URAL 1519. Formula 1
1519. Formula 1
Time limit: 1.0 second
Memory limit: 64 MB
Memory limit: 64 MB
Background
Regardless of the fact, that Vologda could not get rights to hold the Winter Olympic games of 20**, it is well-known, that the city will conduct one of the Formula 1 events. Surely, for such an important thing a new race circuit should be built as well as hotels, restaurants, international airport - everything for Formula 1 fans, who will flood the city soon. But when all the hotels and a half of the restaurants were built, it appeared, that at the site for the future circuit a lot of gophers lived in their holes. Since we like animals very much, ecologists will never allow to build the race circuit over the holes. So now the mayor is sitting sadly in his office and looking at the map of the circuit with all the holes plotted on it.
Problem
Who will be smart enough to draw a plan of the circuit and keep the city from inevitable disgrace? Of course, only true professionals - battle-hardened programmers from the first team of local technical university!.. But our heroes were not looking for easy life and set much more difficult problem: "Certainly, our mayor will be glad, if we find how many ways of building the circuit are there!" - they said.
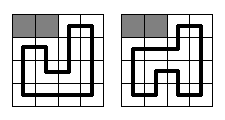
It should be said, that the circuit in Vologda is going to be rather simple. It will be a rectangle
N*
M cells in size with a single circuit segment built through each cell. Each segment should be parallel to one of rectangle's sides, so only right-angled bends may be on the circuit. At the picture below two samples are given for
N =
M = 4 (gray squares mean gopher holes, and the bold black line means the race circuit). There are no other ways to build the circuit here.
Input
The first line contains the integer numbers
N and
M (2 ≤
N,
M ≤ 12). Each of the next
N lines contains
M characters, which are the corresponding cells of the rectangle. Character "." (full stop) means a cell, where a segment of the race circuit should be built, and character "*" (asterisk) - a cell, where a gopher hole is located.
Output
You should output the desired number of ways. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 2
63-1.
Samples
| input | output |
|---|---|
4 4 **.. .... .... .... |
2 |
4 4 .... .... .... .... |
6 |
Problem Author: Nikita Rybak, Ilya Grebnov, Dmitry Kovalioff
Problem Source: Timus Top Coders: Third Challenge
Problem Source: Timus Top Coders: Third Challenge
Tags: none
hide tags for unsolved problems )
解题思路和hdu1693差不多。都是插头DP。只是不能有多个回路所以回路只能在最后一个可到点形成。代码还是用的大牛的模板。很好用!
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int HASH=30007;//哈希表的大小
const int STATE=1000010;//状态数
const int MAXD=15;
int N,M,ex,ey;//ex,ey最后一个可到点
int code[MAXD],maze[MAXD][MAXD],mcod[MAXD];//编码。和存地图。最小表示法
char s[20];
struct HASHMAP//哈希表结构
{
int head[HASH],next[STATE],sz;//哈希表头指针模数相同的状态用链表连接。方便状态查找和判重
long long f[STATE],state[STATE];//f记录对应状态的方法数。next指向模数相同的下一个状态。state记录状态。sz记录状态总数
void init()//哈希表初始化函数
{
sz=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void push(long long st,long long ans)//压入状态和方法数
{
int i,h=st%HASH;
for(i=head[h]; i!=-1; i=next[i])
if(st==state[i])//若状态已经存在。方法数增加就行
{
f[i]+=ans;
return;
}
f[sz]=ans;//存入新的可行状态
state[sz]=st;
next[sz]=head[h];
head[h]=sz++;
}
} hm[2];
void decode(int *code,int m,long long st)//编码从高位到低位m到0编码。对应从左到右的插头
{
int i;
for(i=m; i>=0; i--)
{
code[i]=st&7;
st>>=3;
}
}
long long encode(int *code,int m)//最小表示法解码到st中
{
int i,cnt=1;
long long st=0;
memset(mcod,-1,sizeof mcod);
mcod[0]=0;
for( i=0; i<=m; i++)
{
if(mcod[code[i]]==-1)
mcod[code[i]]=cnt++;
code[i]=mcod[code[i]];
st<<=3;
st|=code[i];
}
return st;
}
void init()//读数据。初始化
{
int i,j;
memset(maze,0,sizeof maze);
ex=0;
for(i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
scanf("%s",s+1);
for( j=1; j<=M; j++)
{
if(s[j]=='.')
{
maze[i][j]=1;
ex=i,ey=j;
}
}
}
}
void shift(int *code,int m)//换行的时候移位
{
int i;
for(i=m; i>0; i--)
code[i]=code[i-1];
code[0]=0;
}
void dpblank(int i,int j,int cur)//处理可到格的情况
{
int k,t,left,up,temp;
for(k=0; k<hm[cur].sz; k++) //遍历j格出轮廓线的状态进行状态转移
{
decode(code,M,hm[cur].state[k]);//对状态进行编码
left=code[j-1];//获取左插头状态
up=code[j];//获取上插头状态
if(left&&up)//11 -> 00
{
if(left==up)//形成回路
{
if(i==ex&&j==ey)//判断是否到了最后一个可到点
{
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;//只能为0一个格子只能两个插头
if(j==M)shift(code,M);//到了边界后换行
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);//压入新状态
}
}
else
{
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;
for(t=0;t<=M;t++)
if(code[t]==up)
{
code[t]=left;
break;
}
if(j==M)shift(code,M);//到了边界后换行
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);//压入新状态
}
}
else if((!left&&up)||(left&&!up))//01 或 10
{
if(up)
temp=up;
else
temp=left;
if(maze[i][j+1])//j==m时maze[i][j]为0也不用shift
{
code[j-1]=0;
code[j]=temp;
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
if(maze[i+1][j])
{
code[j-1]=temp;
code[j]=0;
if(j==M)shift(code,M);//这个不要忘了!
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
else
{
if(maze[i][j+1]&&maze[i+1][j])//若j==m不会合法所以不用shift
{
code[j]=code[j-1]=13;
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
}
}
void dpblock(int i,int j,int cur)//处理不能到格的情况
{
int k;
for(k=0; k<hm[cur].sz; k++) //存入状态均合法不用判断
{
decode(code,M,hm[cur].state[k]);//先编码
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;//肯定不能用插头
if(j==M)shift(code,M);//转移到下一行
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
void solve()
{
int i,j,cur=0;
long long ans=0;
hm[cur].init();//cur用于滚动数组。节约空间。cur存当前格上插头和左插头情况。cur^1用于记录转移出的新状态即下一格
hm[cur].push(0,1);
for(i=1; i<=N; i++)
for(j=1; j<=M; j++)
{
hm[cur^1].init();//初始化
if(maze[i][j])dpblank(i,j,cur);
else dpblock(i,j,cur);
cur^=1;
}
for(i=0; i<hm[cur].sz; i++)
ans+=hm[cur].f[i];
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&N,&M))
{
init();
if(!ex)
printf("0\n");
else
solve();
}
return 0;
}