Notification使用详解之三:通过服务更新进度通知&在Activity中监听服务进度
上次我们讲到如何实现一个可更新的进度通知,实现的方式是启动一个线程模拟一个下载任务,然后根据任务进度向UI线程消息队列发送进度消息,UI线程根据进度消息更新通知的UI界面。可是在实际应用中,我们一般会将上传、下载等比较耗时的后台任务以服务的形式运行,更新进度通知也是交由后台服务来完成的。 不过有的时候,除了在通知里面显示进度信息,我们也要在Activity中显示当前进度,很多下载系统都有这样的功能,例如Android自带浏览器的下载系统、QQ浏览器的下载系统等等。那么如何实现这一功能呢?实现方式有很多,我们今天先来介绍其中的一种:在Activity中主动监听服务的进度。
具体的思路是:让Activity与后台服务绑定,通过中间对象Binder的实例操作后台服务,获取进度信息和服务的状态以及在必要的时候停止服务。
关于服务的生命周期,如果有些朋友们不太熟悉的话,可以去查阅相关资料;如果以后有时间,我可能也会总结一些与服务相关的知识。
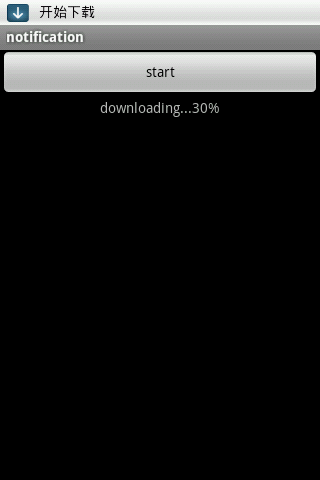
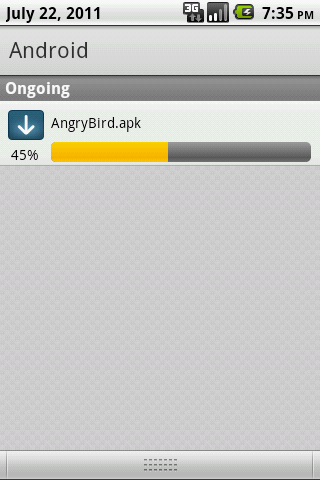
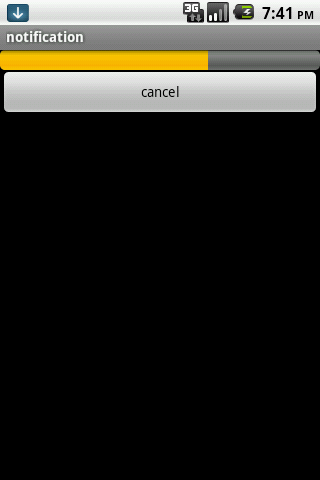
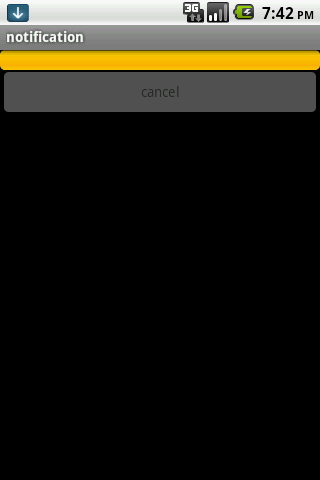
为了让大家对这个过程更清晰一些,在上代码之前,我们先来看看几个截图:
整个过程如上图所示:在我们点击开始按钮后,下载任务开始运行,同事更新通知上的进度,当前Activity也从后台服务获取进度信息,显示到按钮下方;当我们点击通知后,跳转到下载管理界面,在这里我们也从后台服务获取进度,还可以做取消任务等操作。
了解了整个过程的情况后,我们就来分析一下具体的代码实现。
首先是/res/main.xml布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="start"
android:onClick="start"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"/>
</LinearLayout>
其中Button是用来启动服务的,TextView是用来显示进度信息的。
然后再在看一下MainActivity.java的代码:
package com.scott.notification;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private DownloadService.DownloadBinder binder;
private TextView text;
private boolean binded;
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
int progress = msg.arg1;
text.setText("downloading..." + progress + "%");
};
};
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
binder = (DownloadService.DownloadBinder) service;
binded = true;
// 开始下载
binder.start();
// 监听进度信息
listenProgress();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (binded) {
unbindService(conn);
}
}
public void start(View view) {
if (binded) {
binder.start();
listenProgress();
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(this, DownloadService.class);
startService(intent); //如果先调用startService,则在多个服务绑定对象调用unbindService后服务仍不会被销毁
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
/**
* 监听进度
*/
private void listenProgress() {
new Thread() {
public void run() {
while (!binder.isCancelled() && binder.getProgress() <= 100) {
int progress = binder.getProgress();
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = progress;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
if (progress == 100) {
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}.start();
}
}
我们可以看到,当点击开始按钮后,以bindService的方式绑定服务,用获取到的DownloadService.DownloadBinder实例启动服务,并在Activity中启动一个线程监听服务的进度信息,及时的显示到按钮下方。
服务类DownloadService.java代码如下:
package com.scott.notification;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
public class DownloadService extends Service {
private static final int NOTIFY_ID = 0;
private boolean cancelled;
private int progress;
private Context mContext = this;
private NotificationManager mNotificationManager;
private Notification mNotification;
private DownloadBinder binder = new DownloadBinder();
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case 1:
int rate = msg.arg1;
if (rate < 100) {
// 更新进度
RemoteViews contentView = mNotification.contentView;
contentView.setTextViewText(R.id.rate, rate + "%");
contentView.setProgressBar(R.id.progress, 100, rate, false);
} else {
// 下载完毕后变换通知形式
mNotification.flags = Notification.FLAG_AUTO_CANCEL;
mNotification.contentView = null;
Intent intent = new Intent(mContext, FileMgrActivity.class);
// 告知已完成
intent.putExtra("completed", "yes");
//更新参数,注意flags要使用FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT
PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(mContext, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
mNotification.setLatestEventInfo(mContext, "下载完成", "文件已下载完毕", contentIntent);
stopSelf();//停掉服务自身
}
// 最后别忘了通知一下,否则不会更新
mNotificationManager.notify(NOTIFY_ID, mNotification);
break;
case 0:
// 取消通知
mNotificationManager.cancel(NOTIFY_ID);
break;
}
};
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(android.content.Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// 返回自定义的DownloadBinder实例
return binder;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
cancelled = true; // 取消下载线程
}
/**
* 创建通知
*/
private void setUpNotification() {
int icon = R.drawable.down;
