL httpUrl = new URL(url);
HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) httpUrl.openConnection();
//设置请求头header
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("test-header","post-header-value");
httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("POST");
httpURLConnection.setReadTimeout(5000);
//设置请求参数
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(name) && !TextUtils.isEmpty(age)) {
OutputStream outputStream = httpURLConnection.getOutputStream();
// String params="name="+ URLEncoder.encode(name, "utf-8")+"&age="+ URLEncoder.encode(age, "utf-8");
String params="name="+ name+"&age="+ age;
outputStream.write(params.getBytes());
}
//获取内容
InputStream inputStream = httpURLConnection.getInputStream();
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
final StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuffer.append(line);
}
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
show_content.setText(stringBuffer.toString());
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
if (bufferedReader != null) {
try {
bufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
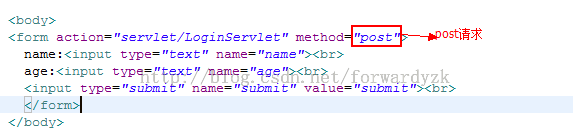
对于Post请求和Get请求有不同的地方
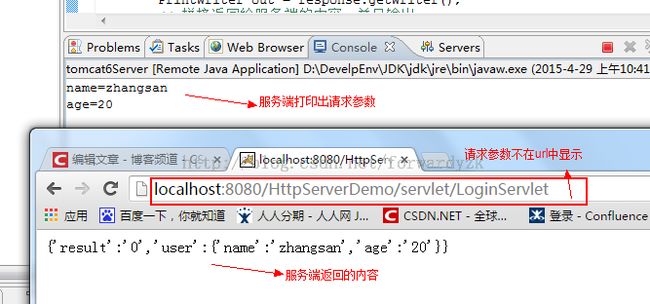
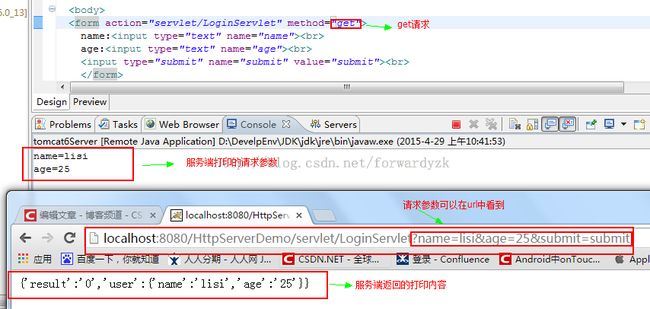
get请求是把请求参数拼接到Url中,可以在url中看到。而post请求不把请求参数放在了请求体中。
给Post设置请求参数
OutputStream outputStream = httpURLConnection.getOutputStream();获取请求连接的写入流
String params="name="+ name+"&age="+ age;拼接请求参数字符串
outputStream.write(params.getBytes());讲请求参数写入到写入流中
其他的地方和get请求是一样的。
3.在MainActivity中开启线程,并发送get和Post请求
/**
* get request
*/
private void getSubmit() {
String url = AddressUtil.LOGIN_URL;
String name = ed_name.getText().toString().trim();
String age = ed_age.getText().toString().trim();
new GetThread(url,name,age ,show_content).start();
}
/**
* post request
*/
private void postSubmot() {
String url = AddressUtil.LOGIN_URL;
String name = ed_name.getText().toString().trim();
String age = ed_age.getText().toString().trim();
new PostThread(url,name,age ,show_content).start();
}
开启GetThread线程,发送get请求
第一个参数:请求地址
第二个参数:登录的名字,写入到了请求参数中
第三个参数:登录的年龄,写入到了请求参数中
第四个参数:展示服务器返回内容的展示的TextView
public class AddressUtil {
public final static String LOCALHOST="http://10.2.52.19:8080";
public final static String LOGIN_URL=LOCALHOST+"/HttpServerDemo/servlet/LoginServlet";
}
3.开发模拟的服务器
新建LoginServlet
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
/**
* The doPost method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to
* post.
