Linux网络协议栈(一) -- socket入门
原文地址:(一) http://www.cnblogs.com/hustcat/archive/2009/09/17/1568738.html
(二)http://www.cnblogs.com/hustcat/archive/2009/09/17/1568765.html
1、TCP/IP参考模型
为了实现各种网络的互连,国际标准化组织(ISO)制定了开放式系统互连(OSI)参考模型。尽管OSI的体系结构从理论上讲是比较完整的,但实际上,完全符合OSI各层协议的商用产品却很少进入市场。而使用TCP/IP 协议的产品却大量涌入市场,几乎所有的工作站都配有TCP/IP协议,使得TCP/IP 成为计算机网络的实际的国际标准。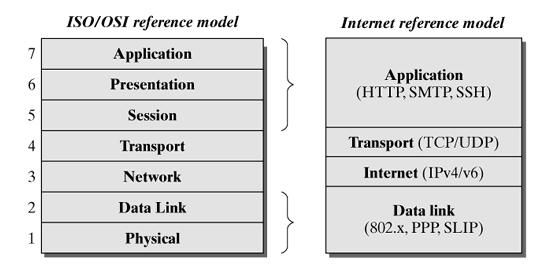
2、套接字(socket)
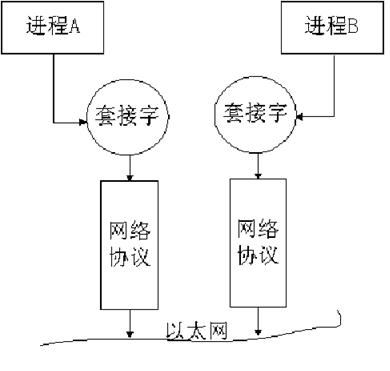
socket是操作系统的重要组成部分之一,它是网络应用程序的基础。从层次上来说,它位于应用层,是操作系统为应用程序员提供的API,通过它,应用程序可以访问传输层协议。
1、socket 位于传输层协议之上,屏蔽了不同网络协议之间的差异;
2、socket是网络编程的入口,它提供了大量的系统调用,构成了网络程序的主体;
3、在Linux系统中,socket属于文件系统的一部分,网络通信可以被看作是对文件的读取,使得我们对网络的控制和对文件的控制一样方便。
2.1、套接字地址
在传输层上,通信端点可由Internet上3个参数描述:所用的协议、IP地址和端口号。这些内容由sockaddr描述:
typedef unsigned short sa_family_t;
// 通用socket地址
struct sockaddr {
sa_family_t sa_family; /* address family, AF_xxx,协议簇 */
char sa_data[ 14 ]; /* 14 bytes of protocol address */
};
// usr/include/netinet/in.h
// INET地址簇的socket地址
struct in_addr {
__u32 s_addr;
};
struct sockaddr_in {
sa_family_t sin_family; /* Address family: AF_INET */
unsigned short int sin_port; /* Port number,端口 */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* Internet address,IP地址 */
/* Pad to size of 'struct sockaddr' . */
unsigned char sin_zero[ sizeof ( struct sockaddr) -
sizeof (sa_family_t) -
sizeof (uint16_t) -
sizeof ( struct in_addr)];
};
| 套接字地址族 |
描述 |
| UNIX |
UNIX 域套接字 |
| INET |
通过 TCP/IP 协议支持的 Internet 地址族 |
| AX25 |
Amater radio X25 |
| APPLETALK |
Appletalk DDP |
| IPX |
Novell IPX |
| X25 |
X25 |
| BSD 套接字类型 |
描述 |
| 流(stream) |
这种套接字提供了可靠的双向顺序数据流,可保证数据不会在传输过程中丢失、破坏或重复出现。流套接字通过 INET 地址族的 TCP 协议实现。 |
| 数据报(datagram) |
这种套接字也提供双向的数据传输,但是并不对数据的传输提供担保,也就是说,数据可能会以错误的顺序传递,甚至丢失或破坏。这种类型的套接字通过 INET 地址族的 UDP 协议实现。 |
| 原始(raw) |
利用这种类型的套接字,进程可以直接访问底层协议(因此称为原始)。例如,可在某个以太网设备上打开原始套接字,然后获取原始的 IP 数据传输信息。 |
| 可靠发送的消息 |
和数据报套接字类似,但保证数据被正确传输到目的端。 |
| 顺序数据包 |
和流套接字类似,但数据包大小是固定的。 |
| 数据包(packet) |
这并不是标准的 BSD 套接字类型,它是 Linux 专有的 BSD 套接字扩展,可允许进程直接在设备级访问数据包。 |
套接字(更确切的说是BSD套接字)为应用程序提供了基本的API,这些API是编写网络应用程序的基础。
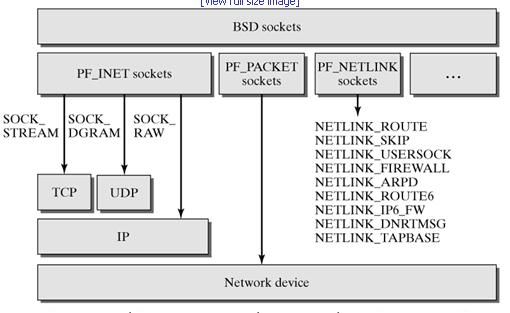
3、套接字的实现
套接字最先是在UNIX的BSD版本实现的,所以也叫做BSD套接字,它隐藏了各个协议之间的差异,并向上提供统一的接口。Linux中实现套接字的基本结构:
3.1、BSD套接字
3.1.1、核心数据结构
