图的邻接矩阵表示
Adjacency Matrix of the Graph
一、邻接矩阵定义
图的邻接矩阵定义:设图G=(V, E)的顶点集为V(G)={v1, v2,v3,…,vp},用aij表示G中顶点vi与vj之间的边数,则n阶方阵M(G)=(aij)pxp称为G的邻接矩阵(Adjacency Matrix)。
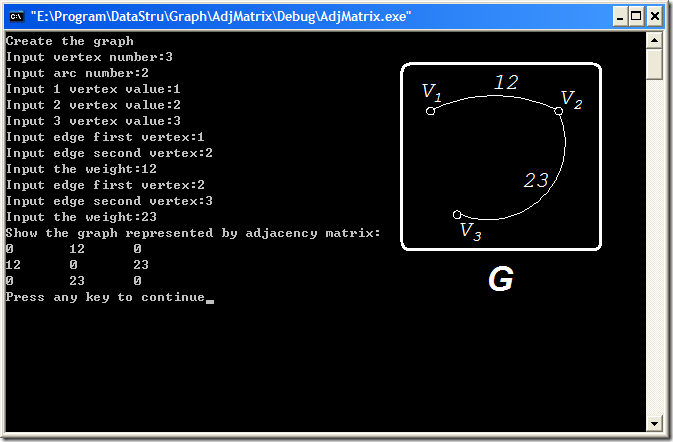
上图所示的图的邻接矩阵如下:
图的邻接矩阵有以下明显的性质:
l 邻接矩阵是一个对称矩阵;
l 若图G为无环图,则M(G)中第i行(列)的元素之和等于顶点的度数;
一般说来,图的邻接矩阵比它的关联矩阵小得多,通常图就以其邻接矩阵的形式存贮在计算机中。
二、图的邻接矩阵表示法的程序实现
图的邻接矩阵表示法的数据结构为:
1: typedef struct SArc
2: {
3: double dWeight;
4: }AdjMatrix[VERTEX_NUM][VERTEX_NUM];
5:
6: typedef struct SGraph
7: {
8: int iVertexNum;
9: int iArcNum;
10: int aVertex[VERTEX_NUM];
11: AdjMatrix mArcs;
12: }Graph;
在此基础上实现图的创建:
程序代码如下:
1: //------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2: // Copyright (c) 2012 eryar All Rights Reserved.
3: //
4: // File : Main.cpp
5: // Author : [email protected]
6: // Date : 2012-4-11 20:33
7: // Version : 1.0v
8: //
9: // Description : Use adjacency matrix of a graph.
10: //
11: //==============================================================================
12:
13: #include <IOSTREAM>
14: using namespace std;
15:
16: const int INFINIY = INT_MAX;
17: const int VERTEX_NUM = 20;
18:
19: typedef struct SArc
20: {
21: double dWeight;
22: }AdjMatrix[VERTEX_NUM][VERTEX_NUM];
23:
24: typedef struct SGraph
25: {
26: int iVertexNum;
27: int iArcNum;
28: int aVertex[VERTEX_NUM];
29: AdjMatrix mArcs;
30: }Graph;
31:
32: void CreateGraph(Graph& graph);
33: int LocateVertex(const Graph& graph, int vertex);
34: void ShowGraph(const Graph& graph);
35:
36: ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
37: // Main function.
38:
39: int main(int argc, char* argv[])
40: {
41: Graph graph;
42:
43: CreateGraph(graph);
44:
45: ShowGraph(graph);
46:
47: return 0;
48: }
49:
50: ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
51: /*
52: * Create a graph.
53: */
54: void CreateGraph(Graph& graph)
55: {
56: cout<<"Create the graph"<<endl;
57: cout<<"Input vertex number:";
58: cin>>graph.iVertexNum;
59:
60: cout<<"Input arc number:";
61: cin>>graph.iArcNum;
62:
63: // Input vertex
64: for (int iVertex = 0; iVertex < graph.iVertexNum; iVertex++)
65: {
66: cout<<"Input "<<iVertex+1<<" vertex value:";
67: cin>>graph.aVertex[iVertex];
68: }
69:
70: // Initialize adjacency matrix.
71: for (int i = 0; i < graph.iVertexNum; i++)
72: {
73: for (int j = 0; j < graph.iVertexNum; j++)
74: {
75: graph.mArcs[i][j].dWeight = 0;
76: }
77: }
78:
79: // Build adjacency matrix.
80: int iFirst = 0;
81: int iSecond = 0;
82: int xPos = 0;
83: int yPos = 0;
84: double dWeight = 0;
85:
86: for (int k = 0; k < graph.iArcNum; k++)
87: {
88: cout<<"Input edge first vertex:";
89: cin>>iFirst;
90:
91: cout<<"Input edge second vertex:";
92: cin>>iSecond;
93:
94: cout<<"Input the weight:";
95: cin>>dWeight;
96:
97: xPos = LocateVertex(graph, iFirst);
98: yPos = LocateVertex(graph, iSecond);
99:
100: //
101: graph.mArcs[xPos][yPos].dWeight = dWeight;
102: graph.mArcs[yPos][xPos].dWeight = dWeight;
103: }
104: }
105:
106: /**
107: * Show a graph.
108: */
109: void ShowGraph(const Graph& graph)
110: {
111: cout<<"Show the graph represented by adjacency matrix:"<<endl;
112:
113: // Output adjacency matrix.
114: for (int m = 0; m < graph.iVertexNum; m++)
115: {
116: for (int n = 0; n < graph.iVertexNum; n++)
117: {
118: cout<<graph.mArcs[m][n].dWeight<<"\t";
119: }
120:
121: cout<<endl;
122: }
123: }
124:
125: /**
126: * Locate vertex position in the adjacency matrix.
127: */
128: int LocateVertex( const Graph& graph, int vertex )
129: {
130: for (int i = 0; i < graph.iVertexNum; i++)
131: {
132: if (graph.aVertex[i] == vertex)
133: {
134: return i;
135: }
136: }
137:
138: return -1;
139: }
程序运行效果如下图所示: