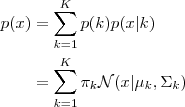高斯混合模型算法
下面介绍一下几种典型的机器算法
首先第一种是高斯混合模型算法:
高斯模型有单高斯模型(SGM)和混合高斯模型(GMM)两种。
(1)单高斯模型:
为简单起见,阈值t的选取一般靠经验值来设定。通常意义下,我们一般取t=0.7-0.75之间。
二维情况如下所示:
(2)混合高斯模型:
对于(b)图所示的情况,很明显,单高斯模型是无法解决的。为了解决这个问题,人们提出了高斯混合模型(GMM),顾名思义,就是数据可以看作是从数个高斯分布中生成出来的。虽然我们可以用不同的分布来随意地构造 XX Mixture Model ,但是 GMM是 最为流行。另外,Mixture Model 本身其实也是可以变得任意复杂的,通过增加 Model 的个数,我们可以任意地逼近任何连续的概率密分布。
每个 GMM 由 K 个 Gaussian 分布组成,每个 Gaussian 称为一个“Component”,这些 Component 线性加成在一起就组成了 GMM 的概率密度函数:
其中,πk表示选中这个component部分的概率,我们也称其为加权系数。
根据上面的式子,如果我们要从 GMM 的分布中随机地取一个点的话,实际上可以分为两步:
(1)首先随机地在这 K 个 Component 之中选一个,每个 Component 被选中的概率实际上就是它的系数 πk,选中了 Component 之后,再单独地考虑从这个 Component 的分布中选取一个点就可以了──这里已经回到了普通的 Gaussian 分布,转化为了已知的问题。假设现在有 N 个数据点,我们认为这些数据点由某个GMM模型产生,现在我们要需要确定 πk,μk,σk 这些参数。很自然的,我们想到利用最大似然估计来确定这些参数,GMM的似然函数如下:
在最大似然估计里面,由于我们的目的是把乘积的形式分解为求和的形式,即在等式的左右两边加上一个log函数,但是由上文博客里的(2)式可以看出,转化为log后,还有log(a+b)的形式,因此,要进一步求解。
我们采用EM算法,分布迭代求解最大值:
EM算法的步骤这里不作详细的介绍,可以参见博客:
http://blog.pluskid.org/?p=39
贴出代码:
1 function varargout = gmm(X, K_or_centroids) 2 % ============================================================ 3 % Expectation-Maximization iteration implementation of 4 % Gaussian Mixture Model. 5 % 6 % PX = GMM(X, K_OR_CENTROIDS) 7 % [PX MODEL] = GMM(X, K_OR_CENTROIDS) 8 % 9 % - X: N-by-D data matrix. 10 % - K_OR_CENTROIDS: either K indicating the number of 11 % components or a K-by-D matrix indicating the 12 % choosing of the initial K centroids. 13 % 14 % - PX: N-by-K matrix indicating the probability of each 15 % component generating each point. 16 % - MODEL: a structure containing the parameters for a GMM: 17 % MODEL.Miu: a K-by-D matrix. 18 % MODEL.Sigma: a D-by-D-by-K matrix. 19 % MODEL.Pi: a 1-by-K vector. 20 % ============================================================ 21 22 threshold = 1e-15; 23 [N, D] = size(X); 24 25 if isscalar(K_or_centroids) 26 K = K_or_centroids; 27 % randomly pick centroids 28 rndp = randperm(N); 29 centroids = X(rndp(1:K), :); 30 else 31 K = size(K_or_centroids, 1); 32 centroids = K_or_centroids; 33 end 34 35 % initial values 36 [pMiu pPi pSigma] = init_params(); 37 38 Lprev = -inf; 39 while true 40 Px = calc_prob(); 41 42 % new value for pGamma 43 pGamma = Px .* repmat(pPi, N, 1); 44 pGamma = pGamma ./ repmat(sum(pGamma, 2), 1, K); 45 46 % new value for parameters of each Component 47 Nk = sum(pGamma, 1); 48 pMiu = diag(1./Nk) * pGamma' * X; 49 pPi = Nk/N; 50 for kk = 1:K 51 Xshift = X-repmat(pMiu(kk, :), N, 1); 52 pSigma(:, :, kk) = (Xshift' * ... 53 (diag(pGamma(:, kk)) * Xshift)) / Nk(kk); 54 end 55 56 % check for convergence 57 L = sum(log(Px*pPi')); 58 if L-Lprev < threshold 59 break; 60 end 61 Lprev = L; 62 end 63 64 if nargout == 1 65 varargout = {Px}; 66 else 67 model = []; 68 model.Miu = pMiu; 69 model.Sigma = pSigma; 70 model.Pi = pPi; 71 varargout = {Px, model}; 72 end 73 74 function [pMiu pPi pSigma] = init_params() 75 pMiu = centroids; 76 pPi = zeros(1, K); 77 pSigma = zeros(D, D, K); 78 79 % hard assign x to each centroids 80 distmat = repmat(sum(X.*X, 2), 1, K) + ... 81 repmat(sum(pMiu.*pMiu, 2)', N, 1) - ... 82 2*X*pMiu'; 83 [dummy labels] = min(distmat, [], 2); 84 85 for k=1:K 86 Xk = X(labels == k, :); 87 pPi(k) = size(Xk, 1)/N; 88 pSigma(:, :, k) = cov(Xk); 89 end 90 end 91 92 function Px = calc_prob() 93 Px = zeros(N, K); 94 for k = 1:K 95 Xshift = X-repmat(pMiu(k, :), N, 1); 96 inv_pSigma = inv(pSigma(:, :, k)); 97 tmp = sum((Xshift*inv_pSigma) .* Xshift, 2); 98 coef = (2*pi)^(-D/2) * sqrt(det(inv_pSigma)); 99 Px(:, k) = coef * exp(-0.5*tmp); 100 end 101 end 102 end
函数返回的 Px 是一个 ![]() 的矩阵,对于每一个
的矩阵,对于每一个 ![]() ,我们只要取该矩阵第
,我们只要取该矩阵第 ![]() 行中最大的那个概率值所对应的那个 Component 为
行中最大的那个概率值所对应的那个 Component 为 ![]() 所属的 cluster 就可以实现一个完整的聚类方法了。
所属的 cluster 就可以实现一个完整的聚类方法了。
参考资料:
【C++代码】
http://www.cppblog.com/Terrile/archive/2011/01/19/120051.html
http://www.autonlab.org/tutorials/gmm.html
http://bubblexc.com/y2011/8/
http://blog.pluskid.org/?p=39&cpage=1#comments