CharSequence tickerText = "开始下载";
long when = System.currentTimeMillis();
mNotification = new Notification(icon, tickerText, when);
// 放置在"正在运行"栏目中
mNotification.flags = Notification.FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT;
RemoteViews contentView = new RemoteViews(mContext.getPackageName(), R.layout.download_notification_layout);
contentView.setTextViewText(R.id.fileName, "AngryBird.apk");
// 指定个性化视图
mNotification.contentView = contentView;
Intent intent = new Intent(this, FileMgrActivity.class);
PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(mContext, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
// 指定内容意图
mNotification.contentIntent = contentIntent;
mNotificationManager.notify(NOTIFY_ID, mNotification);
}
/**
* 下载模块
*/
private void startDownload() {
cancelled = false;
int rate = 0;
while (!cancelled && rate < 100) {
try {
// 模拟下载进度
Thread.sleep(500);
rate = rate + 5;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
msg.what = 1;
msg.arg1 = rate;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
this.progress = rate;
}
if (cancelled) {
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
msg.what = 0;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
/**
* DownloadBinder中定义了一些实用的方法
*
* @author user
*
*/
public class DownloadBinder extends Binder {
/**
* 开始下载
*/
public void start() {
//将进度归零
progress = 0;
//创建通知
setUpNotification();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
//下载
startDownload();
};
}.start();
}
/**
* 获取进度
*
* @return
*/
public int getProgress() {
return progress;
}
/**
* 取消下载
*/
public void cancel() {
cancelled = true;
}
/**
* 是否已被取消
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isCancelled() {
return cancelled;
}
}
}
我们看到,在服务中有个DownloadBinder类,它继承自Binder,定义了一系列方法,获取服务状态以及操作当前服务,刚才我们在MainActivity中获取的就是这个类的实例。最后,不要忘了在AndroidManifest.xml中配置该服务。关于进度通知的布局文件/res/layout/download_notification_layout.xml,在这里就不需贴出了,朋友们可以参考一下Notification使用详解之二中进度通知布局的具体代码。
下面我们来介绍一下FileMgrActivity,它就是点击通知之后跳转到的界面,布局文件/res/filemgr.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progress"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
android:progress="0"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/cancel"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="cancel"
android:onClick="cancel"/>
</LinearLayout>
我们来看一下FileMgrActivity.java具体的代码:
package com.scott.notification;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
public class FileMgrActivity extends Activity {
private DownloadService.DownloadBinder binder;
private ProgressBar progressBar;
private Button cancel;
private boolean binded;
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
int progress = msg.arg1;
progressBar.setProgress(progress);
if (progress == 100) {
cancel.setEnabled(false);
}
};
};
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
binder = (DownloadService.DownloadBinder) service;
//监听进度信息
listenProgress();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.filemgr);
progressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progress);
cancel = (Button) findViewById(R.id.cancel);
if ("yes".equals(getIntent().getStringExtra("completed"))) {
//如果已完成,则不需再绑定service
progressBar.setProgress(100);
cancel.setEnabled(false);
} else {
//绑定service
Intent intent = new Intent(this, DownloadService.class);
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
binded = true;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
//如果是绑定状态,则取消绑定
if (binded) {
unbindService(conn);
}
}
public void cancel(View view) {
//取消下载
binder.cancel();
}
/**
* 监听进度信息
*/
private void listenProgress() {
new Thread() {
public void run() {
while (!binder.isCancelled() && binder.getProgress() <= 100) {
int progress = binder.getProgress();
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = progress;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}.start();
}
}
我们发现,它和MainActivity实现方式很相似,恩,他们都是通过和服务绑定后获取到的Binder对象来跟服务通信的,都是主动和服务打招呼来获取信息和控制服务的。
这两个Activity和一个Service似乎像是复杂的男女关系,两个男人同时喜欢一个女人,都通过自己的手段试图从那个女人获取爱情,两个男人都很主动,那个女人显得很被动。
以上就是今天的全部内容,也许朋友们会有疑问,能不能让Service主动告知Activity当前的进度信息呢?答案是可以。下一次,我就会和大家分享一下,如何变Service为主动方,让一个女人脚踏两只船的方式。