Android SVG动画PathView源码解析与使用教程(API 14)
使用的是一个第三方库android-pathview主要是一个自定义View——PathView,跟所有自定义View一样,重写了三个构造方法。并且最终调用三个参数的构造方法,在里面获取自定义属性。
/** * Default constructor. * * @param context The Context of the application. */
public PathView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
/** * Default constructor. * * @param context The Context of the application. * @param attrs attributes provided from the resources. */
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
/** * Default constructor. * * @param context The Context of the application. * @param attrs attributes provided from the resources. * @param defStyle Default style. */
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
getFromAttributes(context, attrs);
}查看自定义属性的xml,里面共三个自定义属性,pathColor为路径颜色,默认值为绿色0xff00ff00,pathWidth为路径宽度,默认值为8.0f,svg为路径文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="PathView">
<attr name="pathColor" format="color"/>
<attr name="pathWidth" format="float"/>
<attr name="svg" format="reference"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>通过getFromAttributes函数获得这些自定属性,并赋值给成员变量,最后通过finally块回收资源
/** * Get all the fields from the attributes . * * @param context The Context of the application. * @param attrs attributes provided from the resources. */
private void getFromAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PathView);
try {
if (a != null) {
paint.setColor(a.getColor(R.styleable.PathView_pathColor, 0xff00ff00));
paint.setStrokeWidth(a.getFloat(R.styleable.PathView_pathWidth, 8.0f));
svgResourceId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.PathView_svg, 0);
}
} finally {
if (a != null) {
a.recycle();
}
}
}至于成员变量,这里贴出所有成员变量,具体作用见注释
/** * Logging tag. */
public static final String LOG_TAG = "PathView";
/** * The paint for the path. */
private Paint paint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
/** * Utils to catch the paths from the svg. */
private final SvgUtils svgUtils = new SvgUtils(paint);
/** * All the paths provided to the view. Both from Path and Svg. */
private List<SvgUtils.SvgPath> paths = new ArrayList<SvgUtils.SvgPath>(0);
/** * This is a lock before the view is redrawn * or resided it must be synchronized with this object. */
private final Object mSvgLock = new Object();
/** * Thread for working with the object above. */
private Thread mLoader;
/** * The svg image from the raw directory. */
private int svgResourceId;
/** * Object that build the animation for the path. */
