Direct3D Tutorial 4: Creating and Using Lights
这个tutorial我改了下,可以看到圆柱体的线框,也可以让其不转动
默认效果: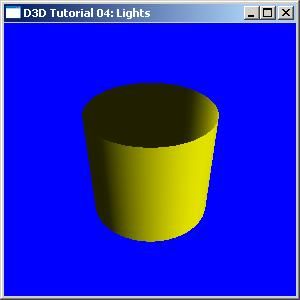
要看到圆柱体的线框,即填充模式改为 D3DFILL_WIREFRAME,
只要改动
bool
g_bWireFrame
=
false
;
//
是否用线框填充模式
把g_bWireFrame改为true,效果:

要让圆柱体不转动,并且看到圆柱体顶点一初始化好的位置,可以改动
bool
g_bNoRotate
=
false
;
//
是否让圆柱体绕x转动
改为true就可以,效果:

//
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// File: Lights.cpp
//
// Desc: Rendering 3D geometry is much more interesting when dynamic lighting
// is added to the scene. To use lighting in D3D, you must create one or
// lights, setup a material, and make sure your geometry contains surface
// normals. Lights may have a position, a color, and be of a certain type
// such as directional (light comes from one direction), point (light
// comes from a specific x,y,z coordinate and radiates in all directions)
// or spotlight. Materials describe the surface of your geometry,
// specifically, how it gets lit (diffuse color, ambient color, etc.).
// Surface normals are part of a vertex, and are needed for the D3D's
// internal lighting calculations.
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include < Windows.h >
#include < mmsystem.h >
#include < d3dx9.h >
#pragma warning( disable : 4996 ) // disable deprecated warning
#include < strsafe.h >
#pragma warning( default : 4996 )
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global variables
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LPDIRECT3D9 g_pD3D = NULL; // Used to create the D3DDevice
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 g_pd3dDevice = NULL; // Our rendering device
LPDIRECT3DVERTEXBUFFER9 g_pVB = NULL; // Buffer to hold vertices
bool g_bWireFrame = false ; // 是否用线框填充模式
bool g_bNoRotate = false ; // 是否让圆柱体绕x转动
// A structure for our custom vertex type. We added a normal, and omitted the
// color (which is provided by the material)
struct CUSTOMVERTEX
{
D3DXVECTOR3 position; // The 3D position for the vertex
D3DXVECTOR3 normal; // The surface normal for the vertex
};
// Our custom FVF, which describes our custom vertex structure
#define D3DFVF_CUSTOMVERTEX (D3DFVF_XYZ|D3DFVF_NORMAL)
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: InitD3D()
// Desc: Initializes Direct3D
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT InitD3D( HWND hWnd )
{
// Create the D3D object.
if ( NULL == ( g_pD3D = Direct3DCreate9( D3D_SDK_VERSION ) ) )
return E_FAIL;
// Set up the structure used to create the D3DDevice. Since we are now
// using more complex geometry, we will create a device with a zbuffer.
D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS d3dpp;
ZeroMemory( & d3dpp, sizeof (d3dpp) );
d3dpp.Windowed = TRUE;
d3dpp.SwapEffect = D3DSWAPEFFECT_DISCARD;
d3dpp.BackBufferFormat = D3DFMT_UNKNOWN;
d3dpp.EnableAutoDepthStencil = TRUE;
d3dpp.AutoDepthStencilFormat = D3DFMT_D16;
// Create the D3DDevice
if ( FAILED( g_pD3D -> CreateDevice( D3DADAPTER_DEFAULT, D3DDEVTYPE_HAL, hWnd,
D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING,
& d3dpp, & g_pd3dDevice ) ) )
{
return E_FAIL;
}
// Turn off culling
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_CULLMODE, D3DCULL_NONE );
// Turn on the zbuffer
// 打开z-buffer
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_ZENABLE, TRUE );
// 填充模式设为线框模式,方便看到顶点位置
if (g_bWireFrame)
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState(D3DRS_FILLMODE, D3DFILL_WIREFRAME );
return S_OK;
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: InitGeometry()
// Desc: Creates the scene geometry
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT InitGeometry()
{
// 圆柱体上口,下口各50个顶点
// Create the vertex buffer.
if ( FAILED( g_pd3dDevice -> CreateVertexBuffer( 50 * 2 * sizeof (CUSTOMVERTEX),
0 , D3DFVF_CUSTOMVERTEX,
D3DPOOL_DEFAULT, & g_pVB, NULL ) ) )
{
return E_FAIL;
}
// Fill the vertex buffer. We are algorithmically generating a cylinder
// here, including the normals, which are used for lighting.
