Linux内核设计的艺术-进程1的创建及执行b
代码路径:init/main.c
...
static inline _syscall0(int,fork) // 对应 fork() 函数
static inline _syscall0(int,pause)
static inline _syscall1(int,setup,void *,BIOS)
...
void main(void)
{
sti();
move_to_user_mode();
if (!fork()) { /* we count on this going ok */
init();
}
for(;;) pause();
} 代码路径:include/unistd.h
...
#define __NR_setup 0 /* used only by init, to get system going */
#define __NR_exit 1
#define __NR_fork 2
#define __NR_read 3
#define __NR_write 4
#define __NR_open 5
#define __NR_close 6
...
#define _syscall0(type,name) \
type name(void) \
{ \
long __res; \
第 3 章 进程 1 的创建及执行 83
__asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
: "=a" (__res) \ #把eax的值赋给__res,为进程1的id号(为1)
: "0" (__NR_##name)); \ #_NR_fork为2,赋值给eax
if (__res >= 0) \ #int 0x80中断压入的eip
return (type) __res; \
errno= -__res; \
return -1; \
}
代码路径:kernel/system_call.s
system_call: cmpl $nr_system_calls-1,%eax ja bad_sys_call push %ds push %es push %fs pushl %edx pushl %ecx # push %ebx,%ecx,%edx as parameters pushl %ebx # to the system call movl $0x10,%edx # set up ds,es to kernel space mov %dx,%ds mov %dx,%es movl $0x17,%edx # fs points to local data space mov %dx,%fs call sys_call_table(,%eax,4) #eax为2,每个项为4个字节 pushl %eax #eax为copy_prcess的返回值,为进程号1 movl current,%eax cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state jne reschedule cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter je reschedule ret_from_sys_call: movl current,%eax # task[0] cannot have signals cmpl task,%eax je 3f cmpw $0x0f,CS(%esp) # was old code segment supervisor ? jne 3f cmpw $0x17,OLDSS(%esp) # was stack segment = 0x17 ? jne 3f movl signal(%eax),%ebx movl blocked(%eax),%ecx notl %ecx andl %ebx,%ecx bsfl %ecx,%ecx je 3f btrl %ecx,%ebx movl %ebx,signal(%eax) incl %ecx pushl %ecx call do_signal popl %eax #返回fork时的eax,为进程号1 3: popl %eax popl %ebx popl %ecx popl %edx pop %fs pop %es pop %ds iret代码路径:include/linux/sys.h
...
extern int sys_fork();
...
...
fn_ptr sys_call_table[]={sys_setup, sys_exit, sys_fork, sys_read,//sys_fork 对应 _sys_call_table 的第三项
sys_write, sys_open, sys_close, sys_waitpid, sys_creat, sys_link,
sys_unlink, sys_execve, sys_chdir, sys_time, sys_mknod, sys_chmod,
...
代码路径:kernel/system_call.s
sys_fork:
call find_empty_process
testl %eax,%eax #eax为返回值进程号1
js 1f
push %gs
pushl %esi
pushl %edi
pushl %ebp
pushl %eax #eax为1,copy_process的参数nr
call copy_process #eax为返回值进程号1
addl $20,%esp
1: ret 代码路径:kernel/fork.c
...
long last_pid=0;
...
int find_empty_process(void) // 为新创建的进程找到一个空闲的位置,NR_TASKS 是 64
{
int i;
repeat:
if ((++last_pid)<0) last_pid=1; // 如果 ++ 后 last_pid 溢出,则置 1
for(i=0;i<NR_TASKS;i++) // 现在,+ + 后 last_pid 为 1。找到有效的 last_pid
if (task[i] && task[i]->pid== last_pid) goto repeat;
for(i=1;i<NR_TASKS;i++) // 返回第一个空闲的 i
if (!task[i])
return i;
return -EAGAIN; // EAGAIN 是 11
}
int 0x80中断,中断描述符中的Selector会把cs置成0x8,中断使CPU硬件自动将SS、ESP、EFLAGS、CS、EIP这 5 个寄存器的数值按照这个顺序压入的 init_task 中的进程 0 内核栈,因为tss->ss0=0x10,tss->esp0=PAGE_SIZE+(long)&init_task。
然后又把ds,es,fs,edx,ecx,ebx都放入进程0的内核栈中。
ds,es设置为0x10,fs设置为0x17。标致着已经处于0特权级。
call sys_call_table(,%eax,4)又把long型的数据放入了进程0的内核栈中。
call find_empty_process返回了一个空的进程号,此时为1,eax就是1。
把gs,esi,edi,ebp,eax压入进程0的内核栈中。eax是上面返回的进程号1。
代码路径:kernel/fork.c
...
int copy_mem(int nr,struct task_struct * p)
{
unsigned long old_data_base,new_data_base,data_limit;
unsigned long old_code_base,new_code_base,code_limit;
code_limit=get_limit(0x0f); //界限是640KB
data_limit=get_limit(0x17); //界限是640KB
old_code_base = get_base(current->ldt[1]); //基地址为0
old_data_base = get_base(current->ldt[2]); //基地址为0
if (old_data_base != old_code_base)
panic("We don't support separate I&D");
if (data_limit < code_limit)
panic("Bad data_limit");
new_data_base = new_code_base = nr * 0x4000000; //新的基地址为64MB
p->start_code = new_code_base;
set_base(p->ldt[1],new_code_base); //新的ldt基地址为64MB,界限为640KB,因为没有修改
set_base(p->ldt[2],new_data_base); //新的ldt基地址为64MB,界限为640KB,因为没有修改
if (copy_page_tables(old_data_base,new_data_base,data_limit)) {
printk("free_page_tables: from copy_mem\n");
free_page_tables(new_data_base,data_limit);
return -ENOMEM;
}
return 0;
}
...