private AnimatorBuilder animatorBuilder;
/** * The progress of the drawing. */
private float progress = 0f;
/** * If the used colors are from the svg or from the set color. */
private boolean naturalColors;
/** * If the view is filled with its natural colors after path drawing. */
private boolean fillAfter;
/** * The width of the view. */
private int width;
/** * The height of the view. */
private int height;然后是一些getter和setter方法。
/** * Set paths to be drawn and animated. * * @param paths - Paths that can be drawn. */
public void setPaths(final List<Path> paths) {
for (Path path : paths) {
this.paths.add(new SvgUtils.SvgPath(path, paint));
}
synchronized (mSvgLock) {
updatePathsPhaseLocked();
}
}
/** * Set path to be drawn and animated. * * @param path - Paths that can be drawn. */
public void setPath(final Path path) {
paths.add(new SvgUtils.SvgPath(path, paint));
synchronized (mSvgLock) {
updatePathsPhaseLocked();
}
}
/** * If the real svg need to be drawn after the path animation. * * @param fillAfter - boolean if the view needs to be filled after path animation. */
public void setFillAfter(final boolean fillAfter) {
this.fillAfter = fillAfter;
}
/** * Animator for the paths of the view. * * @return The AnimatorBuilder to build the animation. */
public AnimatorBuilder getPathAnimator() {
if (animatorBuilder == null) {
animatorBuilder = new AnimatorBuilder(this);
}
return animatorBuilder;
}
/** * Get the path color. * * @return The color of the paint. */
public int getPathColor() {
return paint.getColor();
}
/** * Set the path color. * * @param color -The color to set to the paint. */
public void setPathColor(final int color) {
paint.setColor(color);
}
/** * Get the path width. * * @return The width of the paint. */
public float getPathWidth() {
return paint.getStrokeWidth();
}
/** * Set the path width. * * @param width - The width of the path. */
public void setPathWidth(final float width) {
paint.setStrokeWidth(width);
}
/** * Get the svg resource id. * * @return The svg raw resource id. */
public int getSvgResource() {
return svgResourceId;
}
/** * Set the svg resource id. * * @param svgResource - The resource id of the raw svg. */
public void setSvgResource(int svgResource) {
svgResourceId = svgResource;
}
/** * If the real svg need to be drawn after the path animation. * * @param fillAfter - boolean if the view needs to be filled after path animation. */