CUSTOMVERTEX * pVertices;
if ( FAILED( g_pVB -> Lock( 0 , 0 , ( void ** ) & pVertices, 0 ) ) )
return E_FAIL;
for ( DWORD i = 0 ; i < 50 ; i ++ )
{
FLOAT theta = ( 2 * D3DX_PI * i) / ( 50 - 1 );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 0 ].position = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), - 1.0f , cosf(theta) );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 0 ].normal = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), 0.0f , cosf(theta) );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 1 ].position = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), 1.0f , cosf(theta) );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 1 ].normal = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), 0.0f , cosf(theta) );
}
g_pVB -> Unlock();
return S_OK;
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: Cleanup()
// Desc: Releases all previously initialized objects
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID Cleanup()
{
if ( g_pVB != NULL )
g_pVB -> Release();
if ( g_pd3dDevice != NULL )
g_pd3dDevice -> Release();
if ( g_pD3D != NULL )
g_pD3D -> Release();
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: SetupMatrices()
// Desc: Sets up the world, view, and projection transform matrices.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID SetupMatrices()
{
// Set up world matrix
D3DXMATRIXA16 matWorld;
D3DXMatrixIdentity( & matWorld );
FLOAT Angle = timeGetTime() / 5000.0f ; // 5000.0f位置上的数越大,圆柱体转得越慢
if (g_bNoRotate)
Angle = 0 ; // 看InitGeometry()里顶点刚初始化好的样子
D3DXMatrixRotationX( & matWorld, Angle );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetTransform( D3DTS_WORLD, & matWorld );
// Set up our view matrix. A view matrix can be defined given an eye point,
// a point to lookat, and a direction for which way is up. Here, we set the
// eye five units back along the z-axis and up three units, look at the
// origin, and define "up" to be in the y-direction.
D3DXVECTOR3 vEyePt( 0.0f , 3.0f , - 5.0f );
D3DXVECTOR3 vLookatPt( 0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0f );
D3DXVECTOR3 vUpVec( 0.0f , 1.0f , 0.0f );
D3DXMATRIXA16 matView;
D3DXMatrixLookAtLH( & matView, & vEyePt, & vLookatPt, & vUpVec );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetTransform( D3DTS_VIEW, & matView );
// For the projection matrix, we set up a perspective transform (which
// transforms geometry from 3D view space to 2D viewport space, with
// a perspective divide making objects smaller in the distance). To build
// a perpsective transform, we need the field of view (1/4 pi is common),
// the aspect ratio, and the near and far clipping planes (which define at
// what distances geometry should be no longer be rendered).
D3DXMATRIXA16 matProj;
D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH( & matProj, D3DX_PI / 4 , 1.0f , 1.0f , 100.0f );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetTransform( D3DTS_PROJECTION, & matProj );
}
// File: Lights.cpp
//
// Desc: Rendering 3D geometry is much more interesting when dynamic lighting
// is added to the scene. To use lighting in D3D, you must create one or
// lights, setup a material, and make sure your geometry contains surface
// normals. Lights may have a position, a color, and be of a certain type
// such as directional (light comes from one direction), point (light
// comes from a specific x,y,z coordinate and radiates in all directions)
// or spotlight. Materials describe the surface of your geometry,
// specifically, how it gets lit (diffuse color, ambient color, etc.).
// Surface normals are part of a vertex, and are needed for the D3D's
// internal lighting calculations.