为了实现BSD套接字,内核提供一个重要的数据结构struct socket,它的定义如下:
socket_state state; // 套接字状态
unsigned long flags;
struct proto_ops * ops; // 操作函数集
struct fasync_struct * fasync_list;
struct file * file; // 每个BSD套接字都有一个inode结点,通过文件对象与其关联起来
struct sock * sk; // socket内部结构,与具体的协议簇(比如PF_INET)相关
wait_queue_head_t wait;
short type; // 套接字类型:如SOCK_STREAM, SOCK_DGRAM, SOCK_RAW, SOCK_RDM, SOCK_SEQPACKET, and SOCK_PACKET
unsigned char passcred;
};
struct proto_ops {
int family;
struct module * owner;
int ( * release) ( struct socket * sock);
int ( * bind) ( struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * myaddr, int sockaddr_len);
int ( * connect) ( struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * vaddr, int sockaddr_len, int flags);
int ( * socketpair) ( struct socket * sock1, struct socket * sock2);
int ( * accept) ( struct socket * sock, struct socket * newsock, int flags);
int ( * getname) ( struct socket * sock, struct sockaddr * addr, int * sockaddr_len, int peer);
unsigned int ( * poll) ( struct file * file, struct socket * sock, struct poll_table_struct * wait);
int ( * ioctl) ( struct socket * sock, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
int ( * listen) ( struct socket * sock, int len);
int ( * shutdown) ( struct socket * sock, int flags);
int ( * setsockopt) ( struct socket * sock, int level, int optname, char __user * optval, int optlen);
int ( * getsockopt) ( struct socket * sock, int level, int optname, char __user * optval, int __user * optlen);
int ( * sendmsg) ( struct kiocb * iocb, struct socket * sock, struct msghdr * m, size_t total_len);
int ( * recvmsg) ( struct kiocb * iocb, struct socket * sock, struct msghdr * m, size_t total_len, int flags);
int ( * mmap) ( struct file * file, struct socket * sock, struct vm_area_struct * vma);
ssize_t ( * sendpage) ( struct socket * sock, struct page * page, int offset, size_t size, int flags);
};
typedef enum {
SS_FREE = 0 , /* not allocated */
SS_UNCONNECTED, /* unconnected to any socket */
SS_CONNECTING, /* in process of connecting */
SS_CONNECTED, /* connected to socket */
SS_DISCONNECTING /* in process of disconnecting */
} socket_state;
void __init sock_init( void )
{
int i;
/*
* Initialize all address (protocol) families.
