第十四周项目四—数组的排序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubble_sort(int a[],int b);
void output_array(int a[],int b);//两个函数bubble_sort和output_array的声明
int main( )
{
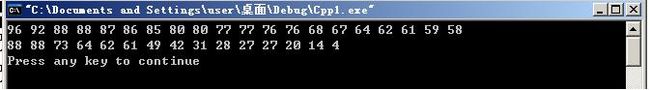
int a[20]={86,76,62,58,77,85,92,80,96,88,77,67,80,68,88,87,64,59,61,76};
int b[15]={27,61,49,88,4,20,28,31,42,62,64,14,88,27,73};
bubble_sort(a,20); //用冒泡法按降序排序a中元素
output_array(a,20); //输出排序后的数组
bubble_sort(b,15); //用冒泡法按降序排序b中元素
output_array(b,15); //输出排序后的数组
return 0;
}
void bubble_sort(int a[],int b)
{int i,j,t,h;
for(i=0;i<b-1;i++)
{ t=i;
{
for(j=i+1;j<b;j++)
if(a[j]<a[t])
t=j;
}
h=a[t];
a[k]=a[i];
a[t]=h;
}
}
void output_array(int a[],int b)
{
int i;
for(i=b-1;i>=0;i--)
{cout<<a[i]<<" ";}
cout<<endl;
}
输出结果:
心得体会:
冒泡法解决实际问题。