MiniDao普通项目集成方案
MiniDao普通项目集成方案
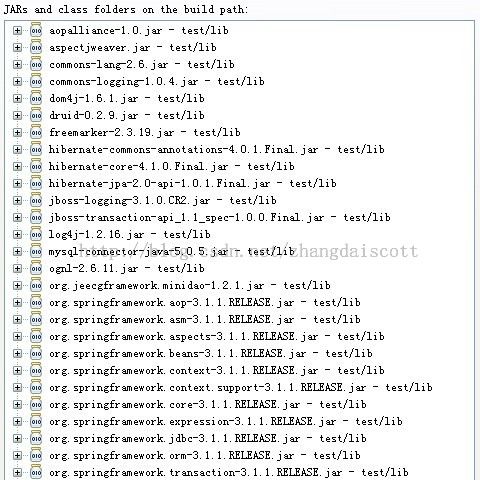
1、导入必要的jar包:
2、spring配置文件增加如下配置:
<!-- Hibernate工具栏配置-->
<bean id="miniDaoHiberCommonDao"
class="org.jeecgframework.minidao.hibernate.dao.impl.GenericBaseCommonDao">
<property name="sessionFactory">
<ref bean="sessionFactory"/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- MiniDao动态代理类 -->
<bean id="miniDaoHandler"class="org.jeecgframework.minidao.aop.MiniDaoHandler">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注册MiniDao接口,配置该bean,在web容器启动时会扫描指定包下的含有@MiniDao注解的接口类,在使用到接口类的方法时会通过动态代理的方式来调用指定方法 -->
<bean class="org.jeecgframework.minidao.factory.MiniDaoBeanFactory">
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>examples.dao.*</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
3、编写数据接口层接口类(该类需增加@MiniDao注解才会被MiniDao所识别)的方式有3种:在其接口方法上增加@Arguments注解或@Sql注解,或者该类继承MiniDaoSupportHiber<T>类的方式来告诉MiniDao的动态代理类需要以哪种方式来进行数据库的交互。
1)@Arguments:如果使用该注解则需要增加对应的sql文件,文件名为“接口名_方法名.sql”,该文件的存放位置与接口类所在的包同级,包名为sql,该注解的数量与sql文件的数量相同,如果有多个参数用逗号分隔,参数名称应与sql文件内的一致,在sql文件中使用参数时应在参数前加“:”(冒号),如果该参数为实体类,则通过“.”(英文状态下的点)导航其属性,该sql文件支持freemarker的语法。
2)@Sql:如果使用该注解则直接在该注解类写sql代码,如果有参数则sql语句的写法与@Arguments方式的sql文件写法相同。
3)继承MiniDaoSupportHiber<T>类:可直接调用该父类的方法。
示例:
接口和SQL文件对应目录
接口定义[EmployeeDao.java]
@MiniDao
public interface EmployeeDao{
@Arguments("employee")
public List<Map>getAllEmployees(Employee employee);
@Arguments("empno")
Employee getEmployee(String empno);
@Arguments({"empno","name"})
Map getMap(String empno,String name);
@Sql("SELECT count(*) FROMemployee")
Integer getCount();
@Arguments("employee")
int update(Employee employee);
@Arguments("employee")
void insert(Employee employee);
}
SQL文件[EmployeeDao_getAllEmployees.sql]
SELECT * FROM employee where1=1
<#if employee.age?exists>
and age = :employee.age
</#if>
<#if employee.name?exists>
and name = :employee.name
</#if>
<#if employee.empno?exists>
and empno = :employee.empno
</#if>
MiniDao接口配置
<!-- 注册MiniDao接口 -->
<beanclass="org.jeecgframework.minidao.factory.MiniDaoBeanFactory">
<propertyname="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>examples.dao.*</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
测试代码
public class Client {
public static voidmain(String args[]) {
BeanFactory factory = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml");
EmployeeDao employeeDao = (EmployeeDao)factory.getBean("employeeDao");
Employee employee = new Employee();
List<Map> list = employeeDao.getAllEmployees(employee);
for(Map mp:list){
System.out.println(mp.get("id"));
System.out.println(mp.get("name"));
System.out.println(mp.get("empno"));
System.out.println(mp.get("age"));
System.out.println(mp.get("birthday"));
System.out.println(mp.get("salary"));
}
}
}
接口定义[JeecgDemoDao.java]
@MiniDao
public interface JeecgDemoDaoextendsMiniDaoSupportHiber<JeecgDemo>{
@Sql("SELECT count(*)FROM jeecg_demo")
Integer getCount();
}
MiniDao接口配置
<!-- 注册MiniDao接口 -->
<beanclass="org.jeecgframework.minidao.factory.MiniDaoBeanFactory">
<propertyname="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>examples.dao.*</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
测试代码
public class Client {
public static voidmain(String args[]) {
BeanFactory factory = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml");
JeecgDemoDaojeecgDemoDao = (JeecgDemoDao) factory.getBean("jeecgDemoDao");
jeecgDemoDao.getCount();
JeecgDemo s =jeecgDemoDao.getByIdHiber(JeecgDemo.class,"402880e7408f53a401408f53a5aa0000");
if(s!=null){
System.out.println(s.getUserName());
}
}
}