直方图之calcHist使用 .
OpenCV图像处理 图像的点运算 ( 灰度直方图 )
OpenCV灰度直方图
Theory :
从图形上看,灰度直方图是一个二维图:
图像的灰度直方图是一个离散函数,它表示图像每一灰度级与该灰度级出现频率的对应关系。假设一幅图像的像素总数为 N,灰度级总数为 L,其中灰度级为 g 的像素总数为 Ng,则这幅数字图像的灰度直方图横坐标即为灰度 g ( 0 ≤ g ≤ L-1 ),纵坐标则为灰度值出现的次数 Ng。实际上,用 N 去除各个灰度值出现的次数 Ng 即可得到各个灰度级出现的概率 Pg = Ng / N = Ng / ∑Ng ,从而得到归一化的灰度直方图,其纵坐标为概率 Pg 。
Quote : ( From [OpenCV 2 Computer Vision Application Programming Cookbook (Robert Langaniere, 2011) ], 引用作直方图的解释 )
- A histogram is a simple table that gives the number of pixels that have a given value in an image (or sometime a set of images). The histogram of a gray-level image will therefore have 256 entries (or bins).
- Histograms can also be normalized such that sum of the bins equals 1. In that case, each bin gives the percentage of pixels having this specific value in the image.
Implementation :
利用 OpenCV 提供的 calcHist 函数 :
void calcHist(const Mat* arrays, int narrays, const int* channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist, int dims, const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, bool accumulate=false );
这个函数用于计算直方图是很强大的,在这里就实现一个最简单的灰度图像的直方图计算。
Code :
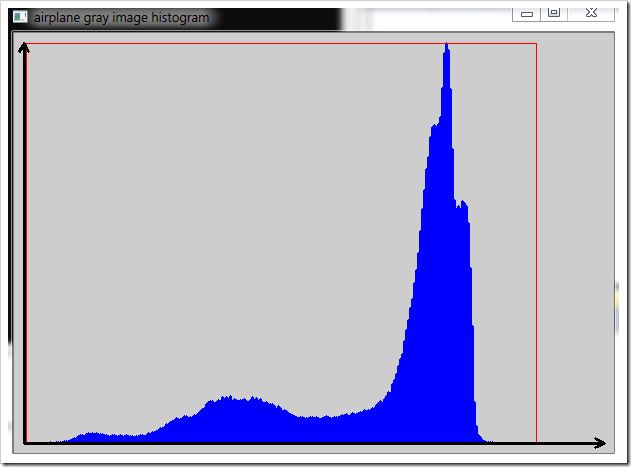
1: int main()2: {3: Mat img = imread("lena.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);4:5: Mat* arrays = &img;6: int narrays = 1;7: int channels[] = { 0 };8: InputArray mask = noArray();9: Mat hist;10: int dims = 1;11: int histSize[] = { 256 };12: float hranges[] = { 0.0, 255.0 };13: const float *ranges[] = { hranges };14: //调用 calcHist 计算直方图, 结果存放在 hist 中15: calcHist(arrays, narrays, channels, mask, hist, dims, histSize, ranges);16:17: //调用一个我自己写的简单的函数用于获取一张显示直方图数据的图片,18: //输入参数为直方图数据 hist 和期望得到的图片的尺寸19: Mat histImg = ggicci::getHistogram1DImage(hist, Size(600, 420));20: imshow("lena gray image histogram", histImg);21: waitKey();22: }23:24: Mat ggicci::getHistogram1DImage(const Mat& hist, Size imgSize)25: {26: Mat histImg(imgSize, CV_8UC3);27: int Padding = 10;28: int W = imgSize.width - 2 * Padding;29: int H = imgSize.height - 2 * Padding;30: double _max;31: minMaxLoc(hist, NULL, &_max);32: double Per = (double)H / _max;33: const Point Orig(Padding, imgSize.height-Padding);34: int bin = W / (hist.rows + 2);35:36: //画方柱37: for (int i = 1; i <= hist.rows; i++)38: {39: Point pBottom(Orig.x + i * bin, Orig.y);40: Point pTop(pBottom.x, pBottom.y - Per * hist.at<float>(i-1));41: line(histImg, pBottom, pTop, Scalar(255, 0, 0), bin);42: }43:44: //画 3 条红线标明区域45: line(histImg, Point(Orig.x + bin, Orig.y - H), Point(Orig.x + hist.rows * bin, Orig.y - H), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);46: line(histImg, Point(Orig.x + bin, Orig.y), Point(Orig.x + bin, Orig.y - H), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);47: line(histImg, Point(Orig.x + hist.rows * bin, Orig.y), Point(Orig.x + hist.rows * bin, Orig.y - H), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);48: drawArrow(histImg, Orig, Orig+Point(W, 0), 10, 30, Scalar::all(0), 2);49: drawArrow(histImg, Orig, Orig-Point(0, H), 10, 30, Scalar::all(0), 2);50:51: return histImg;52: }
Result :
这次再深入学习一下calcHist函数,即用于计算直方图的函数,主要是分析一下该函数的众多的参数,看看应该如何使用,先给出一段代码,其中包括两部分,一部分来自opencv_tutorials中的例子,一部分来自opencv2refman中,都进行了修改,opencv版本为2.3.1。
- #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include <iostream>
- #pragma comment(lib, "opencv_core231d.lib")
- #pragma comment(lib, "opencv_highgui231d.lib")
- #pragma comment(lib, "opencv_imgproc231d.lib")
- using namespace cv;
- using namespace std;