public void setFillAfter(final boolean fillAfter) {
this.fillAfter = fillAfter;
}
/** * Animate this property. It is the percentage of the path that is drawn. * It must be [0,1]. * * @param percentage float the percentage of the path. */
public void setPercentage(float percentage) {
if (percentage < 0.0f || percentage > 1.0f) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("setPercentage not between 0.0f and 1.0f");
}
progress = percentage;
synchronized (mSvgLock) {
updatePathsPhaseLocked();
}
invalidate();
}然后通过一个函数进行路径的更新
/** * This refreshes the paths before draw and resize. */
private void updatePathsPhaseLocked() {
final int count = paths.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
SvgUtils.SvgPath svgPath = paths.get(i);
svgPath.path.reset();
svgPath.measure.getSegment(0.0f, svgPath.length * progress, svgPath.path, true);
// Required only for Android 4.4 and earlier
svgPath.path.rLineTo(0.0f, 0.0f);
}
}接着就一大堆measure啊,draw啊
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(final int w, final int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
if (mLoader != null) {
try {
mLoader.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Unexpected error", e);
}
}
if (svgResourceId != 0) {
mLoader = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
svgUtils.load(getContext(), svgResourceId);
synchronized (mSvgLock) {
width = w - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
height = h - getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom();
paths = svgUtils.getPathsForViewport(width, height);
updatePathsPhaseLocked();
}
}
}, "SVG Loader");
mLoader.start();
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (svgResourceId != 0) {
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
return;
}
int desiredWidth = 0;
int desiredHeight = 0;
final float strokeWidth = paint.getStrokeWidth() / 2;
for (SvgUtils.SvgPath path : paths) {
desiredWidth += path.bounds.left + path.bounds.width() + strokeWidth;
desiredHeight += path.bounds.top + path.bounds.height() + strokeWidth;
}
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int measuredWidth, measuredHeight;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
measuredWidth = desiredWidth;
} else {
measuredWidth = widthSize;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
measuredHeight = desiredHeight;
} else {
measuredHeight = heightSize;
}
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
synchronized (mSvgLock) {