int copy_process(int nr,long ebp,long edi,long esi,long gs,long none,
long ebx,long ecx,long edx,
long fs,long es,long ds,
long eip,long cs,long eflags,long esp,long ss)
{
struct task_struct *p;
int i;
struct file *f;
p = (struct task_struct *) get_free_page();//新task_union的首地址
if (!p)
return -EAGAIN;
task[nr] = p; //连接到整体上
*p = *current; /* NOTE! this doesn't copy the supervisor stack */
p->state = TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE; //不可中断状态
p->pid = last_pid; //1
p->father = current->pid; //0
p->counter = p->priority; //15
p->signal = 0;
p->alarm = 0;
p->leader = 0; /* process leadership doesn't inherit */
p->utime = p->stime = 0;
p->cutime = p->cstime = 0;
p->start_time = jiffies;
p->tss.back_link = 0;
p->tss.esp0 = PAGE_SIZE + (long) p;
p->tss.ss0 = 0x10;
p->tss.eip = eip;
p->tss.eflags = eflags;
p->tss.eax = 0;
p->tss.ecx = ecx;
p->tss.edx = edx;
p->tss.ebx = ebx;
p->tss.esp = esp;
p->tss.ebp = ebp;
p->tss.esi = esi;
p->tss.edi = edi;
p->tss.es = es & 0xffff;
p->tss.cs = cs & 0xffff;
p->tss.ss = ss & 0xffff;
p->tss.ds = ds & 0xffff;
p->tss.fs = fs & 0xffff;
p->tss.gs = gs & 0xffff;
p->tss.ldt = _LDT(nr);
p->tss.trace_bitmap = 0x80000000;
if (last_task_used_math == current)
__asm__("clts ; fnsave %0"::"m" (p->tss.i387));
if (copy_mem(nr,p)) {
task[nr] = NULL;
free_page((long) p);
return -EAGAIN;
}
for (i=0; i<NR_OPEN;i++)
if ((f=p->filp[i]))
f->f_count++;
if (current->pwd)
current->pwd->i_count++;
if (current->root)
current->root->i_count++;
if (current->executable)
current->executable->i_count++;
set_tss_desc(gdt+(nr<<1)+FIRST_TSS_ENTRY,&(p->tss));
set_ldt_desc(gdt+(nr<<1)+FIRST_LDT_ENTRY,&(p->ldt));
p->state = TASK_RUNNING; /* do this last, just in case */
return last_pid;
}
...
union task_union {
struct task_struct task;
char stack[PAGE_SIZE];
};
代码路径:mm/memory.c
...
int copy_page_tables(unsigned long from,unsigned long to,long size)
{
unsigned long * from_page_table;
unsigned long * to_page_table;
unsigned long this_page;
unsigned long * from_dir, * to_dir;
unsigned long nr;
if ((from&0x3fffff) || (to&0x3fffff))//必须是4MB的倍数,from为0,to为64MB
panic("copy_page_tables called with wrong alignment");
from_dir = (unsigned long *) ((from>>20) & 0xffc); //from_dir为0
to_dir = (unsigned long *) ((to>>20) & 0xffc);//to_dir为64
size = ((unsigned) (size+0x3fffff)) >> 22;//(640KB+4MB)/4MB=1,size=1
for( ; size-->0 ; from_dir++,to_dir++) {
if (1 & *to_dir)
panic("copy_page_tables: already exist");
if (!(1 & *from_dir))
continue;
from_page_table = (unsigned long *) (0xfffff000 & *from_dir);//*from_dir(页目录项)为1007,经过与运算后,from_page_table(源页表地址)为1000
if (!(to_page_table = (unsigned long *) get_free_page()))//在倒数第二个位置申请一个页面
return -1; /* Out of memory, see freeing */
*to_dir = ((unsigned long) to_page_table) | 7;//把目的页表地址(还有属性)赋值给第16个页目录项(偏移是64,每个占4个字节)
nr = (from==0)?0xA0:1024;
for ( ; nr-- > 0 ; from_page_table++,to_page_table++) {
this_page = *from_page_table;//源页表地址(1000)的内容
if (!(1 & this_page))
continue;
this_page &= ~2;//改变了属性
*to_page_table = this_page;//赋值给目的页表地址(新申请页的首地址)的内容
if (this_page > LOW_MEM) {
*from_page_table = this_page;
this_page -= LOW_MEM;
this_page >>= 12;
mem_map[this_page]++;
}
}
}
invalidate();
return 0;
}
...
在主内存最后取得一页,原进程的task_union首先完整赋值给这一页(新的task_union),状态设置为不可中断状态,pid为1,父进程id为0,时间片为15。
tss->esp0,tss->ss0描述了进程0的堆栈,tss->eip为int 0x80下一句的地址,其他的tss都是保留了int 0x80执行之前的寄存器值,目的是恢复那时候的状态。
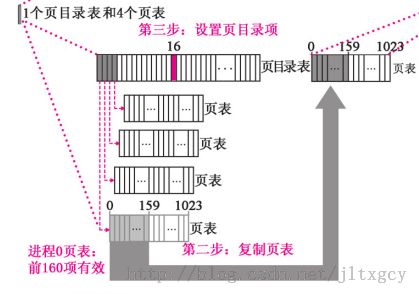
调用copy_mem首先使新的ldt基地址为64MB,界限还是原来设置的640KB,如下图:
调用copy_page_tables,最后形成如下图所示:
第16个页目录存的是新申请页的首地址| 7,即这1024个页表的首地址|7
页表存的是0x0005开始,然后0x1005,0x2005........一共160个
这样,比如线性地址为64MB,那么经过分页机制,得到的物理地址还是0x0首地址
进程1共享进程0的文件,但是所有的p->filp[i],current->pwd,current->root,current->executable均为NULL
最后设置了tss,ldt系统段描述符
然后进程1设置为就绪态,返回进程1的id
addl $20,%esp,跳过gs、esi、edi、ebp、eax
push %eax,把进程1的id号(为1)放入堆栈,1是copy_progress返回last_pid。
cmpl task,%eax je 3f 跳转到3处,依次把堆栈中的值eax(为1),ebx,ecx,edx,fs,es,ds
iret把ss、esp、eflags、cs、eip恢复成原值,从进程0的0特权级又转换到进程0的3特权级
__res为1,所以fork返回1,那么会执行for(;;) pause();
代码路径:kernel/sched.c
...
