1089. Insert or Merge (25)
According to Wikipedia:
Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and growing a sorted output list. Each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list, and inserts it there. It repeats until no input elements remain.
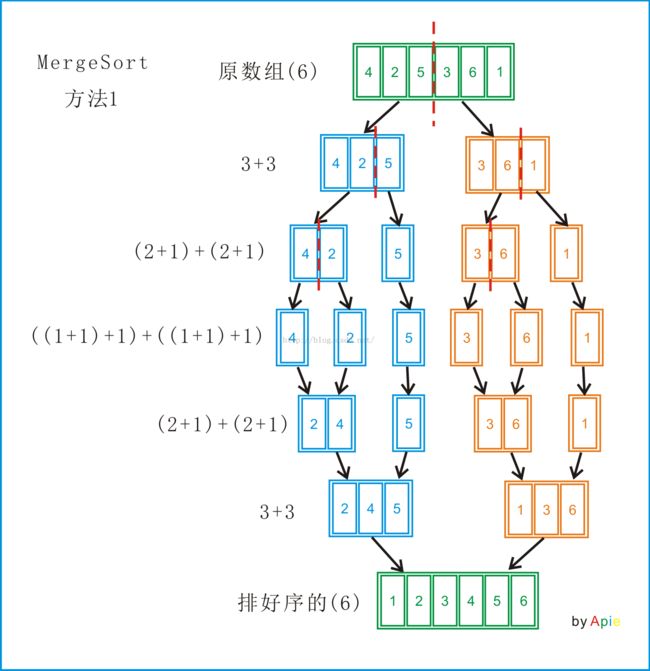
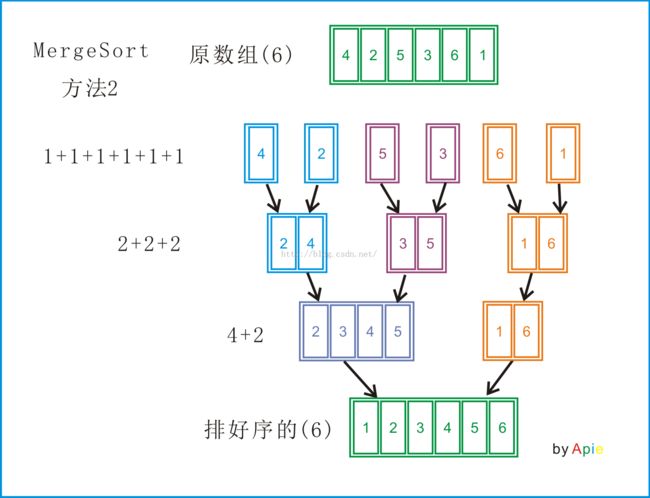
Merge sort works as follows: Divide the unsorted list into N sublists, each containing 1 element (a list of 1 element is considered sorted). Then repeatedly merge two adjacent sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining.
Now given the initial sequence of integers, together with a sequence which is a result of several iterations of some sorting method, can you tell which sorting method we are using?
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (<=100). Then in the next line, N integers are given as the initial sequence. The last line contains the partially sorted sequence of the N numbers. It is assumed that the target sequence is always ascending. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in the first line either "Insertion Sort" or "Merge Sort" to indicate the method used to obtain the partial result. Then run this method for one more iteration and output in the second line the resulting sequence. It is guaranteed that the answer is unique for each test case. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input 1:10 3 1 2 8 7 5 9 4 6 0 1 2 3 7 8 5 9 4 6 0Sample Output 1:
Insertion Sort 1 2 3 5 7 8 9 4 6 0Sample Input 2:
10 3 1 2 8 7 5 9 4 0 6 1 3 2 8 5 7 4 9 0 6Sample Output 2:
Merge Sort 1 2 3 8 4 5 7 9 0 6
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int min(int a, int b){
return a > b ? b : a;
}
bool same(const vector<int>&V1, const vector<int>&V2){//比较两个vector中的元素是否相同
for (int i = 0; i < V1.size(); ++i){
if (V1[i] != V2[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<int> merge2Vectors(vector<int>::iterator V1_begin, vector<int>::iterator V1_end, vector<int>::iterator V2_begin, vector<int>::iterator V2_end){
//合并两个vector为一个,归并排序中merge的部分,其中每个vector都要是递增的
vector<int>::iterator itr1 = V1_begin;
vector<int>::iterator itr2 = V2_begin;
vector<int>ret;
while (itr1 != V1_end && itr2 != V2_end){
if (*itr1 < *itr2){
ret.push_back(*itr1);
itr1++;
}
else{
ret.push_back(*itr2);
itr2++;
}
}
while (itr1 != V1_end){
ret.push_back(*itr1);
itr1++;
}
while (itr2 != V2_end){
ret.push_back(*itr2);
itr2++;
}
return ret;
}
vector<vector<int>>InsertSort_V;//存放插入排序每次的序列变化
vector<vector<int>>MergeSort_V;//存放归并排序每次的序列变化
void do_InsertSort(vector<int>original){//获取插入排序的每一次序列
int length = original.size();
for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i){//插入排序
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && original[j] > original[i]) --j;
int temp = original[i];
for (int k = i; k > j + 1; --k){
original[k] = original[k - 1];
}
original[j + 1] = temp;
if (InsertSort_V.size() == 0 || !same(InsertSort_V[InsertSort_V.size() - 1],original))
//如果序列集为空,或者本次算法后序列有变化,才加入序列集
InsertSort_V.push_back(original);
}
}
void do_MergeSort(vector<int>original){//获取归并排序的每一次序列
//这里采用的是上述的归并排序方法2
for (int i = 1; i < original.size(); i *= 2){//i是每次的步长,每次指数2递增
vector<int>temp;
for (int j = 0; j < original.size(); j += 2*i){//j是每组其实排序的位置,下一组就是j + 2*i
vector<int>temp_sec = merge2Vectors(original.begin() + j, original.begin() +min(j + i, original.size()), original.begin() + min(j + i, original.size()), original.begin() + min(j + 2*i, original.size()));
//注意当到达末尾的情况,需要进行一个min的判断
temp.insert(temp.end(), temp_sec.begin(), temp_sec.end());//把每两个小组排好序的合并到temp中
}
if (MergeSort_V.size() == 0 || !same(MergeSort_V[MergeSort_V.size() - 1], temp))
//如果序列集为空,或者本次算法后序列有变化,才加入序列集
MergeSort_V.push_back(temp);
original = temp;
temp.clear();
}
}
void print(const vector<int>&V){//格式化打印序列
for (int i = 0; i < V.size(); ++i){
if (i == 0)cout << V[i];
else cout << " " << V[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
freopen("F://Temp/input.txt", "r",stdin);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>input;
vector<int>result;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
int num;
cin >> num;
input.push_back(num);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
int num;
cin >> num;
result.push_back(num);
}
do_InsertSort(input);
for (int i = 0; i < InsertSort_V.size(); ++i){
if (same(InsertSort_V[i], result)){
cout << "Insertion Sort" << endl;
if (i == InsertSort_V.size() - 1)//如果是最后一个序列相等,那么下一个序列还是最后一个序列
print(InsertSort_V[i]);
else
print(InsertSort_V[i + 1]);
return 0;
}
}
do_MergeSort(input);
for (int i = 0; i < MergeSort_V.size(); ++i){
if (same(MergeSort_V[i], result)){
cout << "Merge Sort" << endl;
if (i == MergeSort_V.size() - 1)//如果是最后一个序列相等,那么下一个序列还是最后一个序列
print(MergeSort_V[i]);
else
print(MergeSort_V[i + 1]);
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 101;
int num1[N];
int num2[N];
int main(void)
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf("%d", &num1[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf("%d", &num2[i]);
bool isInsert = true;
int i = 1;
while (i < n && num2[i] >= num2[i - 1])
++i;
int j = i;
while (i < n && num2[i] == num1[i])
++i;
if (i != n)
isInsert = false;
if (isInsert)
printf("Insertion Sort\n");
else
printf("Merge Sort\n");
if (isInsert)
{
while (j > 0 && num2[j - 1] > num2[j])
{
int temp = num2[j - 1];
num2[j - 1] = num2[j];
num2[j] = temp;
--j;
}
}
else
{
int k = n;
i = 0;
while (i < n)
{
int currLength = 1;
j = i + 1;
while (j < n && num2[j - 1] <= num2[j])
{
++j;
currLength++;
}
if (j == n)
break;
else
{
k = min(currLength, k);
i = j;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * k)
{
sort(num2 + i, num2 + min(i + 2 * k, n));
}
}
printf("%d", num2[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
printf(" %d", num2[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}