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop());
final int count = paths.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final SvgUtils.SvgPath svgPath = paths.get(i);
final Path path = svgPath.path;
final Paint paint1 = naturalColors ? svgPath.paint : paint;
canvas.drawPath(path, paint1);
}
fillAfter(canvas);
canvas.restore();
}
}
/** * If there is svg , the user called setFillAfter(true) and the progress is finished. * * @param canvas Draw to this canvas. */
private void fillAfter(final Canvas canvas) {
if (svgResourceId != 0 && fillAfter && progress == 1f) {
svgUtils.drawSvgAfter(canvas, width, height);
}
}我们看到他重写了onSizeChanged方法,首先判断线程是否是null,如果不为null,则调用join方法,让该thread执行完run方法里面的东西后,再执行join()方法后面的代码。后面的代码就是起了一个线程获取宽度,高度,路径并更新路径等信息。
onMeasure()方法里就是一些测量内容了。具体测量逻辑见源码。
onDraw()方法主要完成绘制,其实很简单,就是在Canvas上画图,遍历所有Path,画在画布上,画完后调用了fillAfter方法,如果设置了svg资源,以及fillAfter 成员变量为true,动画已完成,则会保持动画
最后这个自定义View类里使用了创建者模式进行创建路径动画,比如动画的时间,插值器,延时,监听器等等。
/** * Object for building the animation of the path of this view. */
public static class AnimatorBuilder {
/** * Duration of the animation. */
private int duration = 350;
/** * Interpolator for the time of the animation. */
private Interpolator interpolator;
/** * The delay before the animation. */
private int delay = 0;
/** * ObjectAnimator that constructs the animation. */
private final ObjectAnimator anim;
/** * Listener called before the animation. */
private ListenerStart listenerStart;
/** * Listener after the animation. */
private ListenerEnd animationEnd;
/** * Animation listener. */
private PathViewAnimatorListener pathViewAnimatorListener;
/** * Default constructor. * * @param pathView The view that must be animated. */
public AnimatorBuilder(final PathView pathView) {
anim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(pathView, "percentage", 0.0f, 1.0f);
}
/** * Set the duration of the animation. * * @param duration - The duration of the animation. * @return AnimatorBuilder. */
public AnimatorBuilder duration(final int duration) {
this.duration = duration;
return this;
}
/** * Set the Interpolator. * * @param interpolator - Interpolator. * @return AnimatorBuilder. */
public AnimatorBuilder interpolator(final Interpolator interpolator) {
this.interpolator = interpolator;
return this;
}
/** * The delay before the animation. * * @param delay - int the delay * @return AnimatorBuilder. */
public AnimatorBuilder delay(final int delay) {
this.delay = delay;
