STL容器之multimap和multiset
map和set容器中,一个键只对应一个实例。而在multimap和multiset中,一个键可以对应多个实例,例如每个人都有一个电话联系人列表,列表中肯定不止一个人。
除了不能对multimap中元素调用下表操作符之外,multimap和multiset提供的操作与map和set相同。但是因multimap和multiset是一个键对应多个元素,所有对应操作有一些改变,对于multimap和multiset中的某个键,要处理多个值得准备。
在multimap和multiset中insert一个元素时总会插入元素,因为一个键可对应多个值。
multimap提供的操作列出如下:
begin() 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回一个元素出现的次数
empty() 如果multimap为空则返回真
end() 返回一个指向multimap末尾的迭代器
equal_range() 返回指向元素的key为指定值的迭代器对
erase() 删除元素
find() 查找元素
get_allocator() 返回multimap的配置器
insert() 插入元素
key_comp() 返回比较key的函数
lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
rbegin() 返回一个指向mulitmap尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向multimap头部的逆向迭代器
size() 返回multimap中元素的个数
swap() 交换两个multimaps
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
multiset提供的操作与multimap完全相同。
本文将只以multimap为例。
本文中将着重介绍lower_bound(),upper_bound()和equal_range()三个函数,其他函数的用法在我的其他《STL容器之。。。》都有过介绍,如想了解可参照之。
m.lower_bound():返回一个迭代器,指向键值不小于k的第一个元素
m.upper_bound():返回一个迭代器,指向键值不大于k的第一个元素
m.equal_range():返回一个迭代器的pair对象,它的first成员等价于m.lower_bound(k),second成员等价于m.upper_bound(k)。
这三个函数主要用来处理每个键所对应的所有值,因为lower_bound和upper_bound构成一个范围,分别指向k对应的第一个元素,和k对应的最后一个元素的下一个位置。
下面举个例子,该例子功能是找到每个作者对应的书名并输出,这个例子将通过三种方式实现,以便读者可以比较一下lower_bound(),upper_bound()
和equal_range()三个函数的用法和好处。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//定义作者名数组
string authors[] = {"Stanley B.Lippman", "Scott Meyers"};
//定义作者名-书名multimap
multimap<string, string> auth_books;
//向auth_books中插入信息
auth_books.insert(make_pair(authors[0], string("c++ primer")));
auth_books.insert(make_pair(authors[0], string("essential c++")));
auth_books.insert(make_pair(authors[1], string("effective c++")));
auth_books.insert(make_pair(authors[1], string("more effective c++")));
auth_books.insert(make_pair(authors[1], string("effective stl")));
/****************************************************/
//第一种方式,使用find和count查找作者对应的书名信息并输出
cout << "========================" << endl;
typedef multimap<string, string>::size_type sz_type;
sz_type num = auth_books.count(authors[0]);
multimap<string, string>::iterator it = auth_books.find(authors[0]);
//因为在multimap和multiset中具有相同键的元素相邻存放,所以可通过迭代器依次访问
//输出查找结果
for (sz_type cnt = 0; cnt != num; ++cnt, ++it)
cout << it->second << endl;
cout << "========================" << endl;
/***************************************************/
//第二种方式,lower_bound和upper_bound
typedef multimap<string, string>::iterator auth_it;
auth_it beg = auth_books.lower_bound(authors[1]);
auth_it end = auth_books.upper_bound(authors[1]);
while (beg != end){
cout << beg->second << endl;
++beg;
}
cout << "========================" << endl;
/***************************************************/
//第三种方式,equal_range
pair<auth_it, auth_it> pos = auth_books.equal_range(authors[0]);
while (pos.first != pos.second){//pos.first等价于lower_bound(),pos.second等价于upper_bound()
cout << pos.first->second << endl;
++pos.first;
}
cout << "========================" << endl;
return 0;
}
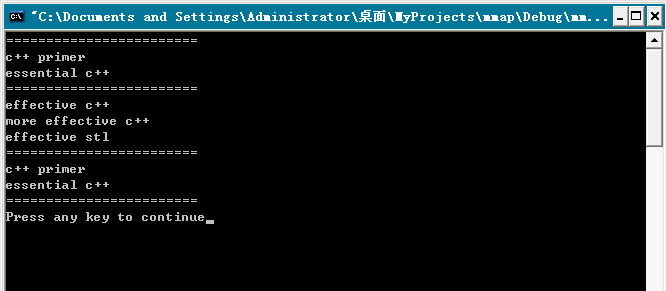
运行结果如图: