Dynamic Programming | Set 6 (Min Cost Path)
Given a cost matrix cost[][] and a position (m, n) in cost[][], write a function that returns cost of minimum cost path to reach (m, n) from (0, 0). Each cell of the matrix represents a cost to traverse through that cell. Total cost of a path to reach (m, n) is sum of all the costs on that path (including both source and destination). You can only traverse down, right and diagonally lower cells from a given cell, i.e., from a given cell (i, j), cells (i+1, j), (i, j+1) and (i+1, j+1) can be traversed. You may assume that all costs are positive integers.
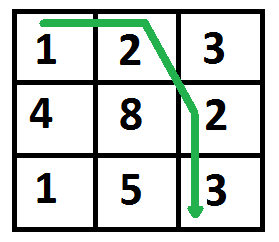
For example, in the following figure, what is the minimum cost path to (2, 2)?

The path with minimum cost is highlighted in the following figure. The path is (0, 0) –> (0, 1) –> (1, 2) –> (2, 2). The cost of the path is 8 (1 + 2 + 2 + 3).
1) Optimal Substructure
The path to reach (m, n) must be through one of the 3 cells: (m-1, n-1) or (m-1, n) or (m, n-1). So minimum cost to reach (m, n) can be written as “minimum of the 3 cells plus cost[m][n]“.
minCost(m, n) = min (minCost(m-1, n-1), minCost(m-1, n), minCost(m, n-1)) + cost[m][n]
2) Overlapping Subproblems
Following is simple recursive implementation of the MCP (Minimum Cost Path) problem. The implementation simply follows the recursive structure mentioned above.
package DP;
public class MinCostPath {
static int R = 3;
static int C = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[][] cost = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
int m = 2, n = 2;
System.out.println(minCostRec(cost, m, n));
System.out.println(minCostDP(cost, m, n));
}
/* A Naive recursive implementation of MCP(Minimum Cost Path) problem */
/* Returns cost of minimum cost path from (0,0) to (m, n) in mat[R][C]*/
public static int minCostRec(int[][] cost, int m, int n) throws Exception{
if(m<0 || n<0){ // 注意这里返回INT_MAX最大值
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
else if(m==0 && n==0){
return cost[0][0];
}else{
return min3(minCostRec(cost, m-1, n-1),
minCostRec(cost, m, n-1),
minCostRec(cost, m-1, n))
+ cost[m][n];
}
}
public static int minCostDP(int[][] cost, int m, int n){
// Instead of following line, we can use int dp[m+1][n+1] or
// dynamically allocate memoery to save space. The following line is
// used to keep the program simple and make it working on all compilers.
int[][] dp = new int[R][C];
dp[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + cost[i][0];
}
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++){
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1] + cost[0][j];
}
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++){
dp[i][j] = min3(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
public static int min3(int x, int y, int z){
return Math.min(Math.min(x, y), z);
}
}
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dynamic-programming-set-6-min-cost-path/