*/
for (i = 0 ; i < NPROTO; i ++ )
net_families[i] = NULL; // 协议簇数组初始化
/*
* Initialize sock SLAB cache.
*/
sk_init();//分配sock缓存
#ifdef SLAB_SKB
/*
* Initialize skbuff SLAB cache
*/
skb_init();
#endif
/*
* Initialize the protocols module.
*/
init_inodecache();
// 注册sockfs文件系统
register_filesystem( & sock_fs_type);
// 安装sockfs
sock_mnt = kern_mount( & sock_fs_type);
/* The real protocol initialization is performed when
* do_initcalls is run.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER
netfilter_init();
#endif
}
// net/socket.c
// sockfs文件系统的安装点
static struct vfsmount * sock_mnt;
// sockfs文件系统类型
static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {
.name = " sockfs " ,
.get_sb = sockfs_get_sb,
.kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
};
// 地址簇及协议信息
static struct net_proto_family * net_families[NPROTO];
实际上,Linux内核只提供了一个与套接字相关的系统调用,即sys_socketcall,应用程序的所有套接字调用都会映射到这个系统调用上。
asmlinkage long sys_socketcall( int call, unsigned long __user * args)
{
unsigned long a[ 6 ];
unsigned long a0,a1;
int err;
if (call < 1 || call > SYS_RECVMSG)
return - EINVAL;
/* copy_from_user should be SMP safe. */
if (copy_from_user(a, args, nargs[call])) // 从用户区拷贝参数
return - EFAULT;
a0 = a[ 0 ];
a1 = a[ 1 ];
switch (call) // 调用相应的函数
{
case SYS_SOCKET:
err = sys_socket(a0,a1,a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_BIND:
err = sys_bind(a0,( struct sockaddr __user * )a1, a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_CONNECT:
err = sys_connect(a0, ( struct sockaddr __user * )a1, a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_LISTEN:
err = sys_listen(a0,a1);
break ;
case SYS_ACCEPT:
err = sys_accept(a0,( struct sockaddr __user * )a1, ( int __user * )a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_GETSOCKNAME:
err = sys_getsockname(a0,( struct sockaddr __user * )a1, ( int __user * )a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_GETPEERNAME:
err = sys_getpeername(a0, ( struct sockaddr __user * )a1, ( int __user * )a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_SOCKETPAIR:
err = sys_socketpair(a0,a1, a[ 2 ], ( int __user * )a[ 3 ]);
break ;
case SYS_SEND:
err = sys_send(a0, ( void __user * )a1, a[ 2 ], a[ 3 ]);
break ;
case SYS_SENDTO:
err = sys_sendto(a0,( void __user * )a1, a[ 2 ], a[ 3 ],
( struct sockaddr __user * )a[ 4 ], a[ 5 ]);
break ;
case SYS_RECV:
err = sys_recv(a0, ( void __user * )a1, a[ 2 ], a[ 3 ]);
break ;
case SYS_RECVFROM:
err = sys_recvfrom(a0, ( void __user * )a1, a[ 2 ], a[ 3 ],
( struct sockaddr __user * )a[ 4 ], ( int __user * )a[ 5 ]);
break ;
case SYS_SHUTDOWN:
err = sys_shutdown(a0,a1);
break ;
case SYS_SETSOCKOPT:
err = sys_setsockopt(a0, a1, a[ 2 ], ( char __user * )a[ 3 ], a[ 4 ]);
break ;
case SYS_GETSOCKOPT:
err = sys_getsockopt(a0, a1, a[ 2 ], ( char __user * )a[ 3 ], ( int __user * )a[ 4 ]);
break ;
case SYS_SENDMSG:
err = sys_sendmsg(a0, ( struct msghdr __user * ) a1, a[ 2 ]);
break ;
case SYS_RECVMSG:
err = sys_recvmsg(a0, ( struct msghdr __user * ) a1, a[ 2 ]);
break ;
default :
err = - EINVAL;
break ;
}
return err;
}
// include/asm/unistd.h
#define __NR_socketcall 102 // 系统调用号
下面来看一下sys_socket的实现:
