mmap系统调用(内核空间到用户空间的映射)
linux中内核空间到用户空间的地址映射让用户层应用可以直接访问内核地址,这就是mmap方法,内核的mmap函数是file_operations中的成员,
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
。。。。。
}
映射一个设备是指把用户空间的一段地址关联到设备内存上。当程序读写这段用户空间的地址时,它实际上是在访问设备;
对于驱动程序编写,这个过程可以细分为三个过程:
1.找到用户空间的地址
2.找到设备内存
3.关联
其中,设备内存的物理地址对于程序员来说是已知的可以通过datasheet查看到,不需驱动程序去实现;找到用户空间的内存,这个其实内核会帮我们完成,所以对于我们驱动程序员,只要实现关联这一环节就行了。
如何关联:
设备内存是物理地址,用户空间地址是虚拟地址,那么如何关联呢?物理地址与虚拟地址的关联就是通过页式管理来实现的,所以mmap设备方法所需要做到就是建立虚拟地址到物理地址的页表。
要实现用户层对内核的访问就是要再驱动程序中实现file_operations中的mmap指针函数,这个函数会在mmap系统调用时被调用,在此之前,内核已经为我们完成了很多工作,为了支持mmap操作,驱动程序需要为它的地址范围建立合适的页表。
对于 :int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *)
其中参数struct vm_area_struct就是内核为我们找到的用户空间的进程虚拟内存区域,这就是我驱动程序需要映射到设备内存的地址。
mmap如何完成页表的建立?:
有两种方法:
1.使用remap_pfn_range一次建立所有页表;
2.使用nopage VMA方法每次建立一个页表
本文只讨论方法1
下面是函数原型:
int remap_pfn_range(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long addr,unsigned long pfn, unsigned long size, pgprot_t prot)
remap_pfn_range 通过你的页帧号来建立页表, 并映射到用户空间!
一般情况是你的驱动分配一块内存,然后在驱动的mmap中使用这块内存的 物理地址转成页帧号, 再调用remap_pfn_range!
假设1你是通过kmalloc(),get_free_pages()等分配的,这种内存页是不能通过remap_pfn_range()映射出去的,要对每个页面调用SetPageReserverd()标记为“保留”才可以,virt_to_phys()函数只是得到其物理地 址,remap_pfn_range()中的第三个参数是要求物理页便的“帧”号,即pfn,所以你的phys还要“> > PAGE_SHIFT”操作
假设2你是通过vmalloc分配得来的,同上,不同的是要用vmalloc_to_pfn
3,用kmalloc,get_free_pages,vmalloc分配的物理内存页面最好还是不要用remap_pfn_page方法,建议使用VMA的nopage方法
4,对于这样的设备内存,最好对调用pgprot_nocached(vma-> vm_page_prot)后传给remap_pfn_range,防止处理器缓存
vma:虚拟内存区域指针
addr:虚拟地知道起始值
pfn:要映射的物理地址所在的物理页帧号,可将物理地址>>PAGE_SHIFT得到
size:要映射的区域的大小
prot:VMA的保护属性
实现实例:
demo.c
:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/pagemap.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include "demo.h"
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("mmap demo driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
struct simple_dev *simple_devices;
static unsigned char simple_inc=0;
static char*buffer=NULL;
static char*buffer_area=NULL;
int simple_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct simple_dev *dev;
simple_inc++;
dev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct simple_dev, cdev);
filp->private_data = dev;
return 0;
}
int simple_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
simple_inc--;
return 0;
}
static int simple_mmap(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
int ret;
ret = remap_pfn_range(vma,
vma->vm_start,
virt_to_phys((void*)((unsigned long)buffer_area)) >> PAGE_SHIFT,//这个地方由于我们是将一段虚拟内存buffer_area虚拟为物理内存,所以这里要使用virt_to_phys,在
//实际的驱动程序中这里就是设备的物理地址,不需要转换了!
vma->vm_end-vma->vm_start,
PAGE_SHARED);
if(ret != 0) {
return -EAGAIN;
}
return 0;
}
struct file_operations simple_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = simple_open,
.mmap = simple_mmap,
.release = simple_release,
};
/*******************************************************
MODULE ROUTINE
*******************************************************/
void simple_cleanup_module(void)
{
dev_t devno = MKDEV(simple_MAJOR, simple_MINOR);
unsigned long virt_addr;
if (simple_devices)
{
cdev_del(&simple_devices->cdev);
kfree(simple_devices);
}
for(virt_addr=(unsigned long)buffer_area; virt_addr<(unsigned long)buffer_area+4096;
virt_addr+=PAGE_SIZE)
{
SetPageReserved(virt_to_page(virt_addr));
}
if (buffer)
kfree(buffer);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno,1);
}
int simple_init_module(void)
{
int result;
dev_t dev = 0;
int i;
unsigned long virt_addr;
dev = MKDEV(simple_MAJOR, simple_MINOR);
result = register_chrdev_region(dev, 1, "DEMO");
if (result < 0)
{
printk(KERN_WARNING "DEMO: can't get major %d\n", simple_MAJOR);
goto out_free;
}
simple_devices = kmalloc(sizeof(struct simple_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!simple_devices)
{
result = -ENOMEM;
goto out_free;
}
memset(simple_devices, 0, sizeof(struct simple_dev));
sema_init(&simple_devices->sem,1);
cdev_init(&simple_devices->cdev, &simple_fops);
simple_devices->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
simple_devices->cdev.ops = &simple_fops;
result = cdev_add (&simple_devices->cdev, dev, 1);
if(result)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding DEMO\n", result);
goto out_free;
}
buffer = kmalloc(4096,GFP_KERNEL);
printk(" mmap buffer = %p\n",buffer);
buffer_area=(int *)(((unsigned long)buffer + PAGE_SIZE -1) & PAGE_MASK);
for (virt_addr=(unsigned long)buffer_area; virt_addr<(unsigned long)buffer_area+4096;
virt_addr+=PAGE_SIZE)
{
/* reserve all pages to make them remapable */
SetPageReserved(virt_to_page(virt_addr));//将页配置为保留,防止映射到用户空间的页面被swap out出去;
}
memset(buffer,'C',100);
return 0;
out_free:
simple_cleanup_module();
return result;
}
module_init(simple_init_module);
module_exit(simple_cleanup_module);
demo.h:
#ifndef _simple_H_
#define _simple_H_
#include <linux/ioctl.h> /* needed for the _IOW etc stuff used later */
/********************************************************
* Macros to help debugging
********************************************************/
#undef PDEBUG /* undef it, just in case */
#ifdef simple_DEBUG
#ifdef __KERNEL__
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) printk( KERN_DEBUG "DEMO: " fmt, ## args)
#else//usr space
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) fprintf(stderr, fmt, ## args)
#endif
#else
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) /* not debugging: nothing */
#endif
#undef PDEBUGG
#define PDEBUGG(fmt, args...) /* nothing: it's a placeholder */
//设备号
#define simple_MAJOR 224
#define simple_MINOR 0
#define COMMAND1 1
#define COMMAND2 2
//设备结构
struct simple_dev
{
struct semaphore sem; /* mutual exclusion semaphore */
struct cdev cdev; /* Char device structure */
};
//函数申明
ssize_t simple_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos);
ssize_t simple_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos);
loff_t simple_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t off, int whence);
int simple_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
#endif /* _simple_H_ */
makefile:
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := demo.o
else
KERNELDIR := /opt/FriendlyARM/mini6410/linux/linux-2.6.38
PWD:=$(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
rm -rf *.ko *.o *.mod.c *.mod.o *.symvers
endif
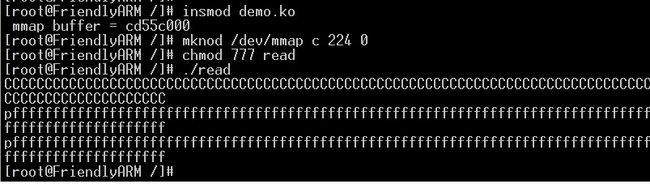
测试用例:read.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd;
char *addr=NULL;
fd = open("/dev/mmap",O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return 0;
}
addr = mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED,
fd, 0);
if(addr == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap");
return 0;
}
printf("%s\n", addr);
memset(addr,'f',100);
addr[0]='p';
printf("%s\n", addr);
munmap(addr,4096);
addr=NULL;
close(fd);
fd = open("/dev/mmap",O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return 0;
}
addr = mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED,
fd, 0);
if(addr == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap");
return 0;
}
printf("%s\n", addr);
munmap(addr,4096);
close(fd);
return(0);
}