void schedule(void)
{
int i,next,c;
struct task_struct ** p;
/* check alarm, wake up any interruptible tasks that have got a signal */
for(p = &LAST_TASK ; p > &FIRST_TASK ; --p)
if (*p) {
if ((*p)->alarm && (*p)->alarm < jiffies) {
(*p)->signal |= (1<<(SIGALRM-1));
(*p)->alarm = 0;
}
if (((*p)->signal & ~(_BLOCKABLE & (*p)->blocked)) &&
(*p)->state==TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE)
(*p)->state=TASK_RUNNING;
}
/* this is the scheduler proper: */
while (1) {
c = -1;
next = 0;
i = NR_TASKS;
p = &task[NR_TASKS];
while (--i) {
if (!*--p)
continue;
if ((*p)->state == TASK_RUNNING && (*p)->counter > c)//找出就绪态中,counter 最大的进程
c = (*p)->counter, next = i;
}
if (c) break;
for(p = &LAST_TASK ; p > &FIRST_TASK ; --p)
if (*p)
(*p)->counter = ((*p)->counter >> 1) +
(*p)->priority;
}
switch_to(next);
}
int sys_pause(void)
{
current->state = TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
schedule();
return 0;
}
... 代码路径:include/sched.h
#define switch_to(n) {\
struct {long a,b;} __tmp; \ // 为 ljmp 的 CS、EIP 准备的数据结构
__asm__("cmpl %%ecx,_current\n\t" \
"je 1f\n\t" \ // 如果进程 n 是当前进程,没必要切换,退出
"movw %%dx,%1\n\t" \ //EDX 的低字赋给 *&__tmp.b,即把 CS 赋给 .b
"xchgl %%ecx,_current\n\t" \ //task[n] 与 task[current] 交换
"ljmp %0\n\t" \ // ljmp 到 __tmp,__tmp 中有偏移、段选择符, 但任务门忽略偏移
"cmpl %%ecx,_last_task_used_math\n\t" \// 比较上次是否使用过协处理器
"jne 1f\n\t" \
"clts\n" \ // 清除 CR0 中的切换任务标志
"1:" \
::"m" (*&__tmp.a),"m" (*&__tmp.b), \ //.a 对应 EIP(忽略) ,.b 对应 CS
"d" (_TSS(n)),"c" ((long) task[n]));\//EDX 是 TSS n 的索引号,ECX 即 task[n]
}
pause()的流程和fork差不多,又一次进入进程0的0特权级,并把进程0设置为不可中断状态,找出就绪态中,counter 最大的进程,目前只有进程1处于就绪态,执行ljmp %0\n\t,所以switch到进程1执行,此时把当前寄存器的所有值都保存在进程0的tss中,TR选择器放入的内容是进程1的TSS的选择子,根据得到的基地址和偏移把进程1的tss赋值寄存器(里面有_LDT(2),也就是会放入LDTR选择器),所以现在整个高速缓冲寄存器的内容都更新了(包括LDTR高速缓存寄存器,TR高速缓冲寄存器)。程序从下面if(__res>=0)开始执行,此时处于进程1的3特权级,因为__res为0,所以fork返回0,所以程序开始执行init()
#define _syscall0(type,name) \
int fork(void)
{
long __res;
__asm__ volatile ("int $0x80"
: "=a" (__res)
: "0" (__NR_ fork));
if (__res >= 0) // 现在从这行开始执行,copy_process 为进程 1 做的 tss.eip 就是指向这一行
return (int) __res;
errno= -__res;
return -1;
}
void main(void)
{
...
if (!fork()) {
init();
}
}
进程 1 为安装硬盘文件系统做准备
代码路径:init/main.c
void init(void)
{
...
setup((void *) &drive_info);
...
} 提醒:前面 pause()函数的那个 int 0x80 中断还没有返回,现在setup()又产生了一个中断。
目前处于进程1的3特权级,同样的int 0x80中断,执行到sys_setup()函数,此时处于进程1的0特权级
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/hd.c
...
#define MAX_HD 2
...
struct hd_i_struct {
int head,sect,cyl,wpcom,lzone,ctl;
};
...
struct hd_i_struct hd_info[]= { {0,0,0,0,0,0},{0,0,0,0,0,0} };
...
static struct hd_struct {
long start_sect; // 起始扇区号
long nr_sects; // 总扇区数
} hd[5*MAX_HD]={{0,0},};
...
int sys_setup(void * BIOS) // 对比调用可以看出 BIOS 就是 drive_info,0x90800
{
static int callable= 1;
int i,drive;
unsigned char cmos_disks;
struct partition *p;
struct buffer_head * bh;
if (!callable) // 控制只调用一次
return -1;
callable= 0;
#ifndef HD_TYPE
for (drive=0;drive<2;drive++){// 读取 drive_info 设置 hd_info
hd_info[drive].cyl= *(unsigned short *) BIOS; // 柱面数
hd_info[drive].head= *(unsigned char *) (2 + BIOS); // 磁头数
hd_info[drive].wpcom= *(unsigned short *) (5 + BIOS);
hd_info[drive].ctl= *(unsigned char *) (8 + BIOS);
hd_info[drive].lzone= *(unsigned short *) (12 + BIOS);
hd_info[drive].sect= *(unsigned char *) (14 + BIOS); // 每磁道扇区数
BIOS += 16;
}
if (hd_info[1].cyl) // 判断有几个硬盘
NR_HD=2;
else
NR_HD=1; //此时只有一个硬盘
#endif
// 一个物理硬盘最多可以分 4 个逻辑盘,0 是物理盘,1 ~ 4 是逻辑盘,共 5 个,第 1 个物理盘是 0*5,第 2 个物理盘是 1*5
for (i=0;i<NR_HD;i++) {
hd[i*5].start_sect= 0; //0物理盘的起始扇区
hd[i*5].nr_sects= hd_info[i].head*
hd_info[i].sect*hd_info[i].cyl;//0物理盘的总共扇区数
}
if ((cmos_disks= CMOS_READ(0x12)) & 0xf0) //暂时不看
if (cmos_disks & 0x0f)
NR_HD= 2;
else
NR_HD= 1;
else
NR_HD= 0;
for (i= NR_HD;i < 2;i++) {
hd[i*5].start_sect= 0;
hd[i*5].nr_sects= 0;
}
// 第 1 个物理盘设备号是 0x300,第 2 个是 0x305,读每个物理硬盘的 0 号块,即引导块,有分区信息
for (drive=0;drive<NR_HD;drive++) {
if (!(bh= bread(0x300 + drive*5,0))) {//执行到这里,开始进行调用
printk("Unable to read partition table of drive %d\n\r",
drive);
panic("");
}
...
