深入学习Tomcat-自己动手写服务器(附服务器源码)
相信大多Web开发者对Tomcat是非常熟悉的,众所周知Tomcat是一款非常好用的开源Servlet容器,您一定对这个最流行的Servlet容器充满好奇,虽然它并不像一个黑盒子那样让人无法触摸但是Tomcat的源码的确让人看起来头疼。笔者就在这里和大家共同分析一个简单的Web服务器是如何工作的
Web服务器
Web服务器是一个复杂的系统,一个Web服务器要为一个Servlet的请求提供服务,需要做三件事:
1、创建一个request对象并填充那些有可能被所引用的Servlet使用的信息,如参数、头部、cookies、查询字符串等等。一个request对象是javax.servlet.ServletRequest或javax.servlet.http.ServletRequest接口的一个实例
2、创建一个response对象,所引用的servlet使用它来给客户端发送响应。一个response对象是javax.servlet.ServletRequest或javax.servlet.http.ServletRequest接口的一个实例。
3、调用servlet的service方法,并传入request和response对象。这里servlet会从request对象取值,给response写值。
在正式展示代码之前还需要了解一些必须额HTTP的知识(如果您对此非常熟悉您可以直接看下面分析代码)
HTTP
HTTP的定义不知道的童鞋可以自己去度娘,这里主要要说的就是HTTP协议的格式
HTTP请求包括三部分
1、方法、统一资源标识符(URI)、协议/版本
2、请求的头部
3、主题内容
下面是一个HTTP请求的例子
- POST /examples/default.jsp HTTP/1.1
- Accept: text/plain; text/html
- Accept-Language: en-gb
- Connection: Keep-Alive
- Host: localhost
- User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 4.01; Windows 98)
- Content-Length: 33
- Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
- lastName=Franks&firstName=Michael
第一行表明这是POST请求方法,/examples/default.jsp是URI,HTTP/1.1是协议以及版本。其中URI指明了一个互联网资源,这里通常是相对服务器根目录解释的,也就是说这个HTTP请求就是告诉服务器我需要这个文件目录如下:根目录/ examples/default.jsp。
最后一行是HTTP的主题内容,Servlet会处理请求的主题内容,然后返回给客户端HTTP响应。
类似于HTTP请求,一个HTTP响应也包括上面三个部分。
1、方法、统一资源标识符(URI)、协议/版本
2、响应的头部
3、主题内容
下面是一个HTTP响应的例子
- HTTP/1.1 200 OK
- Server: Microsoft-IIS/4.0
- Date: Mon, 5 Jan 2004 13:13:33 GMT
- Content-Type: text/html
- Last-Modified: Mon, 5 Jan 2004 13:13:12 GMT
- Content-Length: 112
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>HTTP Response Example</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- Welcome to Brainy Software
- </body>
- </html>
第一行告诉协议版本,以及请求成功(200表示成功)
响应头部和请求头部一样,一些有用的信息。响应的主体就是响应本身HTML内容。
好了基本知识介绍完毕,下面开始解释代码
部分相关代码
- import java.net.Socket;
- import java.net.ServerSocket;
- import java.net.InetAddress;
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.io.OutputStream;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.File;
- public class HttpServer {
- public static final String WEB_ROOT = System.getProperty("user.dir")
- + File.separator + "webroot";
- private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND = "/SHUTDOWN";
- private boolean shutdown = false;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- HttpServer server = new HttpServer();
- server.await();
- }
- public void await() {
- ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
- int port = 8080;
- try {
- serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1,
- InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- System.exit(1);
- }
- while (!shutdown) {
- Socket socket = null;
- InputStream input = null;
- OutputStream output = null;
- try {
- socket = serverSocket.accept();
- input = socket.getInputStream();
- output = socket.getOutputStream();
- Request request = new Request(input);
- request.parse();
- Response response = new Response(output);
- response.setRequest(request);
- response.sendStaticResource();
- socket.close();
- shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- continue;
- }
- }
- }
- }
HttpServer类代表一个web服务器。首先提供一个WEB_ROOT所在的目录和它下面所有的子目录下静态资源。其次定义了一个中止服务的命令,也就是说当得到的请求后面跟/shutdown的时候停止服务,默认是把服务设置为开启。下面就是进入main函数了,首先实例化一个HttpServer类,然后就是通过await方法等待客户端发来的请求。如果客户端输入的URL不是http://localhost:8080/SHUTDOWN则表示不停止服务器,然后就是继续执行await方法中的内容,在await方法中最重要的就是定义两个对象,一个是request一个是response,下面就来说说Request和Response类。
