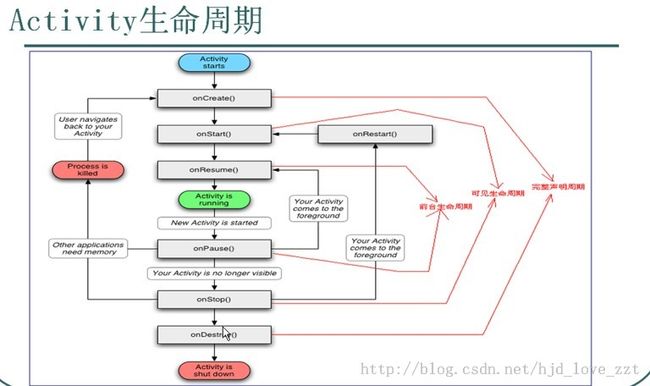
Activity生命周期详解
原理图:
文字描述如下:
Activity的作用:
起显示作用,他是用来和用户交互的。也是一个view的容器
1 完整的生命周期:
onCreate() --> onStart() --> onResume() activiyt已经正常显示
点击回退键
onPause() --> onStop() --> onDetroy()
2 可视的生命周期
onCreate() --> onStart() --> onResume() activiyt已经正常显示
打开一个activity。该activity完全覆盖上一个activity
onPause() ---> onStop()
点击回退键
onRestart() --> onStart() ---> onResume()
点击回退键
onPause() --> onStop() --> onDetroy()
3 android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Dialog"
就可以把activity变成对话框的效果
onCreate() --> onStart() --> onResume() activiyt已经正常显示
打开一个activity。该activity没有完全覆盖上一个activity
onPause()
点击回退键
onResume()
------------如果要将完全覆盖-----(转换成)------>>部分覆盖,只需要在清单文件AndroidManifest.xml中在
<activity/>标签中加上这么一句:android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Dialog"------------------------------
代码如下:
1)main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="get"
android:text="打开" />
</LinearLayout>
2)main2.xml
android:layout_gravity="center" //控件居中
android:gravity="center" //控件中的文本居中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="第二个activity"
android:textColor="#00f"/>
</LinearLayout>
3)MainActivity
package com.njupt.activitylife;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
System.out.println("onCreate");
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
System.out.println("onStart()");
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
System.out.println("onResume()");
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
System.out.println("onPause()");
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
System.out.println("onStop()");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("onDestroy()");
}
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart();
System.out.println("onRestart()");
}
public void get(View v){
Intent intent = new Intent(this,Main2Activity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
4)Main2Activity
package com.njupt.activitylife;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class Main2Activity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main2);
}
}
5)AndroidManifest.xml
最后在清单文件中将Main2Activity注册上去
<activity android:name="com.njupt.activitylife.Main2Activity" android:label="第二个Activity"
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Dialog"/>