return this;
}
/** * Set a listener before the start of the animation. * * @param listenerStart an interface called before the animation * @return AnimatorBuilder. */
public AnimatorBuilder listenerStart(final ListenerStart listenerStart) {
this.listenerStart = listenerStart;
if (pathViewAnimatorListener == null) {
pathViewAnimatorListener = new PathViewAnimatorListener();
anim.addListener(pathViewAnimatorListener);
}
return this;
}
/** * Set a listener after of the animation. * * @param animationEnd an interface called after the animation * @return AnimatorBuilder. */
public AnimatorBuilder listenerEnd(final ListenerEnd animationEnd) {
this.animationEnd = animationEnd;
if (pathViewAnimatorListener == null) {
pathViewAnimatorListener = new PathViewAnimatorListener();
anim.addListener(pathViewAnimatorListener);
}
return this;
}
/** * Starts the animation. */
public void start() {
anim.setDuration(duration);
anim.setInterpolator(interpolator);
anim.setStartDelay(delay);
anim.start();
}
/** * Animation listener to be able to provide callbacks for the caller. */
private class PathViewAnimatorListener implements Animator.AnimatorListener {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
if (listenerStart != null) listenerStart.onAnimationStart();
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
if (animationEnd != null) animationEnd.onAnimationEnd();
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) {
}
}
/** * Called when the animation start. */
public interface ListenerStart {
/** * Called when the path animation start. */
void onAnimationStart();
}
/** * Called when the animation end. */
public interface ListenerEnd {
/** * Called when the path animation end. */
void onAnimationEnd();
}
}SVG文件的加载等工作都在SvgUtils类中完成。依赖了一个jar包,该工具类主要负责资源文件的加载和初始化
构造方法是传入一个画笔
/** * Init the SVGUtils with a paint for coloring. * * @param sourcePaint - the paint for the coloring. */
public SvgUtils(final Paint sourcePaint) {
mSourcePaint = sourcePaint;
} 资源文件的加载
/** * Loading the svg from the resources. * * @param context Context object to get the resources. * @param svgResource int resource id of the svg. */
public void load(Context context, int svgResource) {
if (mSvg != null) return;
try {
mSvg = SVG.getFromResource(context, svgResource);
mSvg.setDocumentPreserveAspectRatio(PreserveAspectRatio.UNSCALED);
} catch (SVGParseException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Could not load specified SVG resource", e);