}
... 下面开始执行bread(0x300 + drive*5,0),设备号为0x300,块号为0,一个块是两个扇区,共1024个字节
代码路径:fs/buffer.c
...
struct buffer_head * hash_table[NR_HASH];
static struct buffer_head * free_list;
...
static inline void wait_on_buffer(struct buffer_head * bh)
{
cli();
while (bh->b_lock)
sleep_on(&bh->b_wait);
sti();
}
...
#define _hashfn(dev,block) (((unsigned)(dev^block))%NR_HASH) //NR_HASH=307
#define hash(dev,block) hash_table[_hashfn(dev,block)]
static struct buffer_head * find_buffer(int dev, int block)
{
struct buffer_head * tmp;
for (tmp = hash(dev,block) ; tmp != NULL ; tmp = tmp->b_next)//因为hash值会重复,所以会有b_next,此时返回NULL
if (tmp->b_dev==dev && tmp->b_blocknr==block)
return tmp;
return NULL;
}
/*
* Why like this, I hear you say... The reason is race-conditions.
* As we don't lock buffers (unless we are readint them, that is),
* something might happen to it while we sleep (ie a read-error
* will force it bad). This shouldn't really happen currently, but
* the code is ready.
*/
struct buffer_head * get_hash_table(int dev, int block)
{
struct buffer_head * bh;
for (;;) {
if (!(bh=find_buffer(dev,block)))
return NULL;
bh->b_count++;
wait_on_buffer(bh);
if (bh->b_dev == dev && bh->b_blocknr == block)
return bh;
bh->b_count--;
}
}
...
#define BADNESS(bh) (((bh)->b_dirt<<1)+(bh)->b_lock)
struct buffer_head * getblk(int dev,int block)
{
struct buffer_head * tmp, * bh;
repeat:
if ((bh = get_hash_table(dev,block)))//根据dev,block在hash_table中找缓冲区,此时没有找到
return bh;
tmp = free_list;
do {
if (tmp->b_count) //不执行
continue;
if (!bh || BADNESS(tmp)<BADNESS(bh)) {
bh = tmp; //buffer_head第一个指针
if (!BADNESS(tmp)) //此时为真
break; //跳出循环
}
/* and repeat until we find something good */
} while ((tmp = tmp->b_next_free) != free_list);
if (!bh) { //此时不执行
sleep_on(&buffer_wait);
goto repeat;
}
wait_on_buffer(bh);
if (bh->b_count) //此时不执行
goto repeat;
while (bh->b_dirt) { //此时不执行
sync_dev(bh->b_dev);
wait_on_buffer(bh);
if (bh->b_count)
goto repeat;
}
/* NOTE!! While we slept waiting for this block, somebody else might */
/* already have added "this" block to the cache. check it */
if (find_buffer(dev,block)) //此时不执行
goto repeat;
/* OK, FINALLY we know that this buffer is the only one of it's kind, */
/* and that it's unused (b_count=0), unlocked (b_lock=0), and clean */
bh->b_count=1; //数量变成1
bh->b_dirt=0; //没有被用
bh->b_uptodate=0; //没有更新
remove_from_queues(bh); //把它在buffer_head链表中移除,并把free_list头指针指向第二个buffer_head
bh->b_dev=dev; //设备号0x300
bh->b_blocknr=block; //扇区0
insert_into_queues(bh); //把刚才的buffer_head放在buffer_head链表的末尾,hash_table[157]中存放着它的地址,下次就能通过hash值找到它了
return bh;
}
...
/*
* bread() reads a specified block and returns the buffer that contains
* it. It returns NULL if the block was unreadable.
*/
struct buffer_head * bread(int dev,int block)
{
struct buffer_head * bh;
if (!(bh=getblk(dev,block)))
panic("bread: getblk returned NULL\n");
if (bh->b_uptodate) //此时不执行
return bh;
ll_rw_block(READ,bh);
wait_on_buffer(bh);
if (bh->b_uptodate)
return bh;
brelse(bh);
return NULL;
}
getblk通过dev,block首先在hash_table寻找合适的buffer_head,但是没有找到,所以就首先申请了第一个buffer_head,并把它在buffer_head链表移除,让free_head头指针指向了第二个buffer_head,然后把它添到buffer_head链表的末尾,并让hash_table[157]存放这个buffer_head的地址。
找到了缓冲块后,开始执行ll_rw_block(READ,bh)
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/ll_rw_block.c
...
struct request request[NR_REQUEST];
...
static inline void lock_buffer(struct buffer_head * bh)
{
cli();
while (bh->b_lock)
sleep_on(&bh->b_wait);
bh->b_lock=1;//上锁了
sti();
}
...
static void add_request(struct blk_dev_struct * dev, struct request * req)
{
struct request * tmp;
req->next = NULL;
cli();
if (req->bh)
req->bh->b_dirt = 0;
if (!(tmp = dev->current_request)) {
dev->current_request = req;//挂载到这里
sti();
(dev->request_fn)();//调用do_hd_request()函数
return;
}
for ( ; tmp->next ; tmp=tmp->next)
if ((IN_ORDER(tmp,req) ||
!IN_ORDER(tmp,tmp->next)) &&
IN_ORDER(req,tmp->next))
break;
req->next=tmp->next;
tmp->next=req;
sti();
}
static void make_request(int major,int rw, struct buffer_head * bh)
{
struct request * req;
int rw_ahead;
/* WRITEA/READA is special case - it is not really needed, so if the */
/* buffer is locked, we just forget about it, else it's a normal read */
if ((rw_ahead = (rw == READA || rw == WRITEA))) { //此时不执行
if (bh->b_lock)
return;
if (rw == READA)
rw = READ;
else
rw = WRITE;
}
if (rw!=READ && rw!=WRITE)
panic("Bad block dev command, must be R/W/RA/WA");
lock_buffer(bh);//上锁
if ((rw == WRITE && !bh->b_dirt) || (rw == READ && bh->b_uptodate)) {//此时不执行
unlock_buffer(bh);
return;
}
repeat:
/* we don't allow the write-requests to fill up the queue completely:
* we want some room for reads: they take precedence. The last third
* of the requests are only for reads.