- #define HIST_DIM1
- int main( int argc, char** argv )
- {
- #ifdef HIST_DIM1
- //----------------------example 1-------------------------------//
- Mat src, dst;
- /// Load image
- src = imread("d:/picture/lena.jpg");
- if( !src.data )
- {
- cout<<"load image failed"<<endl;
- return -1;
- }
- /// Separate the image in 3 places ( R, G and B )
- vector<Mat> rgb_planes;
- #define SHOW_HSV
- #ifdef SHOW_HSV
- Mat hsv;
- cvtColor(src, hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
- split(hsv, rgb_planes );
- #else
- split(src, rgb_planes );
- #endif
- /// Establish the number of bins
- int histSize = 256;
- /// Set the ranges ( for R,G,B) )
- float range[] = { 0, 255 } ;
- const float* histRange = { range };
- bool uniform = true; bool accumulate = false;
- Mat r_hist, g_hist, b_hist;
- /// Compute the histograms:
- calcHist( &rgb_planes[2], 1, 0, Mat(), r_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate );
- calcHist( &rgb_planes[1], 1, 0, Mat(), g_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate );
- calcHist( &rgb_planes[0], 1, 0, Mat(), b_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate );
- // Draw the histograms for R, G and B
- int hist_w = 600; int hist_h = 400;
- int bin_w = cvRound( (double) hist_w/histSize );
- Mat rgb_hist[3];
- for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
- {
- rgb_hist[i] = Mat(hist_h, hist_w, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0));
- }
- Mat histImage(hist_h, hist_w, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,0,0));
- /// Normalize the result to [ 0, histImage.rows-10]
- normalize(r_hist, r_hist, 0, histImage.rows-10, NORM_MINMAX);
- normalize(g_hist, g_hist, 0, histImage.rows-10, NORM_MINMAX);
- normalize(b_hist, b_hist, 0, histImage.rows-10, NORM_MINMAX);
- /// Draw for each channel
- for( int i = 1; i < histSize; i++ )
- {
- line( histImage, Point( bin_w*(i-1), hist_h-cvRound(r_hist.at<float>(i-1)) ) ,
- Point( bin_w*(i), hist_h-cvRound(r_hist.at<float>(i)) ),
- Scalar( 0, 0, 255), 1);
- line( histImage, Point( bin_w*(i-1), hist_h - cvRound(g_hist.at<float>(i-1)) ) ,
- Point( bin_w*(i), hist_h-cvRound(g_hist.at<float>(i)) ),
- Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 1);
- line( histImage, Point( bin_w*(i-1), hist_h - cvRound(b_hist.at<float>(i-1)) ) ,
- Point( bin_w*(i), hist_h-cvRound(b_hist.at<float>(i)) ),
- Scalar( 255, 0, 0), 1);
- }
- for (int j=0; j<histSize; ++j)
- {
- int val = saturate_cast<int>(r_hist.at<float>(j));
- rectangle(rgb_hist[0], Point(j*2+10, rgb_hist[0].rows), Point((j+1)*2+10, rgb_hist[0].rows-val), Scalar(0,0,255),1,8);
- val = saturate_cast<int>(g_hist.at<float>(j));
- rectangle(rgb_hist[1], Point(j*2+10, rgb_hist[1].rows), Point((j+1)*2+10, rgb_hist[1].rows-val), Scalar(0,255,0),1,8);
- val = saturate_cast<int>(b_hist.at<float>(j));
- rectangle(rgb_hist[2], Point(j*2+10, rgb_hist[2].rows), Point((j+1)*2+10, rgb_hist[2].rows-val), Scalar(255,0,0),1,8);
- }
- /// Display
- namedWindow("calcHist Demo", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
- namedWindow("wnd");
- imshow("calcHist Demo", histImage );
- imshow("wnd", src);
- imshow("R", rgb_hist[0]);
- imshow("G", rgb_hist[1]);
- imshow("B", rgb_hist[2]);
- #else
- //----------------------example 2-------------------------------//
- Mat src, hsv;
- if(!(src=imread("d:/picture/lena.bmp")).data)
- return -1;
- cvtColor(src, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV);
- // Quantize the hue to 30 levels
- // and the saturation to 32 levels
- int hbins = 60, sbins = 64;
- int histSize[] = {hbins, sbins};
- // hue varies from 0 to 179, see cvtColor
- float hranges[] = { 0, 180 };
- // saturation varies from 0 (black-gray-white) to
- // 255 (pure spectrum color)
- float sranges[] = { 0, 256};
- const float*ranges[] = { hranges, sranges };
- MatND hist;
- // we compute the histogram from the 0-th and 1-st channels
- int channels[] = {0, 1};
- calcHist( &hsv, 1, channels, Mat(),hist, 2, histSize, ranges,true, false );
- double maxVal=0;
- minMaxLoc(hist, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0);
- int scale = 8;
- Mat histImg = Mat::zeros(sbins*scale, hbins*scale, CV_8UC3);
- for( int h = 0; h < hbins; h++ )
- {
- for( int s = 0; s < sbins; s++ )
- {
- float binVal = hist.at<float>(h, s);
- int intensity = cvRound(binVal*255/maxVal);
- rectangle( histImg, Point(h*scale, s*scale),Point((h+1)*scale-1, (s+1)*scale-1), Scalar::all(intensity), CV_FILLED);
- }
- }
- namedWindow( "Source", 1 );
- imshow( "Source", src );
- namedWindow( "H-S Histogram", 1 );
- imshow( "H-S Histogram", histImg );
- #endif
- //-------------------------------------------------------------------------//
- waitKey(0);
- destroyAllWindows();
- return 0;
- }
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#pragma comment(lib, "opencv_core231d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "opencv_highgui231d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "opencv_imgproc231d.lib")
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
#define HIST_DIM1
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
#ifdef HIST_DIM1
//----------------------example 1-------------------------------//
Mat src, dst;
/// Load image
src = imread("d:/picture/lena.jpg");
if( !src.data )
{
cout<<"load image failed"<<endl;
return -1;
}
/// Separate the image in 3 places ( R, G and B )
vector<Mat> rgb_planes;
#define SHOW_HSV
#ifdef SHOW_HSV
Mat hsv;
cvtColor(src, hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
split(hsv, rgb_planes );
#else
split(src, rgb_planes );
#endif
/// Establish the number of bins
int histSize = 256;
/// Set the ranges ( for R,G,B) )
float range[] = { 0, 255 } ;
const float* histRange = { range };
bool uniform = true; bool accumulate = false;
Mat r_hist, g_hist, b_hist;
/// Compute the histograms:
calcHist( &rgb_planes[2], 1, 0, Mat(), r_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate );
calcHist( &rgb_planes[1], 1, 0, Mat(), g_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate );
calcHist( &rgb_planes[0], 1, 0, Mat(), b_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate );
// Draw the histograms for R, G and B
int hist_w = 600; int hist_h = 400;
int bin_w = cvRound( (double) hist_w/histSize );
Mat rgb_hist[3];
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
rgb_hist[i] = Mat(hist_h, hist_w, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0));
}
Mat histImage(hist_h, hist_w, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,0,0));
/// Normalize the result to [ 0, histImage.rows-10]
normalize(r_hist, r_hist, 0, histImage.rows-10, NORM_MINMAX);
normalize(g_hist, g_hist, 0, histImage.rows-10, NORM_MINMAX);
normalize(b_hist, b_hist, 0, histImage.rows-10, NORM_MINMAX);
/// Draw for each channel
for( int i = 1; i < histSize; i++ )
{
line( histImage, Point( bin_w*(i-1), hist_h-cvRound(r_hist.at<float>(i-1)) ) ,
Point( bin_w*(i), hist_h-cvRound(r_hist.at<float>(i)) ),
Scalar( 0, 0, 255), 1);
line( histImage, Point( bin_w*(i-1), hist_h - cvRound(g_hist.at<float>(i-1)) ) ,
Point( bin_w*(i), hist_h-cvRound(g_hist.at<float>(i)) ),
Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 1);
line( histImage, Point( bin_w*(i-1), hist_h - cvRound(b_hist.at<float>(i-1)) ) ,
Point( bin_w*(i), hist_h-cvRound(b_hist.at<float>(i)) ),
Scalar( 255, 0, 0), 1);
}
for (int j=0; j<histSize; ++j)
{
int val = saturate_cast<int>(r_hist.at<float>(j));
rectangle(rgb_hist[0], Point(j*2+10, rgb_hist[0].rows), Point((j+1)*2+10, rgb_hist[0].rows-val), Scalar(0,0,255),1,8);
val = saturate_cast<int>(g_hist.at<float>(j));
rectangle(rgb_hist[1], Point(j*2+10, rgb_hist[1].rows), Point((j+1)*2+10, rgb_hist[1].rows-val), Scalar(0,255,0),1,8);
val = saturate_cast<int>(b_hist.at<float>(j));
rectangle(rgb_hist[2], Point(j*2+10, rgb_hist[2].rows), Point((j+1)*2+10, rgb_hist[2].rows-val), Scalar(255,0,0),1,8);
}
/// Display
namedWindow("calcHist Demo", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
namedWindow("wnd");
imshow("calcHist Demo", histImage );
imshow("wnd", src);
imshow("R", rgb_hist[0]);
imshow("G", rgb_hist[1]);
imshow("B", rgb_hist[2]);
#else
//----------------------example 2-------------------------------//
Mat src, hsv;
if(!(src=imread("d:/picture/lena.bmp")).data)
return -1;
cvtColor(src, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV);
// Quantize the hue to 30 levels
// and the saturation to 32 levels
int hbins = 60, sbins = 64;
int histSize[] = {hbins, sbins};
// hue varies from 0 to 179, see cvtColor
float hranges[] = { 0, 180 };
// saturation varies from 0 (black-gray-white) to
// 255 (pure spectrum color)
float sranges[] = { 0, 256};
const float*ranges[] = { hranges, sranges };
MatND hist;
// we compute the histogram from the 0-th and 1-st channels
int channels[] = {0, 1};
calcHist( &hsv, 1, channels, Mat(),hist, 2, histSize, ranges,true, false );
double maxVal=0;
minMaxLoc(hist, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0);
int scale = 8;
Mat histImg = Mat::zeros(sbins*scale, hbins*scale, CV_8UC3);
for( int h = 0; h < hbins; h++ )
{
for( int s = 0; s < sbins; s++ )
{
float binVal = hist.at<float>(h, s);
int intensity = cvRound(binVal*255/maxVal);
rectangle( histImg, Point(h*scale, s*scale),Point((h+1)*scale-1, (s+1)*scale-1), Scalar::all(intensity), CV_FILLED);
}
}
namedWindow( "Source", 1 );
imshow( "Source", src );
namedWindow( "H-S Histogram", 1 );
imshow( "H-S Histogram", histImg );
#endif
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------//
waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
上面的例子是对opencv_tutorials以及手册中的计算直方图的程序的修改
其中修改的:
1、原先的程序中对加载的彩色rgb图像的通道有问题(看例子给的图应该是在linux下的,不知道是不是因为linux和windows下加载的不同),在windows下默认加载的通道排列顺序是B-G-R,
原先的程序中是按照R-G-B顺序计算的直方图所以需要变换一下顺序;
2、原先程序的histImage将参数顺序弄错了,该构造函数的第一个参数是rows行数,对应图像的高度,即hist_h,而不是hist_w,这里同时还将大小变换了一下
看着更舒服一些;
下面是对calcHist函数的参数介绍。
calcHist--计算矩阵的直方图函数;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- ###---given in manual---###
- void calcHist(const Mat*arrays, int narrays, const int* channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist, int dims,
- const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, boolaccumulate=false)
- void calcHist(const Mat*arrays, int narrays, const int* channels, InputArray mask, SparseMat& hist, int dims,
- const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, boolaccumulate=false)
- ###---declaration in imgproc.hpp---###
- //! computes the joint dense histogram for a set of images.
- CV_EXPORTS void calcHist( const Mat* images, int nimages, const int* channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist, int dims,
- const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, bool accumulate=false );
- //! computes the joint sparse histogram for a set of images.
- CV_EXPORTS void calcHist( const Mat* images, int nimages, const int* channels, InputArray mask, SparseMat& hist, int dims,
- const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, bool accumulate=false );
- CV_EXPORTS_W void calcHist( InputArrayOfArrays images, const vector<int>& channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist,
- const vector<int>& histSize, const vector<float>& ranges,bool accumulate=false );
###---given in manual---###
void calcHist(const Mat*arrays, int narrays, const int* channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist, int dims,
const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, boolaccumulate=false)
void calcHist(const Mat*arrays, int narrays, const int* channels, InputArray mask, SparseMat& hist, int dims,
const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, boolaccumulate=false)
###---declaration in imgproc.hpp---###
//! computes the joint dense histogram for a set of images.
CV_EXPORTS void calcHist( const Mat* images, int nimages, const int* channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist, int dims,
const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, bool accumulate=false );
//! computes the joint sparse histogram for a set of images.
CV_EXPORTS void calcHist( const Mat* images, int nimages, const int* channels, InputArray mask, SparseMat& hist, int dims,
const int* histSize, const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, bool accumulate=false );
CV_EXPORTS_W void calcHist( InputArrayOfArrays images, const vector<int>& channels, InputArray mask, OutputArray hist,
const vector<int>& histSize, const vector<float>& ranges,bool accumulate=false );
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
手册中和头文件中的函数声明参数稍有不同,主要是前两个参数,手册中是array和narrays而头文件声明中是images和nimages,其实是一样,以手册为准:
这里有一个对opencv_tutorials.pdf即opencv教程的一个翻译。
http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/doc/tutorials/imgproc/histograms/histogram_calculation/histogram_calculation.html
arrays – Source arrays. They all should have the same depth, CV_8U or CV_32F , and the same size. Each of them can have an arbitrary number of channels.
- 源输入(图像)数组,必须是相同深度的CV_8U或者CV_32F(即uchar或者float),相同大小,每一个可以是任意通道的;
[上面的例子1中每次计算一个单通道图像,所以直接对图像取地址赋给了该参数]
narrays – Number of source arrays.
- 源输入数组中的元素个数;
[例子1中只计算一幅图像的直方图,所以这个参数都是1]
channels – List of the dims channels used to compute the histogram. The first array channels are enumerated from 0 to arrays[0].channels()-1 , the second array channels are counted from arrays[0].channels() to arrays[0].channels() + arrays[1].channels()-1, and so on.
- 用来计算直方图的通道维数数组,第一个数组的通道由0到arrays[0].channels()-1列出,第二个数组的通道从arrays[0].channels()到arrays[0].channels()+arrays[1].channels()-1以此类推;
[例子1中为0,即第0个通道??]
mask – Optional mask. If the matrix is not empty, it must be an 8-bit array of the same size as arrays[i]. The non-zero mask elements mark the array elements counted in the histogram.
-可选的掩膜,如果该矩阵不是空的,则必须是8位的并且与arrays[i]的大小相等,掩膜的非零值标记需要在直方图中统计的数组元素;
[例子1中为空的Mat()]
hist – Output histogram, which is a dense or sparse dims -dimensional array.
-输出直方图,是一个稠密或者稀疏的dims维的数组;
[例子1中为保存直方图的Mat]
dims – Histogram dimensionality that must be positive and not greater than CV_MAX_DIMS (equal to 32 in the current OpenCV version).
-直方图的维数,必须为正,并且不大于CV_MAX_DIMS(当前的OpenCV版本中为32,即最大可以统计32维的直方图);
[例子1中为1,因为统计的是每幅单通道图像的灰度直方图]
histSize – Array of histogram sizes in each dimension.
- 用于指出直方图数组每一维的大小的数组,即指出每一维的bin的个数的数组;
[因为例子1只有1维,所以例子1中直接对int取地址作为参数,即该维的bin的个数为256]
ranges – Array of the dims arrays of the histogram bin boundaries in each dimension. When the histogram is uniform ( uniform =true), then for each dimension i it is enough to specify the lower (inclusive) boundary of the 0-th histogram bin and the upper(exclusive) boundary for the last histogram bin histSize[i]-1. That is, in case of a uniform histogram each of ranges[i] is an array of 2 elements. When the histogram is not uniform ( uniform=false ), then each of ranges[i] contains histSize[i]+1 elements:. The array elements, that are not between and , are not counted in the histogram.