/*创建socket
**首先建立一个socket数据结构,然后将其“映射”到一个已打开的文件.
*/
asmlinkage long sys_socket(int family, int type, int protocol)
{
int retval;
struct socket *sock;
//创建socket
retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);
if (retval < 0)
goto out;
//将socket映射到文件描述符
retval = sock_map_fd(sock);
if (retval < 0)
goto out_release;
out:
/* It may be already another descriptor 8) Not kernel problem. */
return retval;
out_release:
sock_release(sock);
return retval;
}
int sock_create(int family, int type, int protocol, struct socket **res)
{
return __sock_create(family, type, protocol, res, 0);
}
static int __sock_create(int family, int type, int protocol, struct socket **res, int kern)
{
int i;
int err;
struct socket *sock;
/*
* Check protocol is in range
*/
//检查协议是否可用
if (family < 0 || family >= NPROTO)
return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (type < 0 || type >= SOCK_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
/* Compatibility.
This uglymoron is moved from INET layer to here to avoid
deadlock in module load.
*/
if (family == PF_INET && type == SOCK_PACKET) {
static int warned;
if (!warned) {
warned = 1;
printk(KERN_INFO "%s uses obsolete (PF_INET,SOCK_PACKET)\n", current->comm);
}
family = PF_PACKET;
}
err = security_socket_create(family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
return err;
#if defined(CONFIG_KMOD)
/* Attempt to load a protocol module if the find failed.
*
* 12/09/1996 Marcin: But! this makes REALLY only sense, if the user
* requested real, full-featured networking support upon configuration.
* Otherwise module support will break!
*/
if (net_families[family]==NULL)
{
request_module("net-pf-%d",family);
}
#endif
net_family_read_lock();
if (net_families[family] == NULL) {
i = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
goto out;
}
/*
* Allocate the socket and allow the family to set things up. if
* the protocol is 0, the family is instructed to select an appropriate
* default.
*/
//从sockfs分配一个inode,并为之分配一个套接字结构
if (!(sock = sock_alloc()))
{
printk(KERN_WARNING "socket: no more sockets\n");
i = -ENFILE; /* Not exactly a match, but its the
closest posix thing */
goto out;
}
//设置类型
sock->type = type;
/*
* We will call the ->create function, that possibly is in a loadable
* module, so we have to bump that loadable module refcnt first.
*/
i = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (!try_module_get(net_families[family]->owner))
goto out_release;
//调用具体协议的create函数
if ((i = net_families[family]->create(sock, protocol)) < 0)
goto out_module_put;
/*
* Now to bump the refcnt of the [loadable] module that owns this
* socket at sock_release time we decrement its refcnt.
*/
if (!try_module_get(sock->ops->owner)) {
sock->ops = NULL;
goto out_module_put;
}
/*
* Now that we're done with the ->create function, the [loadable]
* module can have its refcnt decremented
*/
module_put(net_families[family]->owner);
*res = sock;
security_socket_post_create(sock, family, type, protocol, kern);
out:
net_family_read_unlock();
return i;
out_module_put:
module_put(net_families[family]->owner);
out_release:
sock_release(sock);
goto out;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int sock_map_fd(struct socket *sock)
{
int fd;
struct qstr this;
char name[32];
/*
* Find a file descriptor suitable for return to the user.
