用UFLDL的方法改写Denoising Autoencoder
最近在学Autoencoder的相关知识,已经学习完DFLDL的Sparse_Autoencoder相关知识,想学学Denoising Autoencoder和contractive Autoencoder。
本篇先说说Denoising Autoencoder的学习。
参考大神tornadomeet的博客(http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/p/3261247.html),我准备自己尝试第一个实验。下载完DeepLearnToolbox并且自己把代码test_example_SAE跑了一遍后发现,没有Denoising时候,识别结果error为0.10,然后加上50%的Denoising后,就出现“Too big error”的警告,原来是识别结果error超过0.16,而代码的最后一句为
assert(er < 0.16, 'Too big error')。
但是tornadomeet大神不是说加上50%的Denoising后test的结果会更好吗?仔细对比了一下发现,toolbox里面的代码网络结构是[784 100 10]的,也就是只有一层hidden layer,代码如下:
function test_example_SAE
load ../data/mnist_uint8;
train_x = double(train_x)/255;
test_x = double(test_x)/255;
train_y = double(train_y);
test_y = double(test_y);
addpath('../SAE')
addpath('../NN')
%% ex1 train a 100 hidden unit SDAE and use it to initialize a FFNN
% Setup and train a stacked denoising autoencoder (SDAE)
rand('state',0)
sae = saesetup([784 100]);
sae.ae{1}.activation_function = 'sigm';
sae.ae{1}.learningRate = 1;
sae.ae{1}.inputZeroMaskedFraction = 0.5;
opts.numepochs = 1;
opts.batchsize = 100;
sae = saetrain(sae, train_x, opts);
visualize(sae.ae{1}.W{1}(:,2:end)')
% Use the SDAE to initialize a FFNN
nn = nnsetup([784 100 10]);
nn.activation_function = 'sigm';
nn.learningRate = 1;
nn.W{1} = sae.ae{1}.W{1};
% Train the FFNN
opts.numepochs = 1;
opts.batchsize = 100;
nn = nntrain(nn, train_x, train_y, opts);
[er, bad] = nntest(nn, test_x, test_y);
assert(er < 0.16, 'Too big error');
而tornadomeet大神的代码是两层hidden layer,网络结构是[784 100 100 10]的,存在着这个差别,所以两层hidden layer的结果是:
接下来我自己尝试去写这整个代码,但是toolbox的代码由于是要适合多个test的,所以每个被调用的函数里面都列举了各种的可能性,
switch nn.activation_function
case 'sigm'
% Calculate the unit's outputs (including the bias term)
nn.a{i} = sigm(nn.a{i - 1} * nn.W{i - 1}');
case 'tanh_opt'
nn.a{i} = tanh_opt(nn.a{i - 1} * nn.W{i - 1}');
end
%dropout
if(nn.dropoutFraction > 0)
if(nn.testing)
