Android软键盘softboard(1)
从SDK 1.5版本以后,Android就开放它的IMF(Input Method Framework),让我们能够开发自己的输入法。而开发输入法最好的参考就是Android自带的Sample-SoftKeyboard,虽然这个例子仅包含英文和数字输入,但是它本身还算完整和清楚,对我们开始Android开发实战有很大帮助。
什么是IMF:
IMF(Input Method Framework),Android IMF用于支持各种输入法,如软键盘输入、手写输入、物理键盘输入(soft keyboard, hand-writing recognizers, and hard keyboard translators)。我们关注的重点是软键盘输入。
IMF结构:
一个IMF结构中包含三个主要的部分:
input method manager:管理各部分的交互。它是一个客户端API,存在于各个应用程序的context中,用来沟通管理所有进程间交互的全局系统服务。
input method(IME):实现一个允许用户生成文本的独立交互模块。系统绑定一个当前的输入法。使其创建和生成,决定输入法何时隐藏或者显示它的UI。同一时间只能有一个IME运行。
client application:通过输入法管理器控制输入焦点和IME的状态。一次只能有一个客户端使用IME。
创建一个输入法:
(1)在AndroidManifest.xml中,须把input method声明成一个service,并且加上 intent filter (associated meta data):
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.fastinput">
<application android:label="@string/app_label">
<!-- Declares the input method service -->
<service android:name="FastInputIME"
android:label="@string/fast_input_label"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_INPUT_METHOD">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.view.InputMethod" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name="android.view.im" android:resource="@xml/method" />
</service>
<!-- Optional activities. A good idea to have some user settings. -->
<activity android:name="FastInputIMESettings" android:label="@string/fast_input_settings">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
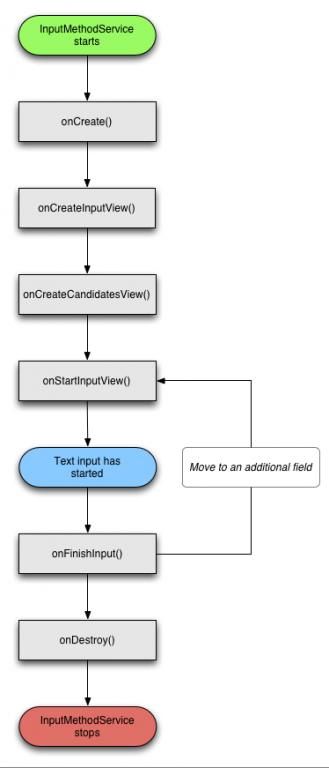
(2)一个
InputMethodService的生命周期如下图:
(3)两类重要的视图:
输入视图和候选词视图(the input view and the candidates view):
输入视图(the input view):是与用户交互的主要发生地:按键,画图或者其他的方式。通常的实现就是简单的用一个视图来处理所有的工作,并且在调用 InputMethodService.onCreateInputView()的时候返回一个新的实例。通过调用系统的onEvaluateInputViewShow()来测试是否需要显示输入视图,它是系统根据当前的上下文环境来实现的。当输入法状态改变的时候,需要调用updateInputViewShown()来重新估计一下。
候选词视图(the candidates view):当用户输入一些字符之后,输入法可能需要提供给用户一些可用的候选词的列表。这个视图的管理和输入视图不大一样,因为这个视图是非常的短暂的,它只是在有候选词的时候才会被显示。调用InputMethodService.onCreateCandidatesView()默认返回NULL. 可以用setCandidatesViewShow()来设置是否需要显示这个视图。正是因为这个显示的频繁性,所以它一般不会被销毁,而且不会改变当前应用程序的视图。
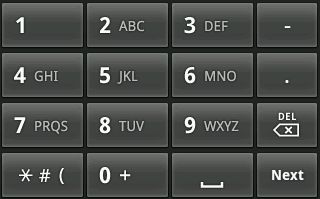
(4)为输入法设计不同的输入类型:
自己可以根据用途设计不同的输入类型。如LatinIME提供以下两种输入界面:

(5)EditorInfo对象
EditorInfo对象提供不同输入类型和文本域的各类值。
(EditorInfo.inputType & EditorInfo.TYPE_CLASS_MASK) 可以提供不同的值,如下:
数字区域:TYPE_CLASS_NUMBER时间:TYPE_CLASS_DATETIME电话:TYPE_CLASS_PHONE文本:TYPE_CLASS_TEXT
其他的还有密码输入等;
(6)发送文本到应用程序(Sending text to the application)
有两种方法将文本提交给应用程序:
1.send individual key events
2.edit the text around the cursor in the application's text field
×发送一个关键事件,可以利用KeyEvent对象和调用InputConnection.sendKeyEvent()方法:
InputConnection ic = getCurrentInputConnection(); long eventTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); ic.sendKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(eventTime, eventTime, KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, keyEventCode, 0, 0, 0, 0, KeyEvent.FLAG_SOFT_KEYBOARD|KeyEvent.FLAG_KEEP_TOUCH_MODE)); ic.sendKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), eventTime, KeyEvent.ACTION_UP, keyEventCode, 0, 0, 0, 0, KeyEvent.FLAG_SOFT_KEYBOARD|KeyEvent.FLAG_KEEP_TOUCH_MODE));
或者也可以利用这个简便方法(推荐方法):
InputMethodService.sendDownUpKeyEvents(keyEventCode);
×在文本域编辑文本(When editing text in a text field),android.view.inputmethod.InputConnection一下有用的方法如下:
getTextBeforeCursor()getTextAfterCursor()deleteSurroundingText()commitText()
例如:
InputConnection ic = getCurrentInputConnection();
ic.deleteSurroundingText(4, 0);
ic.commitText("Hello", 1);
ic.commitText("!", 1);(7)在提交前组合文本(Composing text before committing)
在输入单词或者汉字等组合词时,可以在文本域显示进度或者候选词供输入者选择。
InputConnection ic = getCurrentInputConnection();
ic.setComposingText("Composi", 1);
...
ic.setComposingText("Composin", 1);
...
ic.commitText("Composing ", 1);8)响应物理键盘输入(Intercepting hard key events)
为了响应物理键盘输入,需要重写InputMethodService.onKeyDown()和InputMethodService.onKeyUp()方法。调用super.onKey方法。
具体软键盘实例可参考LatinIME source code