}
} 其余的方法就是跟绘制有关了。有兴趣自己去下源码看看。这里不做展开了。
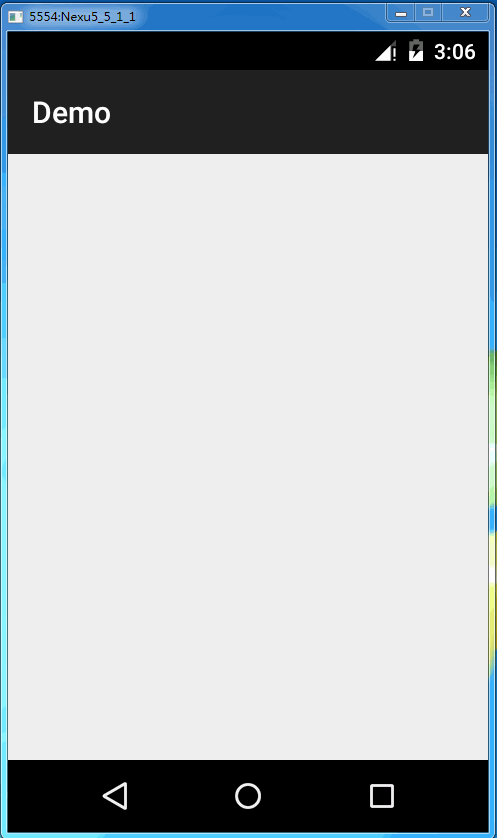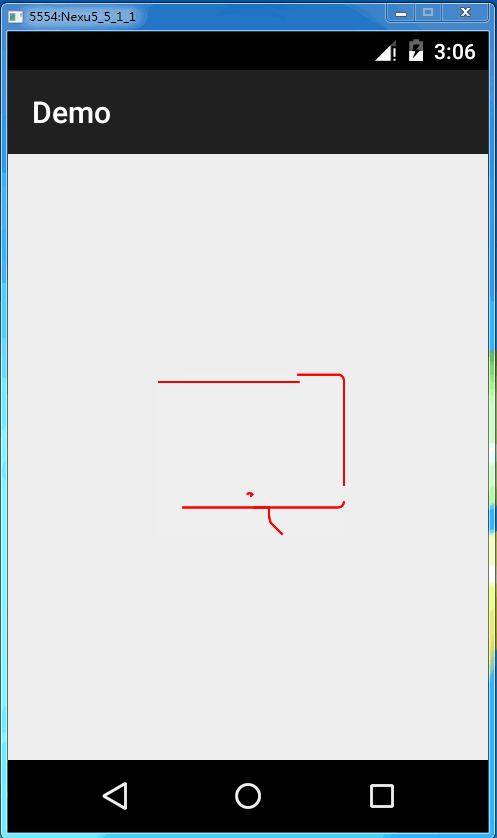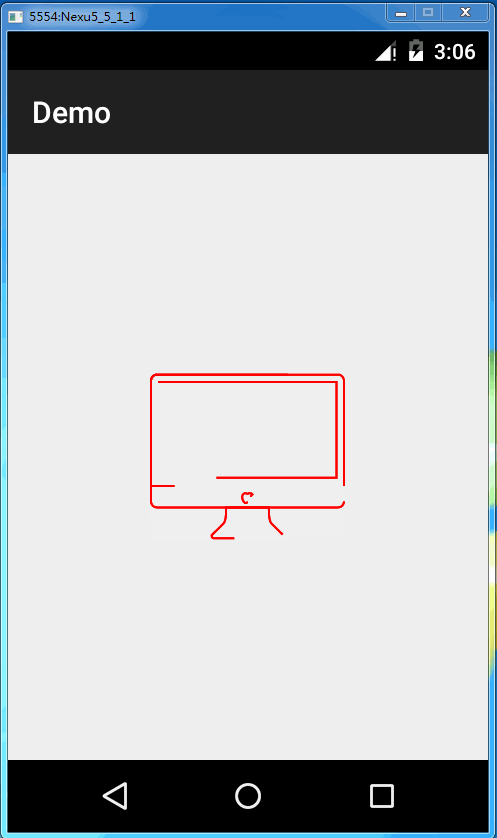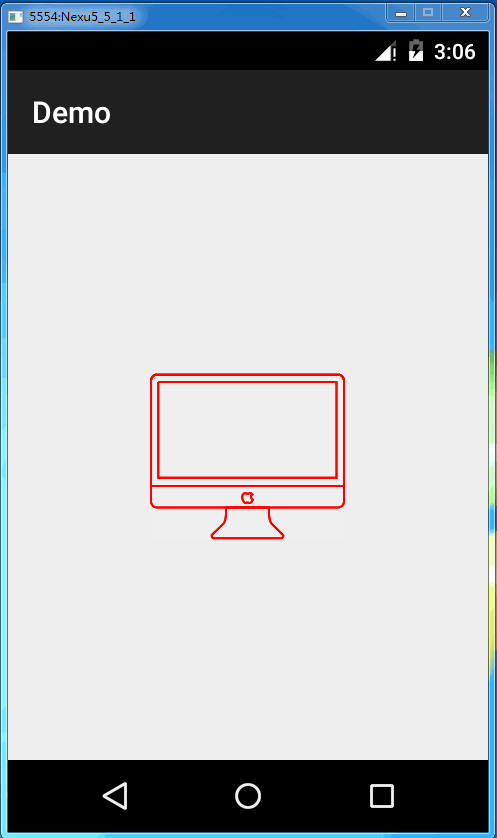
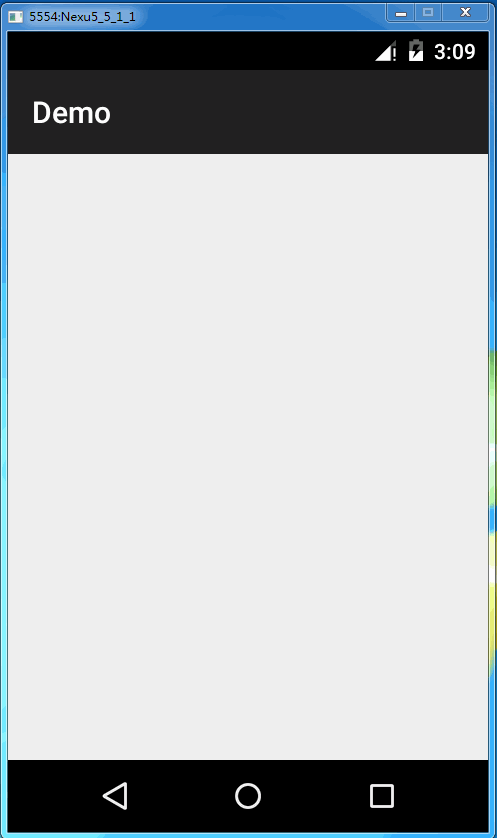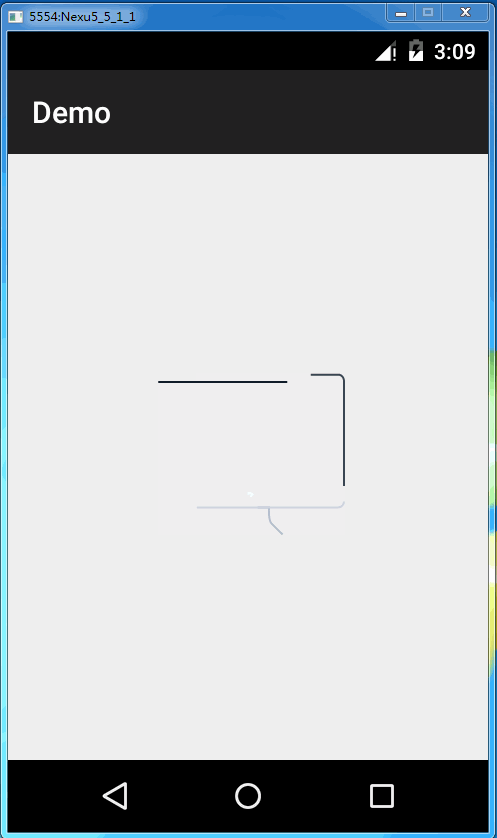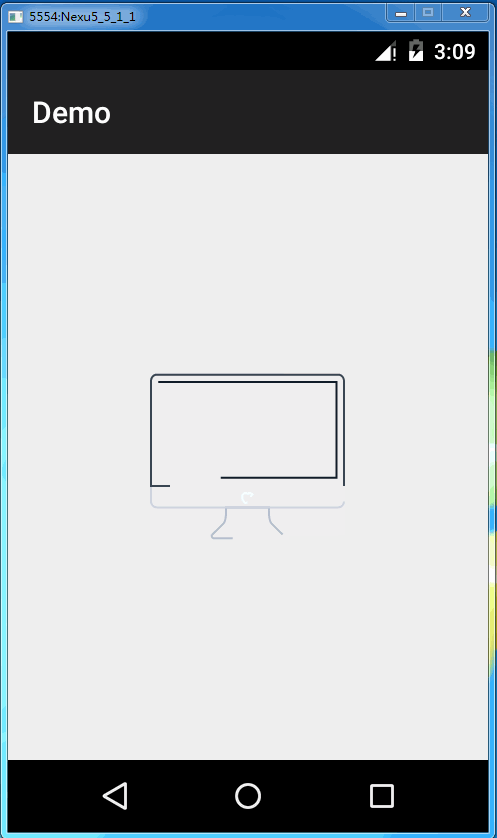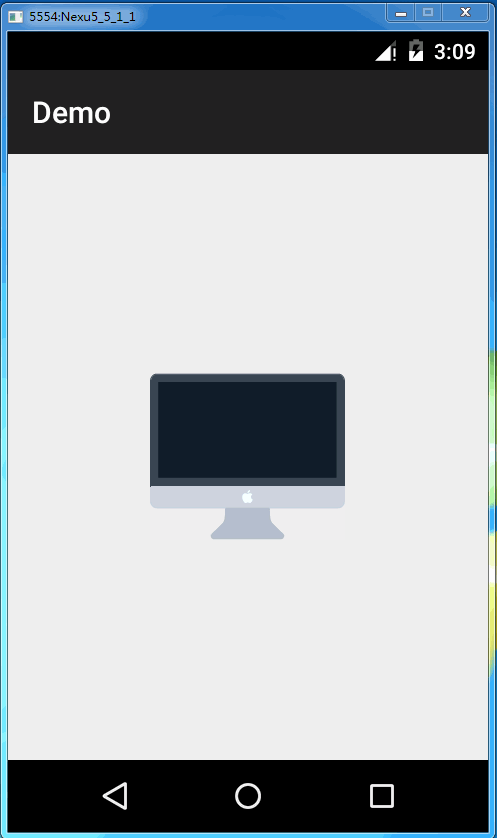
源码解析完毕后,我们使用一下这个库。我们首先使用github上的svg文件做测试。
在布局文件中添加代码
<com.eftimoff.androipathview.PathView
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/pathView"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:svg="@raw/monitor"
app:pathWidth="2"
app:pathColor="#ff0000"
/>
然后就可以通过getPathAnimator方法获得创建者对象,通过一系列的链式调用配置动画,比如延时,动画持续时间,插值器,监听器,最后调用start开始动画。
PathView mPathView= (PathView) findViewById(R.id.pathView);
mPathView.getPathAnimator()
.delay(1000)
.duration(3000)
.interpolator(new BounceInterpolator())
.listenerStart(new PathView.AnimatorBuilder.ListenerStart() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart() {
Log.e("TAG", "start");
}
})
.listenerEnd(new PathView.AnimatorBuilder.ListenerEnd() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd() {
Log.e("TAG","end");
}
}).start();
最终效果就是这样子
当然我们也可以使用svg文件里的颜色,让它绘制完成后绘制最终真正的svg,可以加入以下代码
mPathView.useNaturalColors();
mPathView.setFillAfter(true);当然你可能想让它停留在某个状态点,你可以使用以下函数进行设置,参数值范围为0到1
mPathView.setPercentage(0.8f);甚至你可以不用svg文件,你可以使用Path类
Path path=new Path();
path.moveTo(0.0f, 0.0f);
path.lineTo(length / 4f, 0.0f);
path.lineTo(length, height / 2.0f);
path.lineTo(length / 4f, height);
path.lineTo(0.0f, height);
path.lineTo(length * 3f / 4f, height / 2f);
path.lineTo(0.0f, 0.0f);
path.close();
mPathView.setPath(path);还有List类型
List<Path> paths = new ArrayList<Path>();
//to do paths.add(path)
mPathView.setPaths(paths);当然对于自定义属性,也可以通过代码设置
mPathView.setPathColor(0x00ff00);
mPathView.setPathWidth(5f);
mPathView.setSvgResource(R.raw.logout);最后贴一下svg的一些命令,每个命令都有大小写形式,大写代表后面的参数是绝对坐标,小写表示相对坐标。参数之间用空格或逗号隔开
- M: move to 移动绘制点
- L:line to 直线
- Z:close 闭合
- C:cubic bezier 三次贝塞尔曲线
- Q:quatratic bezier 二次贝塞尔曲线
- A:ellipse 圆弧
详解
- M (x y) 移动到x,y
- L (x y) 直线连到x,y,还有简化命令H(x) 水平连接、V(y)垂直连接
- Z,没有参数,连接起点和终点
- C(x1 y1 x2 y2 x y),控制点x1,y1 x2,y2,终点x,y
- Q(x1 y1 x y),控制点x1,y1,终点x,y
- A(rx ry x-axis-rotation large-arc-flag sweep-flag x y)
rx ry 椭圆半径
x-axis-rotation x轴旋转角度
large-arc-flag 为0时表示取小弧度,1时取大弧度
sweep-flag 0取逆时针方向,1取顺时针方向

更多详情请参考w3c
最后上源码http://download.csdn.net/detail/sbsujjbcy/8989661