*/
if (rw == READ)
req = request+NR_REQUEST;//在请求项最末尾开始申请
else
req = request+((NR_REQUEST*2)/3);
/* find an empty request */
while (--req >= request)
if (req->dev<0) //此时申请的是最末尾的请求项
break;
/* if none found, sleep on new requests: check for rw_ahead */
if (req < request) { //此时不执行
if (rw_ahead) {
unlock_buffer(bh);
return;
}
sleep_on(&wait_for_request);
goto repeat;
}
/* fill up the request-info, and add it to the queue */
req->dev = bh->b_dev;
req->cmd = rw;
req->errors=0;
req->sector = bh->b_blocknr<<1;//起始扇区,块号转成扇区号(1块=2扇区)
req->nr_sectors = 2; //本次请求要读的扇区数
req->buffer = bh->b_data;
req->waiting = NULL;
req->bh = bh;
req->next = NULL;
add_request(major+blk_dev,req);//major为3
}
void ll_rw_block(int rw, struct buffer_head * bh)
{
unsigned int major;
if ((major=MAJOR(bh->b_dev)) >= NR_BLK_DEV || //major为3
!(blk_dev[major].request_fn)) { //为do_hd_request这个函数
printk("Trying to read nonexistent block-device\n\r");
return;
}
make_request(major,rw,bh);
}
...
代码路径:include/linux/fs.h
#define MAJOR(a) (((unsigned)(a))>>8)
ll_rw_block,调用make_request,利用bh来填充req,调用add_request,用req来填充dev,最后调用了do_hd_request()函数
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/hd.c
...
void do_hd_request(void)
{
int i,r;
unsigned int block,dev;
unsigned int sec,head,cyl;
unsigned int nsect;
INIT_REQUEST;
dev= MINOR(CURRENT->dev); //为0
block= CURRENT->sector; //起始扇区
if (dev >= 5*NR_HD || block + 2 > hd[dev].nr_sects) { //判断是否越界
end_request(0);
goto repeat;
}
block += hd[dev].start_sect;
dev /= 5;
__asm__("divl %4":"=a" (block),"=d" (sec):"0" (block),"1" (0),//根据block和dev计算出扇区号(sec),柱面号(cyl),磁头号(head)
"r" (hd_info[dev].sect));
__asm__("divl %4":"=a" (cyl),"=d" (head):"0" (block),"1" (0),
"r" (hd_info[dev].head);
sec++; //扇区号(sec+1)
nsect= CURRENT->nr_sectors;//本次要读的扇区数
if (reset) {
reset= 0; // 置位,防止多次执行 if (reset)
recalibrate= 1; // 置位,确保执行下面的 if(recalibrate)
reset_hd(CURRENT_DEV);// 将通过调用 hd_out 向硬盘发送 WIN_SPECIFY 命令,建立硬盘
// 读盘必要的参数
return;
}
if (recalibrate) {
recalibrate= 0; // 置位,防止多次执行 if (recalibrate)
hd_out(dev,hd_info[CURRENT_DEV].sect,0,0,0,
WIN_RESTORE,&recal_intr); // 将向硬盘发送 WIN_RESTORE 命令,将磁头移动到
//0 柱面,以便从硬盘上读取数据
return;
}
if (CURRENT->cmd== WRITE) {
hd_out(dev,nsect,sec,head,cyl,WIN_WRITE,&write_intr);
for(i=0;i<3000 && !(r=inb_p(HD_STATUS)&DRQ_STAT);i++)
/* nothing */ ;
if (!r) {
bad_rw_intr();
goto repeat;
}
port_write(HD_DATA,CURRENT->buffer,256);
} else if (CURRENT->cmd== READ) {
hd_out(dev,nsect,sec,head,cyl,WIN_READ,&read_intr); // 注意这两个参数
} else
panic("unknown hd-command");
}
...