nn.a{i} = nn.a{i}.*(1 - nn.dropoutFraction);
else
nn.dropOutMask{i} = (rand(size(nn.a{i}))>nn.dropoutFraction);
nn.a{i} = nn.a{i}.*nn.dropOutMask{i};
end
end
%calculate running exponential activations for use with sparsity
if(nn.nonSparsityPenalty>0)
nn.p{i} = 0.99 * nn.p{i} + 0.01 * mean(nn.a{i}, 1);
end
%Add the bias term
nn.a{i} = [ones(m,1) nn.a{i}];
end
switch nn.output
case 'sigm'
nn.a{n} = sigm(nn.a{n - 1} * nn.W{n - 1}');
case 'linear'
nn.a{n} = nn.a{n - 1} * nn.W{n - 1}';
case 'softmax'
nn.a{n} = nn.a{n - 1} * nn.W{n - 1}';
nn.a{n} = exp(bsxfun(@minus, nn.a{n}, max(nn.a{n},[],2)));
nn.a{n} = bsxfun(@rdivide, nn.a{n}, sum(nn.a{n}, 2));
end
代码太冗余,不适合初学者,所以我自己尝试用UFLDL里面的那种代码风格,自己从头到尾写了一遍代码,结果发现,即使是用一层隐含层,网络结构是[784 100 10],用了denoising后,效果也会比没有denoising好。
下面是自己写的代码和结果(本人是初学者,代码不够规范,希望大家见谅并批评指出):
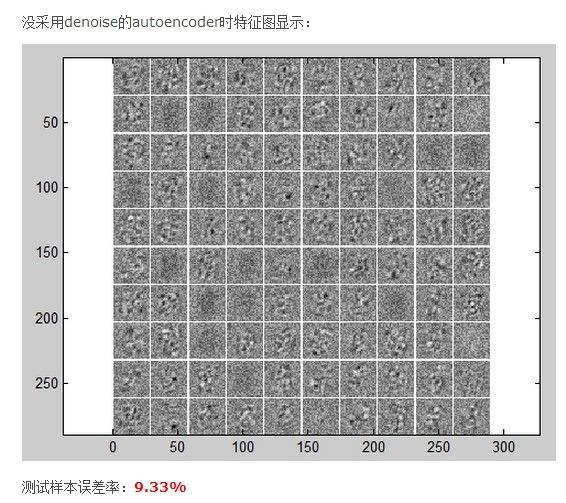
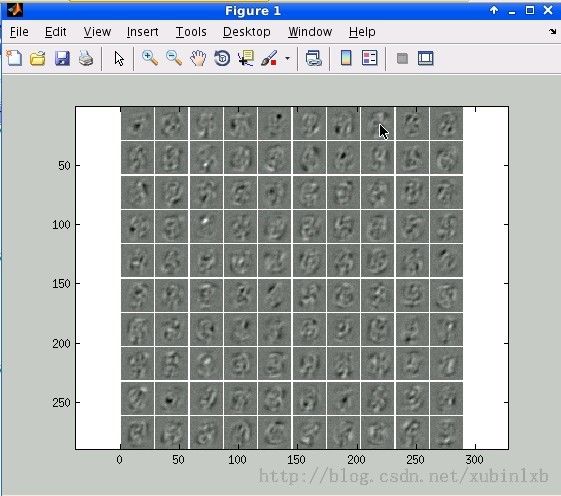
the error rate is 9.3%
加上denoising后,the error rate is 7.3%
%% Code for Denoising Autoencoder
% the network is [784 100 10]
% By xubinlxb
close all
clear
clc
%% load data
load './data/mnist_uint8.mat'
train_x = double(train_x'./255);
train_y = double(train_y');
test_x = double(test_x'./255);
test_y = double(test_y');
%% parameter initialized
nn = struct;
nn.visibleSize = size(train_x,1);
nn.hiddenSize = 100;
nn.outputSize = 10;
nn.lambda = 0.0001;
nn.batchSize=100;
nn.LearnRate = 3;
nn.Method = 'unsupervise';
nn.DenoisingPara = 0.5;
%% build Layer1 network
% configuration the cost funtion
rng('default');
nn = theta_initialization(nn);
disp('unsupervise train...')
[L1, nn] = batch_build(nn, train_x ,train_x);
[cost1,~] = build_one_layer_addWeight(nn,train_x,train_x);
% Visualization
visualize(nn.W1');
% display_network(nn.W1', 12);
%% train the whole network
nn.DenoisingPara = 0;
nn.Method = 'supervise';
W1 = nn.W1;
b1 = nn.b1;
nn = theta_initialization(nn);
nn.W1 = W1;
nn.b1 = b1;
clear W1 b1
disp('supervise train...')