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include < Windows.h >
#include < mmsystem.h >
#include < d3dx9.h >
#pragma warning( disable : 4996 ) // disable deprecated warning
#include < strsafe.h >
#pragma warning( default : 4996 )
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global variables
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LPDIRECT3D9 g_pD3D = NULL; // Used to create the D3DDevice
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 g_pd3dDevice = NULL; // Our rendering device
LPDIRECT3DVERTEXBUFFER9 g_pVB = NULL; // Buffer to hold vertices
bool g_bWireFrame = false ; // 是否用线框填充模式
bool g_bNoRotate = false ; // 是否让圆柱体绕x转动
// A structure for our custom vertex type. We added a normal, and omitted the
// color (which is provided by the material)
struct CUSTOMVERTEX
{
D3DXVECTOR3 position; // The 3D position for the vertex
D3DXVECTOR3 normal; // The surface normal for the vertex
};
// Our custom FVF, which describes our custom vertex structure
#define D3DFVF_CUSTOMVERTEX (D3DFVF_XYZ|D3DFVF_NORMAL)
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: InitD3D()
// Desc: Initializes Direct3D
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT InitD3D( HWND hWnd )
{
// Create the D3D object.
if ( NULL == ( g_pD3D = Direct3DCreate9( D3D_SDK_VERSION ) ) )
return E_FAIL;
// Set up the structure used to create the D3DDevice. Since we are now
// using more complex geometry, we will create a device with a zbuffer.
D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS d3dpp;
ZeroMemory( & d3dpp, sizeof (d3dpp) );
d3dpp.Windowed = TRUE;
d3dpp.SwapEffect = D3DSWAPEFFECT_DISCARD;
d3dpp.BackBufferFormat = D3DFMT_UNKNOWN;
d3dpp.EnableAutoDepthStencil = TRUE;
d3dpp.AutoDepthStencilFormat = D3DFMT_D16;
// Create the D3DDevice
if ( FAILED( g_pD3D -> CreateDevice( D3DADAPTER_DEFAULT, D3DDEVTYPE_HAL, hWnd,
D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING,
& d3dpp, & g_pd3dDevice ) ) )
{
return E_FAIL;
}
// Turn off culling
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_CULLMODE, D3DCULL_NONE );
// Turn on the zbuffer
// 打开z-buffer
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_ZENABLE, TRUE );
// 填充模式设为线框模式,方便看到顶点位置
if (g_bWireFrame)
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState(D3DRS_FILLMODE, D3DFILL_WIREFRAME );
return S_OK;
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: InitGeometry()
// Desc: Creates the scene geometry
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT InitGeometry()
{
// 圆柱体上口,下口各50个顶点
// Create the vertex buffer.
if ( FAILED( g_pd3dDevice -> CreateVertexBuffer( 50 * 2 * sizeof (CUSTOMVERTEX),
0 , D3DFVF_CUSTOMVERTEX,
D3DPOOL_DEFAULT, & g_pVB, NULL ) ) )
{
return E_FAIL;
}
// Fill the vertex buffer. We are algorithmically generating a cylinder
// here, including the normals, which are used for lighting.
CUSTOMVERTEX * pVertices;
if ( FAILED( g_pVB -> Lock( 0 , 0 , ( void ** ) & pVertices, 0 ) ) )
return E_FAIL;
for ( DWORD i = 0 ; i < 50 ; i ++ )
{
FLOAT theta = ( 2 * D3DX_PI * i) / ( 50 - 1 );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 0 ].position = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), - 1.0f , cosf(theta) );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 0 ].normal = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), 0.0f , cosf(theta) );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 1 ].position = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), 1.0f , cosf(theta) );
pVertices[ 2 * i + 1 ].normal = D3DXVECTOR3( sinf(theta), 0.0f , cosf(theta) );
}
g_pVB -> Unlock();
return S_OK;
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: Cleanup()
// Desc: Releases all previously initialized objects
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID Cleanup()
{
if ( g_pVB != NULL )
g_pVB -> Release();
if ( g_pd3dDevice != NULL )
g_pd3dDevice -> Release();
if ( g_pD3D != NULL )
g_pD3D -> Release();
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: SetupMatrices()
// Desc: Sets up the world, view, and projection transform matrices.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID SetupMatrices()
{
// Set up world matrix
D3DXMATRIXA16 matWorld;
D3DXMatrixIdentity( & matWorld );
FLOAT Angle = timeGetTime() / 5000.0f ; // 5000.0f位置上的数越大,圆柱体转得越慢
if (g_bNoRotate)
Angle = 0 ; // 看InitGeometry()里顶点刚初始化好的样子
D3DXMatrixRotationX( & matWorld, Angle );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetTransform( D3DTS_WORLD, & matWorld );
// Set up our view matrix. A view matrix can be defined given an eye point,
// a point to lookat, and a direction for which way is up. Here, we set the
// eye five units back along the z-axis and up three units, look at the
// origin, and define "up" to be in the y-direction.