代码路径:include/linux/fs.h
#define MINOR(a) ((a)&0xff)代码路径:kernel/blk_drv/blk.h
#define CURRENT (blk_dev[MAJOR_NR].current_request) //此时MAJOR_NR为3代码路径: kernel/blk_dev/hd.c
static void hd_out(unsigned int drive,unsigned int nsect,unsigned int sect,
unsigned int head,unsigned int cyl,unsigned int cmd,
void (*intr_addr)(void)) // 对比调用的传参 WIN_READ,&read_intr
{
register int port asm("dx");
if (drive>1 || head>15)
panic("Trying to write bad sector");
if (!controller_ready())
panic("HD controller not ready");
do_hd= intr_addr; // 根据调用的实参决定是 read_intr 还是 write_intr,现在是 read_intr
outb_p(hd_info[drive].ctl,HD_CMD);
port=HD_DATA;
outb_p(hd_info[drive].wpcom>>2,++port);
outb_p(nsect,++port);
outb_p(sect,++port);
outb_p(cyl,++port);
outb_p(cyl>>8,++port);
outb_p(0xA0|(drive<<4)|head,++port);
outb(cmd,++port);
}
此时开始了读硬盘的操作,把指定硬盘中的内容读入了硬盘缓冲区,每读一个扇区,就发出一个硬盘中断。
bread函数继续执行,执行到wait_on_buffer
代码路径:fs/buffer.c
static inline void wait_on_buffer(struct buffer_head * bh)
{
cli();
while (bh->b_lock) //前面已经加锁
sleep_on(&bh->b_wait);
sti();
}
代码路径:kernel/sched.c
void sleep_on(struct task_struct **p)
{
struct task_struct *tmp;
if (!p)
return;
if (current== &(init_task.task))
panic("task[0] trying to sleep");
tmp= *p;//目前为NULL,tmp为NULL
*p= current; //进程1的地址放置在bh->b_wait
current->state= TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE;//进程1设置成不可中断状态
schedule();
if (tmp)
tmp->state=0;
}
schedule函数因为此时没有就绪态的进程,系统switch_to 0,切换到进程0的0特权级(还记得么)
代码路径:kernel/sched.h
#define switch_to(n) {\
struct {long a,b;} __tmp;
__asm__("cmpl %%ecx,_current\n\t" \
"je 1f\n\t" \
"movw %%dx,%1\n\t" \
"xchgl %%ecx,_current\n\t" \
"ljmp %0\n\t" \
"cmpl %%ecx,_last_task_used_math\n\t"\// 从这一行开始执行,此时是进程 0 在执行,0 特权级
"jne 1f\n\t" \
"clts\n" \
"1:" \
::"m" (*&__tmp.a),"m" (*&__tmp.b), \
"d" (_TSS(n)),"c" ((long) task[n])); \
} 进程0循环执行,for(;;) pause(); 当再一次遇到switch_to 0时,cmpl %%ecx,_current\n\t" ,相等,则不调度,所以进程0一致在
for(;;) pause()循环,有可能是进程0的0特权级,也可能是进程0的3特权级。
可能执行到上面循环pause( )、sys_pause( )、schedule( )、switch_to (n) 的任何一句,硬盘已经把一个扇区读入到了硬盘缓冲区,发出中断
代码路径:kernel/system_call.s
...
_hd_interrupt:
pushl %eax // 保存 CPU 的状态
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0xA0
jmp 1f
1: jmp 1f
1: xorl %edx,%edx
xchgl _do_hd,%edx //就是上面的read_intr
testl %edx,%edx
jne 1f
movl $_unexpected_hd_interrupt,%edx
1: outb %al,$0x20
call *%edx //执行read_intr
... 中断时候把cs,eip,ss,esp,eflag压入堆栈(不同特权级有不同的堆栈),cs已经被设置为0x08,因为中断符中seletor是0x08,其他选择器也重新置数
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs 这样中断程序是在0特权级执行的,开始执行read_intr
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/hd.c
static void read_intr(void)
{
if (win_result()) {
bad_rw_intr();
do_hd_request();
return;
}
port_read(HD_DATA,CURRENT->buffer,256);//把刚读入硬盘缓冲区的512个字节放入buffer中,其实req->buffer = bh->data
CURRENT->errors= 0;
CURRENT->buffer += 512; //buffer向后移了512个字节
CURRENT->sector++; //其实扇区加1
if (--CURRENT->nr_sectors) {
do_hd= &read_intr;
return;
}
end_request(1);
do_hd_request();
}
接着pause( )、sys_pause( )、schedule( )、switch_to(0)循环从刚才硬盘中断打断的地方继续循环,硬盘继续读盘......
又过了一段时间后,硬盘剩下的那一半数据也读完了,硬盘产生中断,读盘中断服务程序再次响应这个中断,进入 read_intr( ) 函数后,仍然会判断请求项对应的缓冲块的数据是否读完了,--CURRENT->nr_sectors,此时已经读完了,执行end_request(1)
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/blk.h
extern inline void end_request(int uptodate)
{
DEVICE_OFF(CURRENT->dev);
if (CURRENT->bh) {
CURRENT->bh->b_uptodate= uptodate; // uptodate 是参数,为 1
unlock_buffer(CURRENT->bh); //解锁
}
if (!uptodate) {
printk(DEVICE_NAME " I/O error\n\r");
printk("dev %04x, block %d\n\r",CURRENT->dev,
CURRENT->bh->b_blocknr);
}
wake_up(&CURRENT->waiting);
wake_up(&wait_for_request);
CURRENT->dev= -1;
CURRENT= CURRENT->next;
}
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/blk.h
extern inline void unlock_buffer(struct buffer_head * bh)
{
if (!bh->b_lock)
printk(DEVICE_NAME ": free buffer being unlocked\n");
bh->b_lock=0; //解锁
wake_up(&bh->b_wait);
} 代码路径:kernel/sched.c
void wake_up(struct task_struct **p)
{
if (p && *p) {
(**p).state=0; // 设置为就绪态
*p=NULL; //没有等待的进程
}
}
接着pause( )、sys_pause( )、schedule( )、switch_to(0)循环从刚才硬盘中断打断的地方继续循环,执行到schedule的时候,现在只有进程1处于就绪态,切换回进程1的0特权级,进程1是从"ljmp %0\n\t"\切换走的,所以现在执行它的下一行。现在,返回切换的发起者sleep_on()函数中,并最终返回bread()函数中。
代码路径:fs/buffer.c
struct buffer_head * bread(int dev,int block)
{
struct buffer_head * bh;
if (!(bh=getblk(dev,block)))
panic("bread: getblk returned NULL\n");
if (bh->b_uptodate)
return bh;
ll_rw_block(READ,bh);
wait_on_buffer(bh);
if (bh->b_uptodate)
return bh;
brelse(bh);
return NULL;
}
此时bh->b_uptodate为1,返回bh,接着返回sys_setup
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/hd.c
int sys_setup(void * BIOS)
{
...
for (drive=0;drive<NR_HD;drive++) {
if (!(bh= bread(0x300 + drive*5,0))) {
printk("Unable to read partition table of drive %d\n\r",
drive);
panic("");
}
if (bh->b_data[510]!= 0x55||(unsigned char) // 我们假设引导块的数据没问题
bh->b_data[511]!= 0xAA) {
printk("Bad partition table on drive %d\n\r",drive);
panic("");
}
p= 0x1BE + (void *)bh->b_data; // 根据引导块中的分区信息设置 hd[]
for (i=1;i<5;i++,p++) {
hd[i + 5*drive].start_sect= p->start_sect;
hd[i + 5*drive].nr_sects= p->nr_sects;
}
brelse(bh); // 释放缓冲块(引用计数减 1)
}
if (NR_HD)
printk("Partition table%s ok.\n\r",(NR_HD>1)?"s":"");
rd_load();
mount_root();
return (0);
}
下面开始执行rd_load,注意此时bread是从软盘中读,而不是从硬盘中读,原理一样
代码路径:kernel/blk_dev/ramdisk.c
void rd_load(void)
{
struct buffer_head *bh;
struct super_block s;
int block= 256; /* Start at block 256 */
int I= 1;
int nblocks;
char *cp; /* Move pointer */
if (!rd_length)
return;
printk("Ram disk: %d bytes, starting at 0x%x\n", rd_length,
(int) rd_start);
if (MAJOR(ROOT_DEV) != 2) // 如果根设备不是软盘
return;
bh= breada(ROOT_DEV,block + 1,block,block + 2,-1);//从软盘中读257块,同时预读入256,258块
if (!bh) {
printk("Disk error while looking for ramdisk!\n");
return;
}
*((struct d_super_block *) &s)= *((struct d_super_block *) bh->b_data);//把数据放入超级块
brelse(bh); //释放缓冲区
if (s.s_magic != SUPER_MAGIC) // 如果不等,说明不是 minix 文件系统
/* No ram disk image present, assume normal floppy boot */
return;
nblocks= s.s_nzones << s.s_log_zone_size; // 算出虚拟盘的块数
if (nblocks > (rd_length >> BLOCK_SIZE_BITS)) {
printk("Ram disk image too big! (%d blocks, %d avail)\n",
nblocks, rd_length >> BLOCK_SIZE_BITS);
return;
}
printk("Loading %d bytes into ram disk... 0000k",
nblocks << BLOCK_SIZE_BITS);
cp= rd_start;
while (nblocks) { // 将软盘上准备格式化用的根文件系统复制到虚拟盘上
if (nblocks > 2)
bh= breada(ROOT_DEV, block, block + 1, block + 2, -1);//多于两块,采用提前读的方式
else
bh= bread(ROOT_DEV, block);//少于两块,只读一块
if (!bh) {
printk("I/O error on block %d, aborting load\n",
block);
return;
}
(void) memcpy(cp, bh->b_data, BLOCK_SIZE);
brelse(bh);//b_count减一,释放缓冲区
printk("\010\010\010\010\010%4dk",i);
cp += BLOCK_SIZE; //虚拟盘开始地址每次加1024
block++;//从256块开始加
nblocks--;//总共读取的块数减少,每块1024个字节
i++;
}
printk("\010\010\010\010\010done \n");
ROOT_DEV=0x0101;//根设备为虚拟盘
}
超级块(软盘中的257块)先读入到缓冲区,根据该信息算出虚拟盘的块数。再把从软盘256块开始(以256+虚拟盘块数结束),把软盘中的内容移动到内存虚拟盘,并设置虚拟盘为根设备。
下面执行sys_setup中的mount_root函数
代码路径:fs/super.c
...
struct super_block super_block[NR_SUPER];
...
void mount_root(void)
{
int i,free;
struct super_block * p;
struct m_inode * mi;
if (32 != sizeof (struct d_inode))
panic("bad i-node size");
for(i=0;i<NR_FILE;i++)
file_table[i].f_count=0;
if (MAJOR(ROOT_DEV) == 2) {
printk("Insert root floppy and press ENTER");
wait_for_keypress();
}
for(p = &super_block[0] ; p < &super_block[NR_SUPER] ; p++) {
p->s_dev = 0;
p->s_lock = 0;
p->s_wait = NULL;
}
...
} 代码路径:include/linux/fs.h
struct super_block {
unsigned short s_ninodes;
unsigned short s_nzones;
unsigned short s_imap_blocks;
unsigned short s_zmap_blocks;
unsigned short s_firstdatazone;
unsigned short s_log_zone_size;
unsigned long s_max_size;
unsigned short s_magic;
/* These are only in memory */
struct buffer_head * s_imap[8];
struct buffer_head * s_zmap[8];
unsigned short s_dev;
struct m_inode * s_isup;
struct m_inode * s_imount;
unsigned long s_time;
struct task_struct * s_wait;
unsigned char s_lock;
unsigned char s_rd_only;
unsigned char s_dirt;
};
初始化super_block[NR_SUPER]
代码路径:fs/super.c
void mount_root(void)
{
...
for(p = &super_block[0] ; p < &super_block[NR_SUPER] ; p++) {
p->s_dev = 0;
p->s_lock = 0;
p->s_wait = NULL;
}
if (!(p=read_super(ROOT_DEV)))
panic("Unable to mount root");
...