*/
//分配一个没有使用的描述符
fd = get_unused_fd();
if (fd >= 0) {
struct file *file = get_empty_filp();
if (!file) {
put_unused_fd(fd);
fd = -ENFILE;
goto out;
}
sprintf(name, "[%lu]", SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_ino);
this.name = name;
this.len = strlen(name);
this.hash = SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_ino;
//从sockfs文件系统中分配一个目录项对象
file->f_dentry = d_alloc(sock_mnt->mnt_sb->s_root, &this);
if (!file->f_dentry) {
put_filp(file);
put_unused_fd(fd);
fd = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
file->f_dentry->d_op = &sockfs_dentry_operations;
//将目录项对象与sock的索引节点关联起来
d_add(file->f_dentry, SOCK_INODE(sock));
file->f_vfsmnt = mntget(sock_mnt);
file->f_mapping = file->f_dentry->d_inode->i_mapping;
//设置sock对应的文件对象
sock->file = file;
//设置文件对象的操作函数
file->f_op = SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_fop = &socket_file_ops;
file->f_mode = FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE;
file->f_flags = O_RDWR;
file->f_pos = 0;
fd_install(fd, file);
}
out:
return fd;
}
3.2、INET套接字
INET套接字就是支持 Internet 地址族的套接字,它位于TCP协议之上, BSD套接字之下,如下: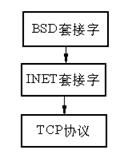
3.2.1、数据结构
//与特定协议相关的socket
struct sock {
/*
* Now struct tcp_tw_bucket also uses sock_common, so please just
* don't add nothing before this first member (__sk_common) --acme
*/
struct sock_common __sk_common;
#define sk_family __sk_common.skc_family
#define sk_state __sk_common.skc_state
#define sk_reuse __sk_common.skc_reuse
#define sk_bound_dev_if __sk_common.skc_bound_dev_if
#define sk_node __sk_common.skc_node
#define sk_bind_node __sk_common.skc_bind_node
#define sk_refcnt __sk_common.skc_refcnt
volatile unsigned char sk_zapped;
unsigned char sk_shutdown;
unsigned char sk_use_write_queue;
unsigned char sk_userlocks;
socket_lock_t sk_lock;
int sk_rcvbuf;
wait_queue_head_t *sk_sleep;
struct dst_entry *sk_dst_cache;
rwlock_t sk_dst_lock;
struct xfrm_policy *sk_policy[2];
atomic_t sk_rmem_alloc;
struct sk_buff_head sk_receive_queue;
atomic_t sk_wmem_alloc;
struct sk_buff_head sk_write_queue;
atomic_t sk_omem_alloc;
int sk_wmem_queued;
int sk_forward_alloc;
unsigned int sk_allocation;
int sk_sndbuf;
unsigned long sk_flags;
char sk_no_check;
unsigned char sk_debug;
unsigned char sk_rcvtstamp;
unsigned char sk_no_largesend;
int sk_route_caps;
unsigned long sk_lingertime;
int sk_hashent;
/*
* The backlog queue is special, it is always used with
* the per-socket spinlock held and requires low latency
* access. Therefore we special case it's implementation.
