Linux内核驱动模块编写概览——ioctl, class_create, device_create
如果你已经入门了内核驱动模块,但是仍感觉有些模糊,不能从整体来了解一个内核驱动模块的结构,请赏读一下这篇拙文。
如果你已经从事内核模块编程N年,并且道行高深,也请不吝赐教一下文中的疏漏错误。
本文中我将实现一个简单的Linux字符设备,旨在大致勾勒出linux内核模块的编写方法的轮廓。其中重点介绍ioctl的用途。
我把这个简单的Linux字符设备模块命名为hello_mod.
设备类型名为hello_class
设备名为hello
该设备是一个虚拟设备,模块加载时会在/sys/class/中创建名为hello_class的逻辑设备,在/dev/中创建hello的物理设备文件。模块名为hello_mod,可接受输入字符串数据(长度小于128),处理该输入字符串之后可向外输出字符串。并且可以接受ioctl()函数控制内部处理字符串的方式。
例如:
a.通过write函数写入"Tom",通过ioctl函数设置langtype=chinese,通过read函数读出的数据将会是"你好! Tom/n"
b.通过write函数写入"Tom",通过ioctl函数设置langtype=english,通过read函数读出的数据将会是"hello! Tom/n"
c.通过write函数写入"Tom",通过ioctl函数设置langtype=pinyin,通过read函数读出的数据将会是"ni hao! Tom/n"
一般的内核模块中不会负责设备类别和节点的创建,我们在编译完之后会得到.o或者.ko文件,然后insmod之后需要mknod来创建相应文件,这个简单的例子中我们让驱动模块加载时负责自动创建设备类别和设备文件。这个功能有两个步骤,
1) 创建设备类别文件 class_create();
2) 创建设备文件 device_create();
关于这两个函数的使用方法请参阅其他资料。
linux设备驱动的编写相对windows编程来说更容易理解一点因为不需要处理IRP,应用层函数和内核函数的关联方式浅显易懂。
比如, 当应用层函数对我的设备调用了open()函数,而最终这个应用层函数会调用我的设备中的自定义open()函数,这个函数要怎么写呢,我在我的设备中定义的函数名是hello_mod_open,注意函数名是可以随意定义,但是函数签名是要符合内核要求的,具体的定义是怎么样请看<linux/fs.h>
static int hello_mod_open(struct inode *, struct file *);
这样就定义了内核中的open函数,这只是定义还需要与我们自己的模块关联起来,这就要用到一个结构:
struct file_operations
这个结构里面的成员是对应于设备操作的各种函数的指针。
我在设备中用到了这些函数所以就如下定义,注意下面的写法不是标准ANSI C的语法,而是GNU扩展语法。
struct file_operations hello_mod_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_mod_open,
.read = hello_mod_read,
.write = hello_mod_write,
.ioctl = hello_mod_ioctl,
.release = hello_mod_release,
};
这个结构体变量定义好之后我们在模块初始化函数中就可以通过register_chrdev()或者填充cdev结构来关联所有的操作到我们的模块函数了。和设备交互的数据我们总称为“数据”,但是大致可划分为两种
“功能数据”:我们要输入设备处理的和设备处理完之后输出的数据。
“控制数据”:我们用来控制设备特性功能的命令和参数。
open,read,write,release等函数是对一个驱动模块的使用,就是我们对“设备的功能”的使用。但是一个设备有可能有很多功能,那么我们要怎么控制设备让设备完成指定的功能呢?
据个例子来说:假如我们有一个翻译机(姑且说机吧,也可能是器)实体设备,主要功能是输入中文,然后可以输出各种语言对应的翻译结果,那这个机的功能就是翻译,我们真正用来处理的数据是我们输入的中文,我们要得到的“设备功能”就是翻译后的输出内容,而各种语言则是我们的选择控制了,我们可设定这个设备翻译成何种语言。这就要求我们要向设备发送命令,设定目标语言。请注意我们要发送的是两个“控制数据”,命令和参数。
命令:一个设备可能有很多种行为,我们的命令就是代表我们要让设备执行何种行为。“复位”,“设定目标语言”,“获得当前目标语言”等
参数:对于某一个命令,可能需要参数可能不需要参数。
比如:
“复位”命令就不需要参数。
“设定目标语言”则需要传入目标语言的类型。
“获取目标语言”则需要传入一个能够接收目标语言类型的参数。
自己画了一个设备“数据流”图,希望能加深理解。
对于我们自己的设备我们就要自己定义设备命令了,如果你要想搞清命令的格式,请参考其他资料关于ioctl的参数的介绍。这里不打算介绍这个,只介绍ioctl实际功能。定义自己的IO控制命令需要用到宏。这里直接写出我的定义而不是介绍宏的实现。
#define HELLO_MAGIC 12
#define HELLO_IOCTL_RESETLANG _IO(HELLO_MAGIC,0) //设置复位,这个命令不带参数
#define HELLO_IOCTL_GETLANG _IOR(HELLO_MAGIC,1,int) //获取当前设备的语言类型参数,参数是int型
#define HELLO_IOCTL_SETLANG _IOW(HELLO_MAGIC,2,int) //设置设备的语言类型,参数是int型
多的不说了,下面贴上完整代码,懒人没写注释。。不好意思。
hello_mod.c
/*
* =====================================================================================
*
* Filename: hello.c
*
* Description: hello_mod
*
* Version: 1.0
* Created: 01/28/2011 05:07:55 PM
* Revision: none
* Compiler: gcc
*
* Author: Tishion (shion), [email protected]
* Company: LIM
*
* =====================================================================================
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include "hello_mod_ioctl.h"
#define MAJOR_NUM 250
#define MINOR_NUM 0
#define IN_BUF_LEN 256
#define OUT_BUF_LEN 512
MODULE_AUTHOR("Tishion");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Hello_mod driver by tishion");
static struct class * hello_class;
static struct cdev hello_cdev;
static dev_t devnum = 0;
static char * modname = "hello_mod";
static char * devicename = "hello";
static char * classname = "hello_class";
static int open_count = 0;
static struct semaphore sem;
static spinlock_t spin = SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED;
static char * inbuffer = NULL;
static char * outbuffer = NULL;
static lang_t langtype;