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.io.IOException;
- public class Request {
- private InputStream input;
- private String uri;
- public Request(InputStream input) {
- this.input = input;
- }
- public void parse() {
- StringBuffer request = new StringBuffer(2048);
- int i;
- byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
- try {
- i = input.read(buffer);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- i = -1;
- }
- for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
- request.append((char) buffer[j]);
- }
- System.out.print(request.toString());
- uri = parseUri(request.toString());
- }
- private String parseUri(String requestString) {
- int index1, index2;
- index1 = requestString.indexOf(' ');
- if (index1 != -1) {
- index2 = requestString.indexOf(' ', index1 + 1);
- if (index2 > index1)
- return requestString.substring(index1 + 1, index2);
- }
- return null;
- }
- public String getUri() {
- return uri;
- }
- }
首先调用InputStream对象中的read方法获取HTTP请求的原始数据,然后在parseUri方法中获得uri也就是要请求的静态资源。说白了Request类的主要作用就是告诉服务器用户要的是什么也就是在http://localhost:8080后面出现的东西。
- import java.io.OutputStream;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.FileInputStream;
- import java.io.File;
- public class Response {
- private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
- Request request;
- OutputStream output;
- public Response(OutputStream output) {
- this.output = output;
- }
- public void setRequest(Request request) {
- this.request = request;
- }
- public void sendStaticResource() throws IOException {
- byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
- FileInputStream fis = null;
- try {
- File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri());
- if (file.exists()) {
- fis = new FileInputStream(file);
- int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
- while (ch != -1) {
- output.write(bytes, 0, ch);
- ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
- }
- } else {
- String errorMessage = "HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r\n"
- + "Content-Type: text/html\r\n"
- + "Content-Length: 23\r\n" + "\r\n"
- + "<h1>File Not Found</h1>";
- /** 请求最终是通过这里写入Socket的输出流中,响应给浏览器 */
- output.write(errorMessage.getBytes());
- }
- } catch (Exception e) {
- System.out.println(e.toString());
- } finally {
- if (fis != null)
- fis.close();
- }
- }
- }
Response类代表一个HTTP响应。首先Response接收一个OutputStream对象,然后通过sendStaticResource方法对接收的Request进行处理,整个处理过程就是根据请求在服务器端进行寻找对应静态资源的过程。找到所需要的资源后发送给客户端然后让客户端显示出来。
运行程序
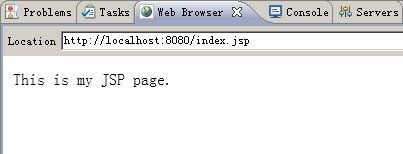
运行上面的HttpServer类,然后在浏览器的地址栏中键入下面的地址:http:localhost:8080/index.jsp,然后你会在浏览器中看到index.jsp页面。
在控制台可以看到类似于下面的HTTP请求
- GET /index.jsp HTTP/1.1
- Host: localhost:8080
- Connection: keep-alive
- Cache-Control: max-age=0
- User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/535.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/16.0.912.75 Safari/535.7 360EE
- Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
- Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch
- Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8
- Accept-Charset: GBK,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.3
小结
上面自己动手写的这个所谓的服务器仅仅有三个类组成,从功能上来说他只能显示一些静态的资源,并不是全部功能。一个优秀的服务器还有很多细节要做,但是出于学习的目的大家现在有这些了解就足够了,后面还会有对服务器的详细介绍,敬请期待。