*
* @param request
* the request send by the client to the server
* @param response
* the response send by the server to the client
* @throws ServletException
* if an error occurred
* @throws IOException
* if an error occurred
*/
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 获取请求头
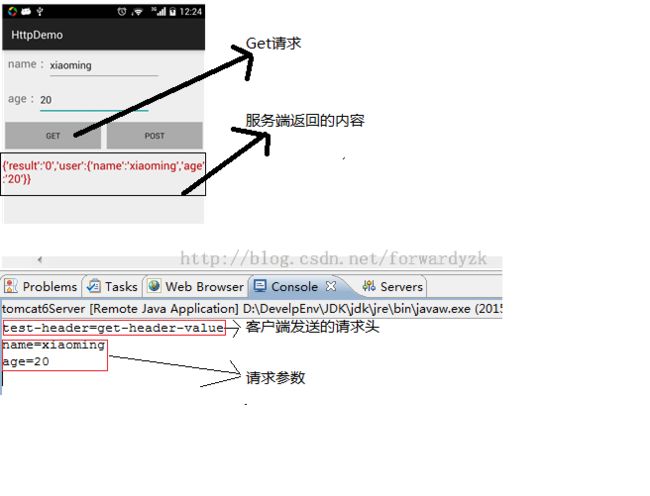
String header = request.getHeader("test-header");
if (header != null && !header.equals(""))
System.out.println("test-header=" + header);
// 获取请求参数
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
// 打印流
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
// 拼接返回给服务端的内容,并且输出
if (name == null || name.equals("") || age == null || age.equals("")) {
out.println("{'result':'1','error':'name and age is null'");
} else {
out.println("{'result':'0','user':{'name':'"
+ new String(name.getBytes("iso-8859-1"), "utf-8")
+ "','age':'"
+ new String(age.getBytes("iso-8859-1"), "utf-8") + "'}}");
System.out.println("name="
+ new String(name.getBytes("iso-8859-1"), "utf-8"));
System.out.println("age="
+ new String(age.getBytes("iso-8859-1"), "utf-8"));
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
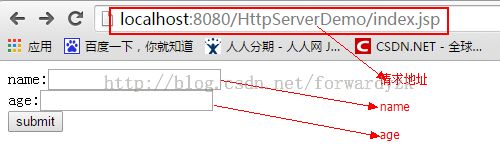
在index.jsp中写登录的界面
3.1代码:Post请求
显示下面的截图,表示post请求成功
3.2 Get请求
如果限制的内容和图片是一样,标识get请求已经成功访问。
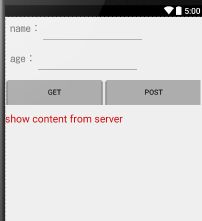
4.下面使用手机端的App访问服务端
使用手机端访问服务端,要把localhost转换成IP地址
请求地址的拼接
public class AddressUtil {
public final static String LOCALHOST="http://10.2.52.19:8080";
public final static String LOGIN_URL=LOCALHOST+"/HttpServerDemo/servlet/LoginServlet";
}
4.1Get请求
代码请求
/**
* get request
*/
private void getSubmit() {
String url = AddressUtil.LOGIN_URL;
String name = ed_name.getText().toString().trim();
String age = ed_age.getText().toString().trim();
new GetThread(url,name,age ,show_content).start();
}
请求结果
4.2 Post请求
代码请求
/**
* post request
*/
private void postSubmot() {
String url = AddressUtil.LOGIN_URL;
String name = ed_name.getText().toString().trim();
String age = ed_age.getText().toString().trim();
new PostThread(url,name,age ,show_content).start();
}
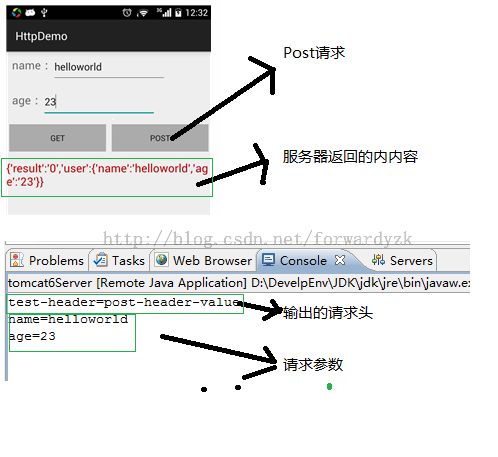
这样客服端和服务端的开发,get和post请求已经成功。
客户端源码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/forwardyzk/8645171
服务端源码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/forwardyzk/8645181