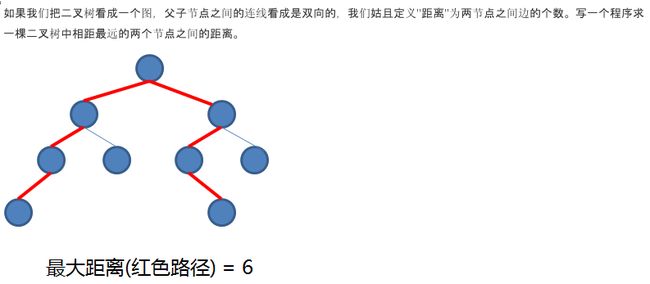
求二叉树中节点的最大距离
问题定义
参考资料
[1] http://www.cs.duke.edu/courses/spring00/cps100/assign/trees/diameter.html
下面计算的为二叉树中节点的最大距离定义为两节点间的顶点个数。
Tree Diameter
The function below returns the diameter of a tree. A tree's diameter is defined after the function. Write a recurrence for this function and solve it yielding the running time using big-Oh in terms of the number of nodes in a tree.
int diameter(Tree * t)
// post: return diameter of t
{
if (t == 0) return 0;
int lheight = height(tree->left);
int rheight = height(tree->right);
int ldiameter = diameter(tree->left);
int rdiameter = diameter(tree->right);
return max(lheight + rheight + 1,
max(ldiameter,rdiameter));
}
The following function returns the height of a tree (the number of nodes on the longest root-to-leaf path).
int height(Tree * t)
// postcondition: returns height of tree with root t
{
if (t == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1 + max(height(t->left),height(t->right));
}
}
where the function max returns the largest of its two integer parameters. The diameter of a tree (sometimes called the width) is the number of nodes on the longest path between two leaves in the tree. The diagram below shows two trees each with diameter nine, the leaves that form the ends of a longest path are shaded (note that there is more than one path in each tree of length nine, but no path longer than nine nodes).
The diameter of a tree T is the largest of the following quantities:
the diameter of T's left subtree
the diameter of T's right subtree
the longest path between leaves that goes through the root of T (this can be computed from the heights of the subtrees of T)
[2]
进行两次BFS:先从树根A出发进行广度优先搜索(BFS),找到最远的结点B,然后再从结点B出BFS,找到离B最远的结点C,BC就是最大距离。
下面是正确性证明
假设存在结点X和Y,它们的距离是所有结点中最大的;分两种情况讨论:
1. 若路径XY与路径AB有交点O,
...A
...|
X-O--Y
...|
...B
由于|OB| >= |OX|且|OB| >= |OY|,所以,|BX| >= |XY|,|BY| >= |XY|。即从B出发可以构造出最长路径。
2.若路径XY与路径AB无交点,
A...B X...Y
A是树根,XY与B分属不同的子树,假设XY的最近祖先为O,由于
|AB| >= |AO| + |AX|,所以|BY| = |AB| + |AO| + |OY| > |XY|。即从B出发构造出长于XY的路径,与假设XY是最长路径矛盾。
[3] http://www.cnblogs.com/miloyip/archive/2010/02/25/binary_tree_distance.html
#include <iostream> using namespace std; struct NODE { NODE *pLeft; NODE *pRight; }; struct RESULT { int nMaxDistance; int nMaxDepth; }; RESULT GetMaximumDistance(NODE* root) { if (!root) { RESULT empty = { 0, -1 }; // trick: nMaxDepth is -1 and then caller will plus 1 to balance it as zero. return empty; } RESULT lhs = GetMaximumDistance(root->pLeft); RESULT rhs = GetMaximumDistance(root->pRight); RESULT result; result.nMaxDepth = max(lhs.nMaxDepth + 1, rhs.nMaxDepth + 1); result.nMaxDistance = max(max(lhs.nMaxDistance, rhs.nMaxDistance), lhs.nMaxDepth + rhs.nMaxDepth + 2); return result; }