*/
struct {
struct sk_buff *head;
struct sk_buff *tail;
} sk_backlog;
rwlock_t sk_callback_lock;
struct sk_buff_head sk_error_queue;
struct proto *sk_prot;
int sk_err,
sk_err_soft;
unsigned short sk_ack_backlog;
unsigned short sk_max_ack_backlog;
__u32 sk_priority;
unsigned short sk_type;
unsigned char sk_localroute;
unsigned char sk_protocol;
struct ucred sk_peercred;
int sk_rcvlowat;
long sk_rcvtimeo;
long sk_sndtimeo;
struct sk_filter *sk_filter;
void *sk_protinfo;
kmem_cache_t *sk_slab;
struct timer_list sk_timer;
struct timeval sk_stamp;
struct socket *sk_socket;
void *sk_user_data;
struct module *sk_owner;
struct page *sk_sndmsg_page;
__u32 sk_sndmsg_off;
struct sk_buff *sk_send_head;
int sk_write_pending;
void *sk_security;
__u8 sk_queue_shrunk;
/* three bytes hole, try to pack */
void (*sk_state_change)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_data_ready)(struct sock *sk, int bytes);
void (*sk_write_space)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_error_report)(struct sock *sk);
int (*sk_backlog_rcv)(struct sock *sk,
struct sk_buff *skb);
void (*sk_destruct)(struct sock *sk);
};
//底层协议的操作函数
struct proto {
void (*close)(struct sock *sk,
long timeout);
int (*connect)(struct sock *sk,
struct sockaddr *uaddr,
int addr_len);
int (*disconnect)(struct sock *sk, int flags);
struct sock * (*accept) (struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err);
int (*ioctl)(struct sock *sk, int cmd,
unsigned long arg);
int (*init)(struct sock *sk);
int (*destroy)(struct sock *sk);
void (*shutdown)(struct sock *sk, int how);
int (*setsockopt)(struct sock *sk, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval,
int optlen);
int (*getsockopt)(struct sock *sk, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval,
int __user *option);
int (*sendmsg)(struct kiocb *iocb, struct sock *sk,
struct msghdr *msg, size_t len);
int (*recvmsg)(struct kiocb *iocb, struct sock *sk,
struct msghdr *msg,
size_t len, int noblock, int flags,
int *addr_len);
int (*sendpage)(struct sock *sk, struct page *page,
int offset, size_t size, int flags);
int (*bind)(struct sock *sk,
struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len);
int (*backlog_rcv) (struct sock *sk,
struct sk_buff *skb);
/* Keeping track of sk's, looking them up, and port selection methods. */
void (*hash)(struct sock *sk);
void (*unhash)(struct sock *sk);
int (*get_port)(struct sock *sk, unsigned short snum);
/* Memory pressure */
void (*enter_memory_pressure)(void);
atomic_t *memory_allocated; /* Current allocated memory. */
atomic_t *sockets_allocated; /* Current number of sockets. */
/*
* Pressure flag: try to collapse.
* Technical note: it is used by multiple contexts non atomically.
* All the sk_stream_mem_schedule() is of this nature: accounting
* is strict, actions are advisory and have some latency.
*/
int *memory_pressure;
int *sysctl_mem;
int *sysctl_wmem;
int *sysctl_rmem;
int max_header;
kmem_cache_t *slab;
int slab_obj_size;
struct module *owner;
char name[32];
struct {
int inuse;
u8 __pad[SMP_CACHE_BYTES - sizeof(int)];
} stats[NR_CPUS];
};
inet_init()函数:
/*系统初始化时被调用
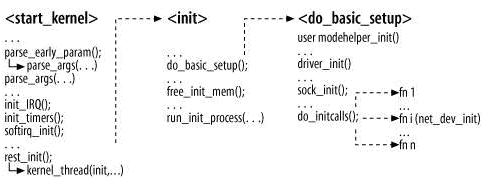
**调用路径:start_kernel() -->init() -->do_basic_setup() -->do_initcalls()-->inet_init()
*/
static int __init inet_init(void)
{
struct sk_buff *dummy_skb;
struct inet_protosw *q;
struct list_head *r;
int rc = -EINVAL;
if (sizeof(struct inet_skb_parm) > sizeof(dummy_skb->cb)) {
printk(KERN_CRIT "%s: panic\n", __FUNCTION__);
goto out;
}
rc = sk_alloc_slab(&tcp_prot, "tcp_sock");
if (rc) {
sk_alloc_slab_error(&tcp_prot);
goto out;
}
rc = sk_alloc_slab(&udp_prot, "udp_sock");
if (rc) {
sk_alloc_slab_error(&udp_prot);
goto out_tcp_free_slab;
}
rc = sk_alloc_slab(&raw_prot, "raw_sock");
if (rc) {
sk_alloc_slab_error(&raw_prot);
goto out_udp_free_slab;
}
/*
* Tell SOCKET that we are alive
*/
//注册Internet协议簇的相关信息
(void)sock_register(&inet_family_ops);
/*
* Add all the base protocols.