D3DXVECTOR3 vEyePt( 0.0f , 3.0f , - 5.0f );
D3DXVECTOR3 vLookatPt( 0.0f , 0.0f , 0.0f );
D3DXVECTOR3 vUpVec( 0.0f , 1.0f , 0.0f );
D3DXMATRIXA16 matView;
D3DXMatrixLookAtLH( & matView, & vEyePt, & vLookatPt, & vUpVec );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetTransform( D3DTS_VIEW, & matView );
// For the projection matrix, we set up a perspective transform (which
// transforms geometry from 3D view space to 2D viewport space, with
// a perspective divide making objects smaller in the distance). To build
// a perpsective transform, we need the field of view (1/4 pi is common),
// the aspect ratio, and the near and far clipping planes (which define at
// what distances geometry should be no longer be rendered).
D3DXMATRIXA16 matProj;
D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH( & matProj, D3DX_PI / 4 , 1.0f , 1.0f , 100.0f );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetTransform( D3DTS_PROJECTION, & matProj );
}
首次用到material,应该翻译为材质吧?texture翻译为纹理,是吧?看定义:
typedef
struct
_D3DMATERIAL9 {
D3DCOLORVALUE Diffuse; /* Diffuse color RGBA 漫反射颜色 */
D3DCOLORVALUE Ambient; /* Ambient color RGB 环境光反射颜色 */
D3DCOLORVALUE Specular; /* Specular 'shininess' 镜面反射颜色 */
D3DCOLORVALUE Emissive; /* Emissive color RGB 发射光颜色 */
float Power; /* Sharpness if specular highlight */
} D3DMATERIAL9;
上面这几个术语也不太明白。哪位大哥给解释下?
D3DCOLORVALUE Diffuse; /* Diffuse color RGBA 漫反射颜色 */
D3DCOLORVALUE Ambient; /* Ambient color RGB 环境光反射颜色 */
D3DCOLORVALUE Specular; /* Specular 'shininess' 镜面反射颜色 */
D3DCOLORVALUE Emissive; /* Emissive color RGB 发射光颜色 */
float Power; /* Sharpness if specular highlight */
} D3DMATERIAL9;
//
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: SetupLights()
// Desc: Sets up the lights and materials for the scene.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID SetupLights()
{
// Set up a material. The material here just has the diffuse and ambient
// colors set to yellow. Note that only one material can be used at a time.
D3DMATERIAL9 mtrl;
ZeroMemory( & mtrl, sizeof (D3DMATERIAL9) );
mtrl.Diffuse.r = mtrl.Ambient.r = 1.0f ;
mtrl.Diffuse.g = mtrl.Ambient.g = 1.0f ;
mtrl.Diffuse.b = mtrl.Ambient.b = 0.0f ;
mtrl.Diffuse.a = mtrl.Ambient.a = 1.0f ;
g_pd3dDevice -> SetMaterial( & mtrl );
// Set up a white, directional light, with an oscillating direction.
