开源搜索引擎Lucene.Net---学习笔记(2) 使用Lucene.Net源码搜索
下面先通过Lucene.Net简单的例子,来看看Lucene.Net建立索引、查询的操作过程。
1、索引的建立:
索引的建立,我把其方法直接放到了Program.Main()中:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CyhTest
{
using Lucene.Net.Analysis;
using Lucene.Net.Analysis.Standard;
using Lucene.Net.Documents;
using Lucene.Net.Index;
using Lucene.Net.QueryParsers;
using Lucene.Net.Search;
using Lucene.Net.Store;
using Lucene.Net.Util;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//索引的建立
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter("IndexDirection", analyzer, true); //创建索引,"IndexDirection”为索引存放目录
writer.SetUseCompoundFile(false); //采用非复合式的索引模式
writer.SetMergeFactor(2); //设置合并频率的大小为2
cyh_CreateIndex(writer); //创建索引
writer.Optimize();
writer.Close();
Console.ReadKey();
}
/// <summary>
/// 创建索引
/// </summary>
static void cyh_CreateIndex(IndexWriter writer)
{
Document doc1 = new Document(); //创建Document对象
Field field1 = new Field("Title1", "term1 term2 term3", Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.TOKENIZED); //索引文件内容
doc1.Add(field1);
writer.AddDocument(doc1); //将Document对象添加到索引中
Document doc2 = new Document(); //创建Document对象
Field field2 = new Field("Title1", "term2 term3 term2", Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.TOKENIZED); //索引文件内容
doc2.Add(field2);
writer.AddDocument(doc2); //将Document对象添加到索引中
Document doc3 = new Document(); //创建Document对象
Field field3 = new Field("Title1", "term3 term3", Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.TOKENIZED); //索引文件内容
doc3.Add(field3);
writer.AddDocument(doc3); //将Document对象添加到索引中
Document doc4 = new Document(); //创建Document对象
Field field4 = new Field("Title2", "Hello Lucene!", Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.TOKENIZED); //索引文件内容
doc4.Add(field4);
writer.AddDocument(doc4); //将Document对象添加到索引中
Document doc5 = new Document(); //创建Document对象
Field field5 = new Field("Title2", "I like Lucene!", Field.Store.NO,Field.Index.UN_TOKENIZED,Field.TermVector.WITH_POSITIONS_OFFSETS); //索引文件内容
doc5.Add(field5);
writer.AddDocument(doc5); //将Document对象添加到索引中
Document doc6 = new Document(); //创建Document对象
Field field61 = new Field("Title3", "Do you want to use it?", Field.Store.NO,Field.Index.TOKENIZED,Field.TermVector.YES); //索引文件内容
Field field62 = new Field("docName", "doc6", Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.UN_TOKENIZED); //索引文件内容
doc6.Add(field61);
doc6.Add(field62);
writer.AddDocument(doc6); //将Document对象添加到索引中
}
}
}
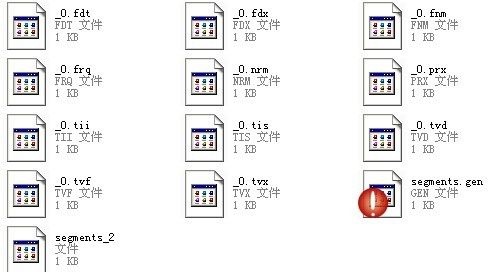
可以看到在bin/debug/IndexDirection文件夹下回生成如下一些文件:
这些即为Lucene存储的索引。
Lucene的索引结果具有层次结构,主要有以下几个层次:
• 索引(Index):
在Lucene中一个索引是放在一个文件夹中的。
如上图,同一文件夹中的所有的文件构成一个Lucene索引。
• 段(Segment):
一个索引可以包含多个段,段与段之间是独立的,添加新文档可以生成新的段,不同的段可以合并。
如上图,具有相同前缀文件的属同一个段,图中共两个段 "_0" 和 "_1"。
segments.gen和segments_5是段的元数据文件,也即它们保存了段的属性信息。
• 文档(Document):
文档是我们建索引的基本单位,不同的文档是保存在不同的段中的,一个段可以包含多篇文档。
新添加的文档是单独保存在一个新生成的段中,随着段的合并,不同的文档合并到同一个段中。
• 域(Field):
一篇文档包含不同类型的信息,可以分开索引,比如标题,时间,正文,作者等,都可以保存在不同的域里。
不同域的索引方式可以不同,在真正解析域的存储的时候,我们会详细解读。
• 词(Term):
词是索引的最小单位,是经过词法分析和语言处理后的字符串。
Lucene的索引结构中,即保存了正向信息,也保存了反向信息。
所谓正向信息:
• 按层次保存了从索引,一直到词的包含关系:索引(Index) –> 段(segment) –> 文档(Document) –>域(Field) –> 词(Term)
• 也即此索引包含了那些段,每个段包含了那些文档,每个文档包含了那些域,每个域包含了那些词。
• 既然是层次结构,则每个层次都保存了本层次的信息以及下一层次的元信息,也即属性信息,比如一本介绍中国地理的书,应该首先介绍中国地理的概况,以及中国包含多少个省,每个省介绍本省的基本概况及包含多少个市,每个市介绍本市的基本概况及包含多少个县,每个县具体介绍每个县的具体情况。
• 如上图,包含正向信息的文件有:
segments_N保存了此索引包含多少个段,每个段包含多少篇文档。
XXX.fnm保存了此段包含了多少个域,每个域的名称及索引方式。
XXX.fdx,XXX.fdt保存了此段包含的所有文档,每篇文档包含了多少域,每个域保存了那些信息。
XXX.tvx,XXX.tvd,XXX.tvf保存了此段包含多少文档,每篇文档包含了多少域,每个域包含了多少词,每个词的字符串,位置等信息。
所谓反向信息:
• 保存了词典到倒排表的映射:词(Term) –> 文档(Document)
• 如上图,包含反向信息的文件有:
XXX.tis,XXX.tii保存了词典(Term Dictionary),也即此段包含的所有的词按字典顺序的排序。
XXX.frq保存了倒排表,也即包含每个词的文档ID列表。
XXX.prx保存了倒排表中每个词在包含此词的文档中的位置。
2、进行搜索查询
为了便于今后搜索查询能够方便,因此我将构造一个CyhClass类,并将搜索所用到的一些方法放入这个类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CyhTest
{
using Lucene.Net.Analysis;
using Lucene.Net.Analysis.Standard;
using Lucene.Net.Documents;
using Lucene.Net.Index;
using Lucene.Net.QueryParsers;
using Lucene.Net.Search;
using Lucene.Net.Store;
using Lucene.Net.Util;
public class CyhClass
{
/// <summary>
/// 通过索引,搜索信息
/// </summary>
public static void doSearch(string docName, string keyword, string indexDir)
{
Query query = null;
QueryParser queryParser = null;
try
{
Directory dir = FSDirectory.GetDirectory(indexDir, false);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(dir); //打开索引
queryParser = new QueryParser(docName, new StandardAnalyzer());
query = queryParser.Parse(keyword); //对keyword解析
Hits hits = searcher.Search(query); //检索索引,hits是用来存储内容的容器
printResult(hits,keyword,docName); //打印结果
}
catch (Exception e) {
Console.WriteLine("Wrong!!!----'{0}'",e.ToString());
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 打印结果
/// </summary>
public static void printResult(Hits hits, string keyword,string docName)
{
Console.WriteLine("搜索结果:");
if (hits.Length() != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("搜索 {0},一共找到 {1} 个文档!",keyword, hits.Length());
Console.WriteLine("您要查的内容可以在下列文档中查找到:");
for (int i = 0; i < hits.Length(); i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(" 得分:{0}\n信息:{1}\n内部ID: {2}\n", hits.Score(i), hits.Doc(i).Get(docName), hits.Id(i));
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("未搜索到相关内容!");
}
}
}
}
有了这些搜索时使用的方法,便可以在Main()中方便的使用了,只需修改上述的Program.Main()函数:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//索引的建立
//Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
//IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter("IndexDirection", analyzer, true); //创建索引
//writer.SetUseCompoundFile(false); //采用非复合式的索引模式
//writer.SetMergeFactor(2); //设置合并频率的大小为2
//cyh_CreateIndex(writer); //创建索引
//writer.Optimize();
//writer.Close();
//查询过程
string tempDir = "IndexDirection";
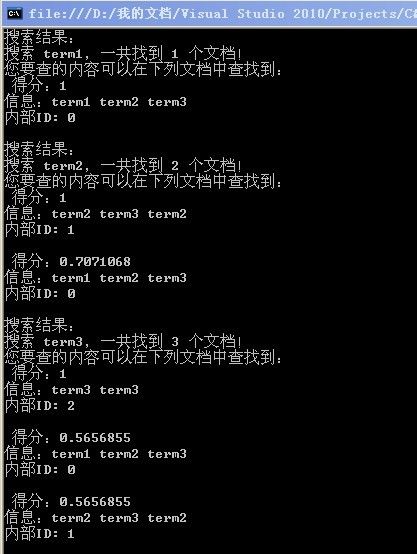
CyhClass.doSearch("Title1", "term1", tempDir);
CyhClass.doSearch("Title1", "term2", tempDir);
CyhClass.doSearch("Title1", "term3", tempDir);
CyhClass.doSearch("Title2", "Lucene", tempDir);
Console.ReadKey();
}
可得到以下结果:
以上即为Lucene.Net建立索引与搜索的简单例子,至于细节,将在下一章中进行分析。