- 用于指出直方图每一维的每个bin的上下界范围数组的数组,当直方图是均匀的(uniform =true)时,对每一维i指定直方图的第0个bin的下界(包含即[)L0和最后一个即第histSize[i]-1个bin的上界(不包含的即))U_histSize[i]-1,也就是说对均匀直方图来说,每一个ranges[i]都是一个两个元素的数组【指出该维的上下界】。当直方图不是均匀的时,每一个ranges[i]数组都包含histSize[i]+1个元素:L0,U0=L1,U1=L1,...,U_histSize[i]-2 = L_histSize[i]-1,U_histSize[i]-1.不在L0到U_histSize[i]-1之间的数组元素将不会统计进直方图中;
[在例子1中采用的是均匀直方图,所以范围为0-255]
uniform – Flag indicates that whether the histogram is uniform or not (see above).
- 直方图是否均匀的标志;【指定直方图每个bin统计的是否是相同数量的灰度级】
[例子1中为true]
accumulate – Accumulation flag. If it is set, the histogram is not cleared in the beginning when it is allocated.
This feature enables you to compute a single histogram from several sets of arrays, or to update the histogram in time.
-累加标志;
[单幅图像不进行累计所以例子1中为false]
参数中最难理解的应该就是channels和ranges这两个参数,以及histSize和ranges这两个参数的关系,关于histSize和ranges的关系也就涉及了ranges的意义,关于它们的关系在《学习OpenCV中文版》09.10第一版的page:219-220有比较清楚的说明。
【channels参数,自己也不是很明确,等看看该函数的源码之后再说】。
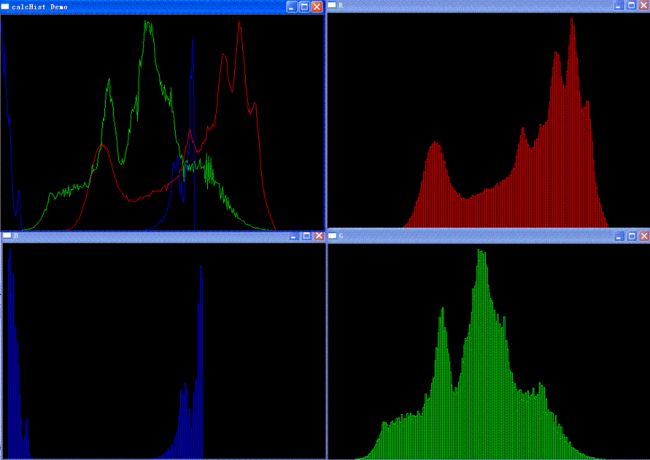
使用上面第一个例子获得的lena的hsv直方图如下:直接在RGB基础上修改的,所以窗口名字对应R-V,G-S,B-H。
手册中该函数的介绍之后有个例子,是计算图像的2维H-S直方图的,就是上面的例子2(稍微进行了一点修改);
这个例子中的参数分别为:
参数1:&hsv,一幅HSV三通道的彩色图像指针;
参数2:1,因为参数1是一幅图像;
参数3:channels,数组包含两个元素:0,1;--指明要统计的是通道0和通道1的数据??--不确定是否是这样的!
参数4:Mat(),为空,不使用掩膜;
参数5:hist,输出2D直方图,MatND,也就是Mat;
参数6:2,2维直方图;
参数7:histSize,两个元素的数组,指明每一维的bin的个数,上面的例子2中,h的为60,s的为64;
参数8:ranges,指出bin的范围的数组的数组,因为后面的uniform标志为true,也就是均匀直方图,所以每一维由一个两个元素的数组指出上下限;
参数9:true,也就是采用均匀直方图;
参数10:false,不使用累积;
第二个例子给出的2维直方图中,水平的是h分量,垂直的是s分量,下面是lena的H-S直方图图像:

可以看出,h分量也就是H-S直方图的垂直投影集中在0和60左右,对应到hsv空间也就是色相为红色部分,从例子1的h分量直方图以及直观的看lena原始图像也可以看出来,
而s分量,也就是水平投影,集中在中间部分,从例子1的s分量的直方图中也可以看出;
而且如果将这个H-S二维直方图的每一维的bin数量设置的与上面的例1中一样,然后在分别向垂直方向和水平方向投影,获得的两个投影直方图应该与例1中的对应
直方图是一样的。