static int hello_mod_open(struct inode *, struct file *);
static int hello_mod_release(struct inode *, struct file *);
static ssize_t hello_mod_read(struct file *, char *, size_t, loff_t *);
static ssize_t hello_mod_write(struct file *, const char *, size_t, loff_t *);
static int hello_mod_ioctl(struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
struct file_operations hello_mod_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_mod_open,
.read = hello_mod_read,
.write = hello_mod_write,
.ioctl = hello_mod_ioctl,
.release = hello_mod_release,
};
static int hello_mod_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *pfile)
{
printk("+hello_mod_open()!/n");
spin_lock(&spin);
if(open_count)
{
spin_unlock(&spin);
return -EBUSY;
}
open_count++;
spin_unlock(&spin);
printk("-hello_mod_open()!/n");
return 0;
}
static int hello_mod_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *pfile)
{
printk("+hello_mod_release()!/n");
open_count--;
printk("-hello_mod_release()!/n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t hello_mod_read(struct file *pfile, char *user_buf, size_t len, loff_t *off)
{
printk("+hello_mod_read()!/n");
if(down_interruptible(&sem))
{
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
memset(outbuffer, 0, OUT_BUF_LEN);
printk(" +switch()/n");
switch(langtype)
{
case english:
printk(" >in case: english/n");
sprintf(outbuffer, "Hello! %s.", inbuffer);
break;
case chinese:
printk(" >in case: chinese/n");
sprintf(outbuffer, "你好! %s.", inbuffer);
break;
case pinyin:
printk(" >in case: pinyin/n");
sprintf(outbuffer, "ni hao! %s.", inbuffer);
break;
default:
printk(" >in case: default/n");
break;
}
printk(" -switch()/n");
if(copy_to_user(user_buf, outbuffer, len))
{
up(&sem);
return -EFAULT;
}
up(&sem);
printk("-hello_mod_read()!/n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t hello_mod_write(struct file *pfile, const char *user_buf, size_t len, loff_t *off)
{
printk("+hello_mod_write()!/n");
if(down_interruptible(&sem))
{
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
if(len > IN_BUF_LEN)
{
printk("Out of input buffer/n");
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
if(copy_from_user(inbuffer, user_buf, len))
{
up(&sem);
return -EFAULT;
}
up(&sem);
printk("-hello_mod_write()!/n");
return 0;
}
static int hello_mod_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *pfile, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int err = 0;
printk("+hello_mod_ioctl()!/n");
printk(" +switch()/n");
switch(cmd)
{
case HELLO_IOCTL_RESETLANG:
printk(" >in case: HELLO_IOCTL_RESETLANG/n");
langtype = english;
break;
case HELLO_IOCTL_GETLANG:
printk(" >in case: HELLO_IOCTL_GETLANG/n");
err = copy_to_user((int *)arg, &langtype, sizeof(int));
break;
case HELLO_IOCTL_SETLANG:
printk(" >in case: HELLO_IOCTL_SETLANG/n");
err = copy_from_user(&langtype,(int *)arg, sizeof(int));
break;
default:
printk(" >in case: default/n");
err = ENOTSUPP;
break;
}
printk(" -switch()/n");
printk("-hello_mod_ioctl()!/n");
return err;
}
static int __init hello_mod_init(void)
{
int result;
printk("+hello_mod_init()!/n");
devnum = MKDEV(MAJOR_NUM, MINOR_NUM);
result = register_chrdev_region(devnum, 1, modname);
if(result < 0)
{
printk("hello_mod : can't get major number!/n");
return result;
}
cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hello_mod_fops);
hello_cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
hello_cdev.ops = &hello_mod_fops;
result = cdev_add(&hello_cdev, devnum, 1);
if(result)
printk("Failed at cdev_add()");
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, classname);
