Android控件之ListView
ListView是Android中最常用的控件之一. ListView中一个重要的概念就是适配器(Adapter),它是控件与数据源之间的桥梁.
常见的数据源有数组/集合(Array/List),游标(Cursor).
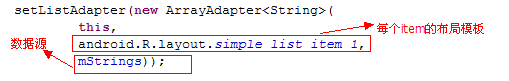
1, 从数组中获取数据:
运行结果:
2, 从Cursor中获取数据:
// Get a cursor with all people
Cursor c = getContentResolver().query(People.CONTENT_URI, null, null, null, null);
startManagingCursor(c);//使用的cursor的生命周期随Activity生命周期变化而变化.
ListAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
// Use a template that displays a text view
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,
// Give the cursor to the list adatper
c,
// Map the NAME column in the people database to...
new String[] {People.NAME} ,
// The "text1" view defined in the XML template
new int[] {android.R.id.text1});
setListAdapter(adapter);
3, 使用自定义Adapter
private class SpeechListAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
public SpeechListAdapter(Context context) {
mContext = context;
}
public int getCount() {
return mTitles.length;
}
public Object getItem(int position) {//每个条目对应的对象
return position;
}
public long getItemId(int position) {//每个条目的id
return position;
}
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {//ListView每个item对应的view
SpeechView sv;
if (convertView == null) {
sv = new SpeechView(mContext, mTitles[position],
mDialogue[position]);
} else {
sv = (SpeechView) convertView;
sv.setTitle(mTitles[position]);
sv.setDialogue(mDialogue[position]);
}
return sv;
}
} 结果:
一些ListView效果
1, 带有分隔符的ListView.
效果所下图所示(红框表示的是分隔条):
private class MyListAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
public MyListAdapter(Context context) {
mContext = context;
}
public int getCount() {
return mStrings.length;
}
@Override
public boolean areAllItemsEnabled() {//是否所有的item都可点击和选中
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled(int position) {//如果字符串是以"-"开头,那么对应的item为分隔item
return !mStrings[position].startsWith("-");
}
public Object getItem(int position) {
return position;
}
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
TextView tv;
if (convertView == null) {
tv = (TextView) LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(
android.R.layout.simple_expandable_list_item_1, parent, false);
} else {
tv = (TextView) convertView;
}
tv.setText(mStrings[position]);
return tv;
}
private Context mContext;
}
2, 带收缩和展开效果的ListView
效果如下图所示:
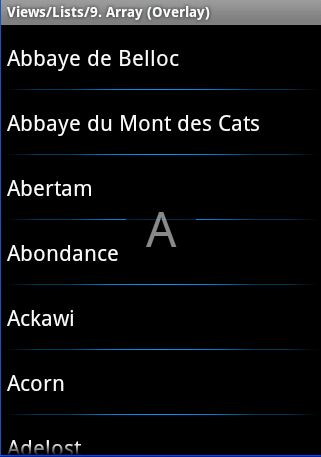
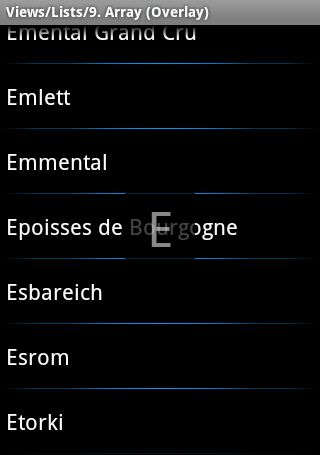
3 ,类似带悬浮字母效果的ListView(类似通讯录导航的效果 )
如下图所示
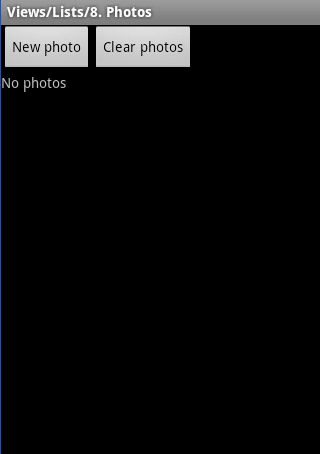
下面来演示notifyDataSetChanged()方法的作用:
每次添加图片的时候都notifyDataSetChanged(),也就是数据源改变了执行notifyDataSetChanged(),可以刷新界面.
ListView效率问题.
我们知道一个item的显示都会调用getView()方法,并且在不停的滑动时候也会不停的调用.
下面来看一下延迟加载的效果:在不停滑动的时候用"Loading"作为显示文本,当停止滑动显示真实的文本.
优化Adapter,提高ListView执行效率.
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// A ViewHolder keeps references to children views to avoid unneccessary calls
// to findViewById() on each row.
ViewHolder holder;
// When convertView is not null, we can reuse it directly, there is no need
// to reinflate it. We only inflate a new View when the convertView supplied
// by ListView is null.
if (convertView == null) {//当有老的item view的时候借用老的view,这样避免每次都去解析xml
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item_icon_text, null);
// Creates a ViewHolder and store references to the two children views
// we want to bind data to.
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.text = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.text);
holder.icon = (ImageView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.icon);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
// Get the ViewHolder back to get fast access to the TextView
// and the ImageView.
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
// Bind the data efficiently with the holder.
holder.text.setText(DATA[position]);
holder.icon.setImageBitmap((position & 1) == 1 ? mIcon1 : mIcon2);
return convertView;
}
static class ViewHolder {
TextView text;
ImageView icon;
}
这样做的好处有:
1>重用了 convertView,避免当不需要解析xml文件的时候去解析xml,填充视图.
2>使用ViewHolder避免当不需要的时候调用findViewById()方法.
欢迎转载,http://blog.csdn.net/johnny901114/article/details/7867934