[L2, nn] = batch_build(nn, train_x, train_y);
[cost2,~] = build_one_layer_addWeight(nn,train_x,train_y);
%% test the whole network
label = predict(nn,test_x);
[~,expected] = max(test_y,[],1);
badNum = numel(find(label~=expected));
er = badNum/size(test_y,2);
assert(er<0.16,'Too big error')
fprintf('the errror rate is %f\n',er)
function [ L, nn ] = batch_build( nn, train_x ,train_y)
m = size(train_x,2);
batchSize = nn.batchSize;
batchNum = m/ batchSize;
L = [];
for i = 1:batchNum
if (mod(i,100) == 0)
fprintf('batch %d,\n',i);
end
kk = randperm(m);
batch_x = train_x( :, kk(((i-1)*batchSize+1): i*batchSize) );
batch_y = train_y( :, kk(((i-1)*batchSize+1): i*batchSize) );
[cost, nn] = build_one_layer_addWeight(nn, batch_x ,batch_y);
L = [L,cost];
end
end
function [ cost, nn ] = build_one_layer_addWeight( nn, x, y )
% initialize the parameter
lambda = nn.lambda;
LearnRate = nn.LearnRate;
W1 = nn.W1;
b1 = nn.b1;
W2 = nn.W2;
b2 = nn.b2;
W1grad = zeros(size(W1));
b1grad = zeros(size(b1));
W2grad = zeros(size(W2));
b2grad = zeros(size(b2));
%% BP algorithm
m = size(x,2);
% Denoising Autoencoder
x = x.*(rand(size(x)) > nn.DenoisingPara);
% feedforward
z2 = W1* x+ repmat(b1,1,m);
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
z3 = W2* a2+ repmat(b2,1,m);
a3 = sigmoid(z3);
cost = 0.5/m.* sum(sum((y - a3).^2))+ 0.5*lambda.* (sum(W1(:).^2)+sum(W2(:).^2));
% Back forword calculator the grad
d3 = -(y - a3).* a3 .*(1-a3);
d2 = W2'* d3 .* a2 .*(1-a2);
W2grad = 1.0/m.* (d3 *a2')+ lambda.* W2;
b2grad = 1.0/m.* sum(d3,2);
W1grad = 1.0/m.* (d2 *x')+ lambda.*W1;
b1grad = 1.0/m.* sum(d2,2);
W2 = W2 - LearnRate*W2grad;
b2 = b2 - LearnRate*b2grad;
W1 = W1 - LearnRate*W1grad;
b1 = b1 - LearnRate*b1grad;
%grad = [ W1grad(:);b1grad(:);W2grad(:);b2grad(:) ];
nn.W1 = W1;
nn.b1 = b1;
nn.W2 = W2;
nn.b2 = b2;
end
function sigm = sigmoid(x)
sigm = 1./(1+exp(-x));
end
function [ nn ] = theta_initialization( nn )
visibleSize = nn.visibleSize;
hiddenSize = nn.hiddenSize;
switch nn.Method
case 'unsupervise'
outputSize = nn.visibleSize;
case 'supervise'
outputSize = nn.outputSize;
otherwise
error('nn.Method error');
end
r = sqrt(6) / sqrt(hiddenSize+visibleSize+1); % weights uniformly from the interval [-r, r]
W1 = rand(hiddenSize, visibleSize) * 2 * r - r;
r = sqrt(6) / sqrt(hiddenSize+outputSize+1);
W2 = rand(outputSize, hiddenSize) * 2 * r - r;
b1 = zeros(hiddenSize, 1);
b2 = zeros(outputSize, 1);
nn.W1 = W1;
nn.b1 = b1;
nn.W2 = W2;
nn.b2 = b2;
end
function label = predict( nn, x)
%UNTITLED3 Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
W1 = nn.W1;
b1 = nn.b1;
W2 = nn.W2;
b2 = nn.b2;
m = size(x,2);
label = zeros(1,m);
z2 = W1*x +repmat(b1,1,m);
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
z3 = W2*a2 +repmat(b2,1,m);
a3 = sigmoid(z3);
[~,label] = max(a3,[],1);
end
function sigm = sigmoid(x)
sigm = 1./(1+exp(-x));
end
function r=visualize(X, mm, s1, s2)
%FROM RBMLIB http://code.google.com/p/matrbm/
%Visualize weights X. If the function is called as a void method,
%it does the plotting. But if the function is assigned to a variable
%outside of this code, the formed image is returned instead.
if ~exist('mm','var')
mm = [min(X(:)) max(X(:))];
end
if ~exist('s1','var')
s1 = 0;
end
if ~exist('s2','var')
s2 = 0;
end
[D,N]= size(X);
s=sqrt(D);
if s==floor(s) || (s1 ~=0 && s2 ~=0)
if (s1 ==0 || s2 ==0)
s1 = s; s2 = s;
end
%its a square, so data is probably an image
num=ceil(sqrt(N));
a=mm(2)*ones(num*s2+num-1,num*s1+num-1);
x=0;
y=0;
for i=1:N
im = reshape(X(:,i),s1,s2)';
a(x*s2+1+x : x*s2+s2+x, y*s1+1+y : y*s1+s1+y)=im;
x=x+1;
if(x>=num)
x=0;
y=y+1;
end
end
d=true;
else
%there is not much we can do
a=X;
end
%return the image, or plot the image
if nargout==1
r=a;
else
imagesc(a, [mm(1) mm(2)]);
axis equal
colormap gray
end