void Link(NODE* nodes, int parent, int left, int right) { if (left != -1) nodes[parent].pLeft = &nodes[left]; if (right != -1) nodes[parent].pRight = &nodes[right]; } void main() { // P. 241 Graph 3-12 NODE test1[9] = { 0 }; Link(test1, 0, 1, 2); Link(test1, 1, 3, 4); Link(test1, 2, 5, 6); Link(test1, 3, 7, -1); Link(test1, 5, -1, 8); cout << "test1: " << GetMaximumDistance(&test1[0]).nMaxDistance << endl; // P. 242 Graph 3-13 left NODE test2[4] = { 0 }; Link(test2, 0, 1, 2); Link(test2, 1, 3, -1); cout << "test2: " << GetMaximumDistance(&test2[0]).nMaxDistance << endl; // P. 242 Graph 3-13 right NODE test3[9] = { 0 }; Link(test3, 0, -1, 1); Link(test3, 1, 2, 3); Link(test3, 2, 4, -1); Link(test3, 3, 5, 6); Link(test3, 4, 7, -1); Link(test3, 5, -1, 8); cout << "test3: " << GetMaximumDistance(&test3[0]).nMaxDistance << endl; // P. 242 Graph 3-14 // Same as Graph 3-2, not test // P. 243 Graph 3-15 NODE test4[9] = { 0 }; Link(test4, 0, 1, 2); Link(test4, 1, 3, 4); Link(test4, 3, 5, 6); Link(test4, 5, 7, -1); Link(test4, 6, -1, 8); cout << "test4: " << GetMaximumDistance(&test4[0]).nMaxDistance << endl; }
[4] 《编程之美》上的不太清晰的解决办法
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 数据结构定义 struct NODE { NODE* pLeft; // 左子树 NODE* pRight; // 右子树 int nMaxLeft; // 左子树中的最长距离 int nMaxRight; // 右子树中的最长距离 char chValue; // 该节点的值 }; int nMaxLen = 0; // 寻找树中最长的两段距离 void FindMaxLen(NODE* pRoot) { // 遍历到叶子节点,返回 if(pRoot == NULL) { return; } // 如果左子树为空,那么该节点的左边最长距离为0 if(pRoot -> pLeft == NULL) { pRoot -> nMaxLeft = 0; } // 如果右子树为空,那么该节点的右边最长距离为0 if(pRoot -> pRight == NULL) { pRoot -> nMaxRight = 0; } // 如果左子树不为空,递归寻找左子树最长距离 if(pRoot -> pLeft != NULL) { FindMaxLen(pRoot -> pLeft); } // 如果右子树不为空,递归寻找右子树最长距离 if(pRoot -> pRight != NULL) { FindMaxLen(pRoot -> pRight); } // 计算左子树最长节点距离 if(pRoot -> pLeft != NULL) { int nTempMax = 0; if(pRoot -> pLeft -> nMaxLeft > pRoot -> pLeft -> nMaxRight) { nTempMax = pRoot -> pLeft -> nMaxLeft; } else { nTempMax = pRoot -> pLeft -> nMaxRight; } pRoot -> nMaxLeft = nTempMax + 1; } // 计算右子树最长节点距离 if(pRoot -> pRight != NULL) { int nTempMax = 0; if(pRoot -> pRight -> nMaxLeft > pRoot -> pRight -> nMaxRight) { nTempMax = pRoot -> pRight -> nMaxLeft; } else { nTempMax = pRoot -> pRight -> nMaxRight; } pRoot -> nMaxRight = nTempMax + 1; } // 更新最长距离 if(pRoot -> nMaxLeft + pRoot -> nMaxRight > nMaxLen) { nMaxLen = pRoot -> nMaxLeft + pRoot -> nMaxRight; } } void Link(NODE* nodes, int parent, int left, int right) { if (left != -1) nodes[parent].pLeft = &nodes[left]; if (right != -1) nodes[parent].pRight = &nodes[right]; } int main() { // P. 241 Graph 3-12 NODE test1[9] = { 0 }; Link(test1, 0, 1, 2); Link(test1, 1, 3, 4); Link(test1, 2, 5, 6); Link(test1, 3, 7, -1); Link(test1, 5, -1, 8); nMaxLen = 0; FindMaxLen(&test1[0]); cout << "test1: " << nMaxLen << endl; // P. 242 Graph 3-13 left NODE test2[4] = { 0 }; Link(test2, 0, 1, 2); Link(test2, 1, 3, -1); nMaxLen = 0; FindMaxLen(&test2[0]); cout << "test2: " << nMaxLen << endl; // P. 242 Graph 3-13 right NODE test3[9] = { 0 }; Link(test3, 0, -1, 1); Link(test3, 1, 2, 3); Link(test3, 2, 4, -1); Link(test3, 3, 5, 6); Link(test3, 4, 7, -1); Link(test3, 5, -1, 8); nMaxLen = 0; FindMaxLen(&test3[0]); cout << "test3: " << nMaxLen << endl; // P. 242 Graph 3-14 // Same as Graph 3-2, not test // P. 243 Graph 3-15 NODE test4[9] = { 0 }; Link(test4, 0, 1, 2); Link(test4, 1, 3, 4); Link(test4, 3, 5, 6); Link(test4, 5, 7, -1); Link(test4, 6, -1, 8); nMaxLen = 0; FindMaxLen(&test4[0]); cout << "test4: " << nMaxLen << endl; return 0; }
这种办法其实说它不太清晰是因为:全局变来nMaxLen维护着节点间的最长距离,而递归过程显式的计算了树的最大高度,隐式的计算节点间的最长距离。