*/
//添加基本的协议
if (inet_add_protocol(&icmp_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMP) < 0)
printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add ICMP protocol\n");
if (inet_add_protocol(&udp_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP) < 0)
printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add UDP protocol\n");
if (inet_add_protocol(&tcp_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP) < 0)
printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add TCP protocol\n");
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST
if (inet_add_protocol(&igmp_protocol, IPPROTO_IGMP) < 0)
printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add IGMP protocol\n");
#endif
/* Register the socket-side information for inet_create. */
for (r = &inetsw[0]; r < &inetsw[SOCK_MAX]; ++r)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(r);
//将inetsw_array中元素加入到inetsw链表中
for (q = inetsw_array; q < &inetsw_array[INETSW_ARRAY_LEN]; ++q)
inet_register_protosw(q);
/*
* Set the ARP module up
*/
arp_init(); //ARP协议初始化
/*
* Set the IP module up
*/
ip_init(); //IP协议初始化
tcp_v4_init(&inet_family_ops);
/* Setup TCP slab cache for open requests. */
tcp_init();
/*
* Set the ICMP layer up
*/
icmp_init(&inet_family_ops);
/*
* Initialise the multicast router
*/
#if defined(CONFIG_IP_MROUTE)
ip_mr_init();
#endif
/*
* Initialise per-cpu ipv4 mibs
*/
if(init_ipv4_mibs())
printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot init ipv4 mibs\n"); ;
ipv4_proc_init();
ipfrag_init();
rc = 0;
out:
return rc;
out_tcp_free_slab:
sk_free_slab(&tcp_prot);
out_udp_free_slab:
sk_free_slab(&udp_prot);
goto out;
}
//net/ipv4/af_inet.c
//INET协议簇信息
static struct net_proto_family inet_family_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.create = inet_create,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
static struct list_head inetsw[SOCK_MAX];
//该数组中的所有元素都会插入到inetsw的链表中
static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] =
{
{
.type = SOCK_STREAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
.prot = &tcp_prot,
.ops = &inet_stream_ops,
.capability = -1,
.no_check = 0,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP,
.prot = &udp_prot,
.ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
.capability = -1,
.no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
},
{
.type = SOCK_RAW,
.protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */
.prot = &raw_prot,
.ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
.capability = CAP_NET_RAW,
.no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
}
};
//流套接字操作函数
struct proto_ops inet_stream_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.release = inet_release,
.bind = inet_bind,
.connect = inet_stream_connect,
.socketpair = sock_no_socketpair,
.accept = inet_accept,
.getname = inet_getname,
.poll = tcp_poll,
.ioctl = inet_ioctl,
.listen = inet_listen,
.shutdown = inet_shutdown,
.setsockopt = sock_common_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = sock_common_getsockopt,
.sendmsg = inet_sendmsg,
.recvmsg = sock_common_recvmsg,
.mmap = sock_no_mmap,
.sendpage = tcp_sendpage
};
//tcp协议
static struct net_protocol tcp_protocol = {
.handler = tcp_v4_rcv,
.err_handler = tcp_v4_err,
.no_policy = 1,
};
static struct net_protocol udp_protocol = {
.handler = udp_rcv,
.err_handler = udp_err,
.no_policy = 1,
};
static struct net_protocol icmp_protocol = {
.handler = icmp_rcv,
};
//net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c
//tcp协议的操作函数
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.name = "TCP",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = tcp_close,
.connect = tcp_v4_connect,
.disconnect = tcp_disconnect,
.accept = tcp_accept,
.ioctl = tcp_ioctl,
.init = tcp_v4_init_sock,
.destroy = tcp_v4_destroy_sock,
.shutdown = tcp_shutdown,
.setsockopt = tcp_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = tcp_getsockopt,
.sendmsg = tcp_sendmsg,
.recvmsg = tcp_recvmsg,
.backlog_rcv = tcp_v4_do_rcv,
.hash = tcp_v4_hash,
.unhash = tcp_unhash,
.get_port = tcp_v4_get_port,
.enter_memory_pressure = tcp_enter_memory_pressure,
.sockets_allocated = &tcp_sockets_allocated,
.memory_allocated = &tcp_memory_allocated,
.memory_pressure = &tcp_memory_pressure,
.sysctl_mem = sysctl_tcp_mem,
.sysctl_wmem = sysctl_tcp_wmem,
.sysctl_rmem = sysctl_tcp_rmem,
.max_header = MAX_TCP_HEADER,
.slab_obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock),
};
sock_register()函数:
int sock_register(struct net_proto_family *ops)
{
int err;
if (ops->family >= NPROTO) {
printk(KERN_CRIT "protocol %d >= NPROTO(%d)\n", ops->family, NPROTO);
return -ENOBUFS;
}
net_family_write_lock();
err = -EEXIST;
if (net_families[ops->family] == NULL) {
net_families[ops->family]=ops;
err = 0;
}
net_family_write_unlock();
printk(KERN_INFO "NET: Registered protocol family %d\n",
ops->family);
return err;
}
inet_create()函数
static int inet_create(struct socket *sock, int protocol)
{
struct sock *sk;
struct list_head *p;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
struct inet_opt *inet;
struct proto *answer_prot;
unsigned char answer_flags;
char answer_no_check;
int err;
sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
/* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */
answer = NULL;
rcu_read_lock();
list_for_each_rcu(p, &inetsw[sock->type]) {
answer = list_entry(p, struct inet_protosw, list);
/* Check the non-wild match. */
if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
break;
} else {
/* Check for the two wild cases. */
if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) {
protocol = answer->protocol;
break;
}
if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol)
break;
}
answer = NULL;
}
err = -ESOCKTNOSUPPORT;
if (!answer)
goto out_rcu_unlock;
err = -EPERM;
if (answer->capability > 0 && !capable(answer->capability))
goto out_rcu_unlock;
err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT;
if (!protocol)
goto out_rcu_unlock;
//BSD socket的操作函数
sock->ops = answer->ops;
answer_prot = answer->prot;
answer_no_check = answer->no_check;
answer_flags = answer->flags;
rcu_read_unlock();
BUG_TRAP(answer_prot->slab != NULL);
err = -ENOBUFS;
sk = sk_alloc(PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL,
answer_prot->slab_obj_size,
answer_prot->slab);
if (sk == NULL)
goto out;
err = 0;
//特定协议套接字的操作函数
sk->sk_prot = answer_prot;
sk->sk_no_check = answer_no_check;
if (INET_PROTOSW_REUSE & answer_flags)
sk->sk_reuse = 1;
inet = inet_sk(sk);
if (SOCK_RAW == sock->type) {
inet->num = protocol;
if (IPPROTO_RAW == protocol)
inet->hdrincl = 1;
}
if (ipv4_config.no_pmtu_disc)
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT;
else
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT;
inet->id = 0;
//将sock与sk关联起来
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
sk_set_owner(sk, sk->sk_prot->owner);
sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
sk->sk_family = PF_INET;
sk->sk_protocol = protocol;
sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
inet->uc_ttl = -1;
inet->mc_loop = 1;
inet->mc_ttl = 1;
inet->mc_index = 0;
inet->mc_list = NULL;
#ifdef INET_REFCNT_DEBUG
atomic_inc(&inet_sock_nr);
#endif
if (inet->num) {
/* It assumes that any protocol which allows
* the user to assign a number at socket
* creation time automatically
* shares.
*/
inet->sport = htons(inet->num);
/* Add to protocol hash chains. */
sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
}
//调用init函数
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
if (err)
sk_common_release(sk);
}
out:
return err;
out_rcu_unlock:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out;
}