} 代码路径:fs/super.c
static struct super_block * read_super(int dev)
{
struct super_block * s;
struct buffer_head * bh;
int i,block;
if (!dev)
return NULL;
check_disk_change(dev);
if ((s = get_super(dev)))//获取不到
return s;
for (s = 0+super_block ;; s++) {
if (s >= NR_SUPER+super_block)
return NULL;
if (!s->s_dev)//因为刚刚初始化,第一个就是空
break;
}
s->s_dev = dev;//第一个超级块,dev为虚拟盘0x101
s->s_isup = NULL;
s->s_imount = NULL;
s->s_time = 0;
s->s_rd_only = 0;
s->s_dirt = 0;
lock_super(s);//锁定超级块
if (!(bh = bread(dev,1))) {//把虚拟盘超级块的数据读到缓冲区中,本质是从内存到内存,第2块
s->s_dev=0;
free_super(s);
return NULL;
}
*((struct d_super_block *) s) =
*((struct d_super_block *) bh->b_data);//把缓冲区的数据读到内存超级块中
brelse(bh); //释放缓冲区
if (s->s_magic != SUPER_MAGIC) {
s->s_dev = 0;
free_super(s);
return NULL;
}
for (i=0;i<I_MAP_SLOTS;i++) //为8,初始化
s->s_imap[i] = NULL;
for (i=0;i<Z_MAP_SLOTS;i++) //为8,初始化
s->s_zmap[i] = NULL;
block=2;
for (i=0 ; i < s->s_imap_blocks ; i++) //i节点位图总共的块数已经保存在数据结构中了(虚拟盘超级块的数据)
if ((s->s_imap[i]=bread(dev,block)))//加载i节点位图,从第3块开始
block++;
else
break;
for (i=0 ; i < s->s_zmap_blocks ; i++)
if ((s->s_zmap[i]=bread(dev,block)))//加载逻辑块位图,从i节点结束的块开始
block++;
else
break;
if (block != 2+s->s_imap_blocks+s->s_zmap_blocks) {//如果此时的块数不是2 + i节点位图块数 + 逻辑块位图块数,则报错
for(i=0;i<I_MAP_SLOTS;i++)
brelse(s->s_imap[i]);
for(i=0;i<Z_MAP_SLOTS;i++)
brelse(s->s_zmap[i]);
s->s_dev=0;
free_super(s);
return NULL;
}
s->s_imap[0]->b_data[0] |= 1;//i节点位图第一个字节的最后一个位 置为1
s->s_zmap[0]->b_data[0] |= 1;//逻辑块位图第一个字节的最后一个位 置为1
free_super(s);//解锁
return s;
} 如下图:

read_supe,把虚拟盘超级块信息赋给了内存super_block[0]。又把虚拟盘i节点位图,逻辑块位图的信息赋给了s_imap[8],s_zmap[8],如下图
代码路径:fs/super.c
void mount_root(void)
{
...
if (!(mi=iget(ROOT_DEV,ROOT_INO))) //ROOT_INO为1
panic("Unable to read root i-node");
...
} 代码路径:fs/inode.c
...
struct m_inode inode_table[NR_INODE]={{0,},};NR_INODE为32
...
struct m_inode * iget(int dev,int nr)
{
struct m_inode * inode, * empty;
if (!dev)
panic("iget with dev==0");
empty = get_empty_inode();//获取了第一个inode,也就是inode_table中第一个元素,i_count=1
inode = inode_table;
while (inode < NR_INODE+inode_table) {
if (inode->i_dev != dev || inode->i_num != nr) {
inode++;
continue;//此时一直continue,没有向下执行
}
wait_on_inode(inode);
if (inode->i_dev != dev || inode->i_num != nr) {
inode = inode_table;
continue;
}
inode->i_count++;
if (inode->i_mount) {
int i;
for (i = 0 ; i<NR_SUPER ; i++)
if (super_block[i].s_imount==inode)
break;
if (i >= NR_SUPER) {
printk("Mounted inode hasn't got sb\n");
if (empty)
iput(empty);
return inode;
}
iput(inode);
dev = super_block[i].s_dev;
nr = ROOT_INO;
inode = inode_table;
continue;
}
if (empty)
iput(empty);
return inode;
}
if (!empty)
return (NULL);
inode=empty;
inode->i_dev = dev;//虚拟盘0x101
inode->i_num = nr;//1
read_inode(inode);
return inode;
} 代码路径:fs/inode.c
static void read_inode(struct m_inode * inode)
{
...
lock_inode(inode); // 锁定 inode
if (!(sb=get_super(inode->i_dev))) // 获得 inode 所在设备的超级块,就是上面的内存超级块
...
block= 2 + sb->s_imap_blocks + sb->s_zmap_blocks +
(inode->i_num-1)/INODES_PER_BLOCK;
if (!(bh=bread(inode->i_dev,block))) // 读 inode 所在逻辑块进缓冲块,整个块读入了
panic("unable to read i-node block");
*(struct d_inode *)inode= // 只复制对应的i节点数据到inode
((struct d_inode *)bh->b_data)
[(inode->i_num-1)%INODES_PER_BLOCK];
brelse(bh); // 释放缓冲块
unlock_inode(inode); // 解锁
}
将虚拟盘根节点读到内存inode(inode_table第一个元素)
void mount_root(void)
{
...mi->i_count += 3 ;//i_count=4
p->s_isup = p->s_imount = mi;
current->pwd = mi;
current->root = mi;
free=0;
i=p->s_nzones;
while (-- i >= 0)
if (!set_bit(i&8191,p->s_zmap[i>>13]->b_data))
free++;
printk("%d/%d free blocks\n\r",free,p->s_nzones);
free=0;
i=p->s_ninodes+1;
while (-- i >= 0)
if (!set_bit(i&8191,p->s_imap[i>>13]->b_data))
free++;
printk("%d/%d free inodes\n\r",free,p->s_ninodes);
} 将根节点挂载到 super_block[0] 的 s_isup 、s_imount 指针上
当前进程1的pwd,root也指向这个根i节点
sys_setup执行结束,返回到ret_from_sys_call
...
ret_from_sys_call:
movl _current,%eax # task[0] cannot have signals
cmpl _task,%eax
je 3f
cmpw $0x0f,CS(%esp) # was old code segment supervisor ?
jne 3f
cmpw $0x17,OLDSS(%esp) # was stack segment= 0x17 ?
jne 3f
movl signal(%eax),%ebx # 下面是取信号位图...
movl blocked(%eax),%ecx
notl %ecx
andl %ebx,%ecx
bsfl %ecx,%ecx
je 3f
btrl %ecx,%ebx
movl %ebx,signal(%eax)
incl %ecx
pushl %ecx
call _do_signal # 调用 do_signal()
popl %eax
3: popl %eax
popl %ebx
popl %ecx
popl %edx
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
iret
现在,当前进程(进程 1)并没有接收到信号,调用 do_signal( ) 函数并没有实际的意义。
此时返回进程1的3特权级,见如下代码,路径init/main.c
void init(void)
{
...
int pid,i;
setup((void *) &drive_info);
(void) open("/dev/tty0",O_RDWR,0);
(void) dup(0);
(void) dup(0);
printf("%d buffers= %d bytes buffer space\n\r",NR_BUFFERS,
NR_BUFFERS*BLOCK_SIZE);
...
}
以后的执行,请看下篇文章分析。