if(IS_ERR(hello_class))
{
printk("Failed at class_create().Please exec [mknod] before operate the device/n");
}
else
{
device_create(hello_class, NULL, devnum,NULL, devicename);
}
open_count = 0;
langtype = english;
inbuffer = (char *)kmalloc(IN_BUF_LEN, GFP_KERNEL);
outbuffer = (char *)kmalloc(OUT_BUF_LEN, GFP_KERNEL);
init_MUTEX(&sem);
printk("-hello_mod_init()!/n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_mod_exit(void)
{
printk("+hello_mod_exit!/n");
kfree(inbuffer);
kfree(outbuffer);
cdev_del(&hello_cdev);
device_destroy(hello_class, devnum);
class_destroy(hello_class);
unregister_chrdev_region(devnum, 1);
printk("-hello_mod_exit!/n");
return ;
}
module_init(hello_mod_init);
module_exit(hello_mod_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
hello_mod_iotcl.h
/*
* =====================================================================================
*
* Filename: hello_mod_ioctl.h
*
* Description: define the cmd supported by hello_mod
*
* Version: 1.0
* Created: 06/19/2011 10:24:20 PM
* Revision: none
* Compiler: gcc
*
* Author: Tishion (shion), [email protected]
* Company: LIM
*
* =====================================================================================
*/
#ifndef __HELLO_MOD_IOCTL_H__
#define __HELLO_MOD_IOCTL_H__
#define HELLO_MAGIC 12
#define HELLO_IOCTL_RESETLANG _IO(HELLO_MAGIC,0) //set langtype = english
#define HELLO_IOCTL_GETLANG _IOR(HELLO_MAGIC,1,int) //get langtype
#define HELLO_IOCTL_SETLANG _IOW(HELLO_MAGIC,2,int) //set langtype
typedef enum _lang_t
{
english, chinese, pinyin
}lang_t;
#endif
Makefile
#**********************************************
# Makefile linux 2.6 Module
# This makefile is written for Ubuntu 10.10
# It may not perfomance without erros on the
# other version or distributions.
#**********************************************
# BY:tishion
# Mail:[email protected]
# 2011/06/19
#**********************************************
obj-m += hello_mod.o
CURRENT_PATH := $(shell pwd)
LINUX_KERNEL := $(shell uname -r)
LINUX_KERNEL_PATH := /usr/src/linux-headers-$(LINUX_KERNEL)
all:
make -C $(LINUX_KERNEL_PATH) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) modules
clean:
make -C $(LINUX_KERNEL_PATH) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) clean
install:
insmod hello_mod.ko
unistall:
rmmod hello_mod
附上一用户层测试文件,编译后需要root身份执行。
/*
* =====================================================================================
*
* Filename: hell_mod_test.c
*
* Description: hell_mod test app
*
* Version: 1.0
* Created: 06/20/2011 01:44:11 AM
* Revision: none
* Compiler: gcc
*
* Author: Tishion (shion), [email protected]
* Company: LIM
*
* =====================================================================================
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include "../hello_mod_ioctl.h"
int main()
{
char outbuf[512];
char * myname = "tishion";
lang_t langtype = english;
int fd = open("/dev/hello", O_RDWR, S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR);
if(fd != -1)
{
write(fd, myname, strlen(myname)+1);
langtype = chinese;
ioctl(fd, HELLO_IOCTL_SETLANG, &langtype);
read(fd, outbuf, 512);
printf("langtype=chinese:%s/n", outbuf);
memset(outbuf, 0, 512);
langtype = pinyin;
ioctl(fd, HELLO_IOCTL_SETLANG, &langtype);
read(fd, outbuf, 512);
printf("langtype=pinyin:%s/n", outbuf);
memset(outbuf, 0, 512);
ioctl(fd, HELLO_IOCTL_RESETLANG, &langtype);
read(fd, outbuf, 512);
printf("langtype=english:%s/n", outbuf);
}
else
{
perror("Failed at open():");
}
return 0;
}
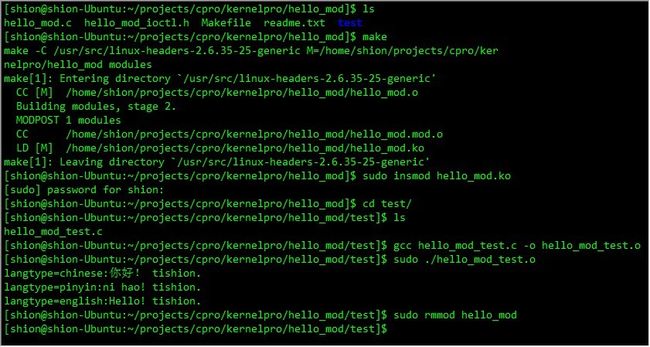
编译和运行过程图
http://blog.csdn.net/otishiono/article/details/6558383