应用Backtracking解一道算法题
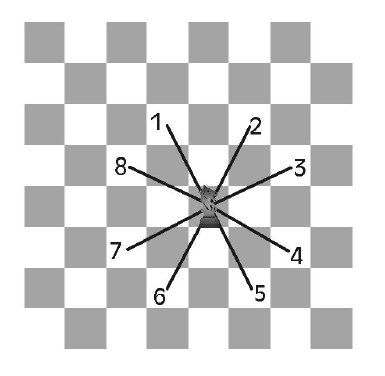
在一个n乘n的棋盘上有一匹马,要求这匹马不重复的把每个格子都跳一边。这里马的走法和中国象棋里的马一样。如下图所示,一步只能跳到位于棋盘内的1到8的八个格子里。
对这道题目,一个最直观的解法就是使用所谓的Backtracking的思路,从起点开始,一直跳,没格子可跳了,就退回一步,接着往下跳。在这个过程中,记下所有跳过的格子,不重复跳到跳过的格子里。直到所有的格子都跳完为止,也就是发现一个解法,或者所有可能的跳法都试过,还没有找到一个跳法,也就是没有解法。
很简单的思路,但是如果你不熟悉Recursion的编程的话,要实现却不那么简单。Recursion是计算机科学中最重要的一个概念和工具,也是计算机科学强大动力的源泉,怎么强调都不过分。Recursion在计算机的各个学科都有着非常重要的作用。所有可计算的函数可以归结在Partial Recursive Function下。掌握和熟悉Recursion的思路可以说是您步入计算机科学殿堂的第一步。
下面是我用Java编写的跳马题的Recursive的解法
1
private
static
int
[][] board;
2 private static int length;
3
4 /**
5 * search a solution of Springerproblem
6 *
7 * @param n board of n*n fields
8 * @param x [1 .. n] horizontal coordinate
9 * @param y [1 .. n] vertical coordinate
10 * @return true found, false no
11 */
12 public static boolean search( int n, int x, int y) {
13 if (n < 1 || x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > n) {
14 System.out.println( " wrong input dimension. " );
15 return false ;
16 }
17
18 board = new int [n + 1 ][n + 1 ];
19 length = n;
20 for ( int i = 1 ; i <= length; i ++ )
21 for ( int j = 1 ; j < length; j ++ )
22 board[i][j] = 0 ;
23
24 return research(x, y, 1 );
25 }
26
27 /**
28 * recursive search
29 *
30 * @param x 起点x
31 * @param y 起点y
32 * @param step 第几步
33 * @return true 找到解法,false,失败了
34 */
35 private static boolean research( int x, int y, int step) {
36 if (x < 1 || x > length || y < 1 || y > length)
37 return false ;
38 if (board[x][y] > 0 )
39 return false ;
40
41 board[x][y] = step;
42 if (step == length * length)
43 return true ;
44
45 if (research(x - 1 , y - 2 , step + 1 ))
46 return true ;
47 if (research(x - 1 , y + 2 , step + 1 ))
48 return true ;
49 if (research(x + 1 , y - 2 , step + 1 ))
50 return true ;
51 if (research(x + 1 , y + 2 , step + 1 ))
52 return true ;
53 if (research(x - 2 , y - 1 , step + 1 ))
54 return true ;
55 if (research(x - 2 , y + 1 , step + 1 ))
56 return true ;
57 if (research(x + 2 , y - 1 , step + 1 ))
58 return true ;
59 if (research(x + 2 , y + 1 , step + 1 ))
60 return true ;
61
62 board[x][y] = 0 ;
63 return false ;
64 }
2 private static int length;
3
4 /**
5 * search a solution of Springerproblem
6 *
7 * @param n board of n*n fields
8 * @param x [1 .. n] horizontal coordinate
9 * @param y [1 .. n] vertical coordinate
10 * @return true found, false no
11 */
12 public static boolean search( int n, int x, int y) {
13 if (n < 1 || x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > n) {
14 System.out.println( " wrong input dimension. " );
15 return false ;
16 }
17
18 board = new int [n + 1 ][n + 1 ];
19 length = n;
20 for ( int i = 1 ; i <= length; i ++ )
21 for ( int j = 1 ; j < length; j ++ )
22 board[i][j] = 0 ;
23
24 return research(x, y, 1 );
25 }
26
27 /**
28 * recursive search
29 *
30 * @param x 起点x
31 * @param y 起点y
32 * @param step 第几步
33 * @return true 找到解法,false,失败了
34 */
35 private static boolean research( int x, int y, int step) {
36 if (x < 1 || x > length || y < 1 || y > length)
37 return false ;
38 if (board[x][y] > 0 )
39 return false ;
40
41 board[x][y] = step;
42 if (step == length * length)
43 return true ;
44
45 if (research(x - 1 , y - 2 , step + 1 ))
46 return true ;
47 if (research(x - 1 , y + 2 , step + 1 ))
48 return true ;
49 if (research(x + 1 , y - 2 , step + 1 ))
50 return true ;
51 if (research(x + 1 , y + 2 , step + 1 ))
52 return true ;
53 if (research(x - 2 , y - 1 , step + 1 ))
54 return true ;
55 if (research(x - 2 , y + 1 , step + 1 ))
56 return true ;
57 if (research(x + 2 , y - 1 , step + 1 ))
58 return true ;
59 if (research(x + 2 , y + 1 , step + 1 ))
60 return true ;
61
62 board[x][y] = 0 ;
63 return false ;
64 }
初学Recursion的时候,很不习惯他的思维方式。有时候甚至会奇怪这样就把问题解决了。在使用Recursion编程的时候,可以假定您已经有一个要找的函数f了,然后应用f 较小的情况来解决大的情况,最小的情况另外特殊求解。这个过程中最关键的就是设计f的接口和功能,在解题的过程中,您可能要不断的调整f的接口和功能。
转载请保留 http://www.blogjava.net/xilaile/archive/2007/04/06/109001.html