// Note that many lights may be active at a time (but each one slows down
// the rendering of our scene). However, here we are just using one. Also,
// we need to set the D3DRS_LIGHTING renderstate to enable lighting
D3DXVECTOR3 vecDir;
D3DLIGHT9 light;
ZeroMemory( & light, sizeof (D3DLIGHT9) );
light.Type = D3DLIGHT_DIRECTIONAL; // 定向光?
light.Diffuse.r = 1.0f ; // 白光
light.Diffuse.g = 1.0f ;
light.Diffuse.b = 1.0f ;
// 灯的方向会变
vecDir = D3DXVECTOR3(cosf(timeGetTime() / 350.0f ),
1.0f ,
sinf(timeGetTime() / 350.0f ) );
D3DXVec3Normalize( (D3DXVECTOR3 * ) & light.Direction, & vecDir ); // 向量规格化,啥玩意?
light.Range = 1000.0f ;
g_pd3dDevice -> SetLight( 0 , & light );
g_pd3dDevice -> LightEnable( 0 , TRUE );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_LIGHTING, TRUE );
// Finally, turn on some ambient light.
// 打开环境光
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_AMBIENT, 0x00202020 );
}
// Name: SetupLights()
// Desc: Sets up the lights and materials for the scene.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID SetupLights()
{
// Set up a material. The material here just has the diffuse and ambient
// colors set to yellow. Note that only one material can be used at a time.
D3DMATERIAL9 mtrl;
ZeroMemory( & mtrl, sizeof (D3DMATERIAL9) );
mtrl.Diffuse.r = mtrl.Ambient.r = 1.0f ;
mtrl.Diffuse.g = mtrl.Ambient.g = 1.0f ;
mtrl.Diffuse.b = mtrl.Ambient.b = 0.0f ;
mtrl.Diffuse.a = mtrl.Ambient.a = 1.0f ;
g_pd3dDevice -> SetMaterial( & mtrl );
// Set up a white, directional light, with an oscillating direction.
// Note that many lights may be active at a time (but each one slows down
// the rendering of our scene). However, here we are just using one. Also,
// we need to set the D3DRS_LIGHTING renderstate to enable lighting
D3DXVECTOR3 vecDir;
D3DLIGHT9 light;
ZeroMemory( & light, sizeof (D3DLIGHT9) );
light.Type = D3DLIGHT_DIRECTIONAL; // 定向光?
light.Diffuse.r = 1.0f ; // 白光
light.Diffuse.g = 1.0f ;
light.Diffuse.b = 1.0f ;
// 灯的方向会变
vecDir = D3DXVECTOR3(cosf(timeGetTime() / 350.0f ),
1.0f ,
sinf(timeGetTime() / 350.0f ) );
D3DXVec3Normalize( (D3DXVECTOR3 * ) & light.Direction, & vecDir ); // 向量规格化,啥玩意?
light.Range = 1000.0f ;
g_pd3dDevice -> SetLight( 0 , & light );
g_pd3dDevice -> LightEnable( 0 , TRUE );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_LIGHTING, TRUE );
// Finally, turn on some ambient light.
// 打开环境光
g_pd3dDevice -> SetRenderState( D3DRS_AMBIENT, 0x00202020 );
}
//
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: Render()
// Desc: Draws the scene
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID Render()
{
// Clear the backbuffer and the zbuffer
g_pd3dDevice -> Clear( 0 , NULL, D3DCLEAR_TARGET | D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER,
D3DCOLOR_XRGB( 0 , 0 , 255 ), 1.0f , 0 );
// Begin the scene
if ( SUCCEEDED( g_pd3dDevice -> BeginScene() ) )
{
// Setup the lights and materials
SetupLights();
// Setup the world, view, and projection matrices
SetupMatrices();
// Render the vertex buffer contents
g_pd3dDevice -> SetStreamSource( 0 , g_pVB, 0 , sizeof (CUSTOMVERTEX) );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetFVF( D3DFVF_CUSTOMVERTEX );
g_pd3dDevice -> DrawPrimitive( D3DPT_TRIANGLESTRIP, 0 , 2 * 50 - 2 );
// End the scene
g_pd3dDevice -> EndScene();
}
// Present the backbuffer contents to the display
g_pd3dDevice -> Present( NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL );
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: MsgProc()
// Desc: The window's message handler
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT WINAPI MsgProc( HWND hWnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam )
{
switch ( msg )
{
case WM_DESTROY:
Cleanup();
PostQuitMessage( 0 );
return 0 ;
}
return DefWindowProc( hWnd, msg, wParam, lParam );
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: WinMain()
// Desc: The application's entry point
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI WinMain( HINSTANCE hInst, HINSTANCE, LPSTR, INT )
{
// Register the window class
WNDCLASSEX wc = { sizeof (WNDCLASSEX), CS_CLASSDC, MsgProc, 0L , 0L ,
GetModuleHandle(NULL), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL,
" D3D Tutorial " , NULL };
RegisterClassEx( & wc );
// Create the application's window
HWND hWnd = CreateWindow( " D3D Tutorial " , " D3D Tutorial 04: Lights " ,
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, 100 , 100 , 300 , 300 ,
NULL, NULL, wc.hInstance, NULL );
// Initialize Direct3D
if ( SUCCEEDED( InitD3D( hWnd ) ) )
{
// Create the geometry
if ( SUCCEEDED( InitGeometry() ) )
{
// Show the window
ShowWindow( hWnd, SW_SHOWDEFAULT );
UpdateWindow( hWnd );
// Enter the message loop
MSG msg;
ZeroMemory( & msg, sizeof (msg) );
while ( msg.message != WM_QUIT )
{
if ( PeekMessage( & msg, NULL, 0U , 0U , PM_REMOVE ) )
{
TranslateMessage( & msg );
DispatchMessage( & msg );
}
else
Render();
}
}
}
UnregisterClass( " D3D Tutorial " , wc.hInstance );
return 0 ;
}
// Name: Render()
// Desc: Draws the scene
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID Render()
{
// Clear the backbuffer and the zbuffer
g_pd3dDevice -> Clear( 0 , NULL, D3DCLEAR_TARGET | D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER,
D3DCOLOR_XRGB( 0 , 0 , 255 ), 1.0f , 0 );
// Begin the scene
if ( SUCCEEDED( g_pd3dDevice -> BeginScene() ) )
{
// Setup the lights and materials
SetupLights();
// Setup the world, view, and projection matrices
SetupMatrices();
// Render the vertex buffer contents
g_pd3dDevice -> SetStreamSource( 0 , g_pVB, 0 , sizeof (CUSTOMVERTEX) );
g_pd3dDevice -> SetFVF( D3DFVF_CUSTOMVERTEX );
g_pd3dDevice -> DrawPrimitive( D3DPT_TRIANGLESTRIP, 0 , 2 * 50 - 2 );
// End the scene
g_pd3dDevice -> EndScene();
}
// Present the backbuffer contents to the display
g_pd3dDevice -> Present( NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL );
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: MsgProc()
// Desc: The window's message handler
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT WINAPI MsgProc( HWND hWnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam )
{
switch ( msg )
{
case WM_DESTROY:
Cleanup();
PostQuitMessage( 0 );
return 0 ;
}
return DefWindowProc( hWnd, msg, wParam, lParam );
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: WinMain()
// Desc: The application's entry point
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI WinMain( HINSTANCE hInst, HINSTANCE, LPSTR, INT )
{
// Register the window class
WNDCLASSEX wc = { sizeof (WNDCLASSEX), CS_CLASSDC, MsgProc, 0L , 0L ,
GetModuleHandle(NULL), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL,
" D3D Tutorial " , NULL };
RegisterClassEx( & wc );
// Create the application's window
HWND hWnd = CreateWindow( " D3D Tutorial " , " D3D Tutorial 04: Lights " ,
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, 100 , 100 , 300 , 300 ,
NULL, NULL, wc.hInstance, NULL );
// Initialize Direct3D
if ( SUCCEEDED( InitD3D( hWnd ) ) )
{
// Create the geometry
if ( SUCCEEDED( InitGeometry() ) )
{
// Show the window
ShowWindow( hWnd, SW_SHOWDEFAULT );
UpdateWindow( hWnd );
// Enter the message loop
MSG msg;
ZeroMemory( & msg, sizeof (msg) );
while ( msg.message != WM_QUIT )
{
if ( PeekMessage( & msg, NULL, 0U , 0U , PM_REMOVE ) )
{
TranslateMessage( & msg );
DispatchMessage( & msg );
}
else
Render();
}
}
}
UnregisterClass( " D3D Tutorial " , wc.hInstance );
return 0 ;
}