在uclinux for bf561中使用B核(3):corebld的实现
在有了/dev/coreb之后,uclinux还提供了一个工具corebld。它用于将elf格式的文件作为一个普通文件读出来,提取出相应的可执行代码,再调用/dev/coreb提供的功能将这些可执行代码写入到B核的L1 Instruction Memory或者SDRAM中,最后再调用驱动程序的功能开始执行这些代码。它的实现在user/blkfin-apps/corebld/corebld.c中。
目前corebld只能分析elf格式的文件,但是经过适当的修改,它应该也可以分析在vdsp下生成的可执行代码。
1
、
elf
格式简介
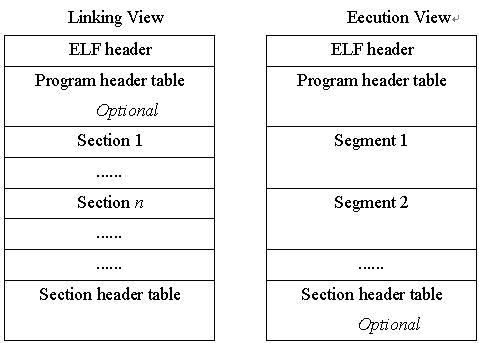
Executable and linking format(ELF)文件是x86 Linux系统下的一种常用目标文件(object file)格式,为了方便和高效,ELF文件内容有两个平行的视角:一个是程序连接角度,另一个是程序运行角度,如下图所示。
ELF header在文件开始处描述了整个文件的组织,Section提供了目标文件的各项信息(如指令、数据、符号表、重定位信息等),Program header table指出怎样创建进程映像,含有每个program header的入口,Section header table包含每一个section的入口,给出名字、大小等信息。
下面的结构体给出了ELF header所能提供的信息:
typedef
struct {
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* File identification. */
Elf32_Half e_type; /* File type. */
Elf32_Half e_machine; /* Machine architecture. */
Elf32_Word e_version; /* ELF format version. */
Elf32_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point. */
Elf32_Off e_phoff; /* Program header file offset. */
Elf32_Off e_shoff; /* Section header file offset. */
Elf32_Word e_flags; /* Architecture-specific flags. */
Elf32_Half e_ehsize; /* Size of ELF header in bytes. */
Elf32_Half e_phentsize; /* Size of program header entry. */
Elf32_Half e_phnum; /* Number of program header entries. */
Elf32_Half e_shentsize; /* Size of section header entry. */
Elf32_Half e_shnum; /* Number of section header entries. */
Elf32_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section name strings section. */
} Elf32_Ehdr;
下面的结构体给出了每个section所能提供的信息:
typedef
struct {
Elf32_Word sh_name; /* Section name (index into the
section header string table). */
Elf32_Word sh_type; /* Section type. */
Elf32_Word sh_flags; /* Section flags. */
Elf32_Addr sh_addr; /* Address in memory image. */
Elf32_Off sh_offset; /* Offset in file. */
Elf32_Size sh_size; /* Size in bytes. */
Elf32_Word sh_link; /* Index of a related section. */
Elf32_Word sh_info; /* Depends on section type. */
Elf32_Size sh_addralign; /* Alignment in bytes. */
Elf32_Size sh_entsize; /* Size of each entry in section. */
} Elf32_Shdr;
因为我们的目标只是将每个Section中的可执行代码提取出来放在Core B中的适当位置,因此只要使用这两个结构体就足够了。至于ELF的更详细的信息可查阅ELF手册或者文档。
2
、
corebld
的实现
corebld的实现其实很简单,就是把每一个section中的可执行代码提取出来,再写入到Elf32_Shdr结构体中的sh_addr指定的位置。最后调用/dev/coreb提供的功能启动B核。
下面的代码说明了这一过程:
#define
COMPILER_VDSP 0
#define
COMPILER_GCC 1
int
elf_load(const char *buf)
{
Elf32_Ehdr *ehdr = (Elf32_Ehdr*)buf;
int compiler;
if (!IS_ELF(*ehdr)) {
printf("File is not an ELF file./n");
return -1;
}
if (ehdr->e_flags == 4 && ehdr->e_machine == 0x6a)
compiler = COMPILER_VDSP;
else if (ehdr->e_flags == 0 && ehdr->e_machine == 0x6a)
compiler = COMPILER_GCC;
else {
printf("File is not a Blackfin ELF file/n");
return -1;
}
{
//
取第一个section所在的偏移量、此文件中的section的数量和每个section的大小
unsigned int section_ptr = (unsigned int)buf + ehdr->e_shoff;
unsigned int section_cnt = ehdr->e_shnum;
unsigned int section_sz = ehdr->e_shentsize;
int i;
//
将每个section中的可执行代码写入到指定的区域
for (i = 0; i < section_cnt; ++i) {
Elf32_Shdr *shdr = (Elf32_Shdr*)((char*)section_ptr + i*section_sz);
unsigned long addr = shdr->sh_addr;
unsigned long size = shdr->sh_size;
if ((compiler == COMPILER_VDSP && (shdr->sh_flags & 0x408000) == 0x8000)
|| (compiler == COMPILER_GCC && (shdr->sh_flags & 0x0003) == 0x0003)) {
printf("Write %zi bytes to 0x%p/n", size, (void*)addr);
put_region((char*)addr, buf + shdr->sh_offset, size);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
下面再看一看每个section中的代码是如何写入到指定的区域的:
static
void put_region(char *dst, const char *src, size_t count)
{
int f = open("/dev/coreb", O_RDWR);
int index = 0, ret = 0;
unsigned long seek = 0;
//
根据要写入的不同区域指定调用驱动时要使用的命令和参数
if (((unsigned long)dst >= 0xff600000) &&
((unsigned long)dst < 0xff604000)) {
if ((unsigned long)dst + count < 0xff604000) {
index = 0;
seek = (unsigned long)dst & 0x3fff;
}
} else if (((unsigned long)dst >= 0xff610000) &&
((unsigned long)dst < 0xff614000)) {
if ((unsigned long)dst + count < 0xff614000) {
index = 1;
seek = (unsigned long)dst & 0x3fff;
}
} else if (((unsigned long)dst >= 0xff500000) &&
((unsigned long)dst < 0xff508000)) {
if ((unsigned long)dst + count < 0xff508000) {
index = 2;
seek = (unsigned long)dst & 0x7fff;
}
} else if (((unsigned long)dst >= 0xff400000) &&
((unsigned long)dst < 0xff408000)) {
if ((unsigned long)dst + count < 0xff408000) {
index = 3;
seek = (unsigned long)dst & 0x7fff;
}
/* copy sdram code */
} else if (((unsigned long)dst >= 0x3C00000) &&
((unsigned long)dst < 0x4000000)) {
memcpy(dst, src, count);
} else {
printf("Cowardly refusing to load an incorrectly linked binary./n"
"Please make sure the binary you are trying to load is linked for BF561 Core B./n"
"You will need a specially crafted linker definition file to do this for you./n");
close(f);
return;
}
//
调用功能设置后面要写入区域的基地址
if ((ret = ioctl(f, 1, &index)) != 0)
printf("ioctl return %d/n", ret);
//
设置要读写的偏移量
if (seek)
if ((ret = lseek(f, seek, SEEK_SET)) < 0)
printf("seek failed!/n");
if (write(f, src, count) != count)
printf("write failed!/n");
close(f);
printf("wrote %zi bytes to 0x%p/n", count, dst);
}