理解linux虚拟文件系统VFS - 路径查找 path_lookup
路径查找是VFS的一个主要操作:给定一个文件名,获取该文件名的inode。路径查找是VFS中相当繁琐的一部分,主要是符号链接,文件系统装载点,以及. ..和//等奇怪路径 引入了复杂性。
nameidata数据结构
查找过程涉及到很多函数调用,在这些调用过程中,nameidata起到了很重要的作用:1. 向查找函数传递参数;2. 保存查找结果。
struct nameidata {
struct dentry *dentry;
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct qstr last;
unsigned int flags;
int last_type;
unsigned depth;
char *saved_names[MAX_NESTED_LINKS + 1];
/* Intent data */
union {
struct open_intent open;
} intent;
};
查找完成后@dentry 包含了找到文件的dentry目录项; @mnt 包含了文件目录项所在的vfsmount
@last 包含了需要查找的名称,这是一个快速字符串,除了路径字符串本身外,还包含字符串的长度和一个散列值
@depth 当前路径深度。
@saved_names: 由于在符号链接处理时,nd的名字一直发生变化,这里用来保存符号链接处理中的路径名
内核路径查找的函数很多,我们这里以 path_lookup为列,内核版本2.6.24
path_lookup
int fastcall path_lookup(const char *name, unsigned int flags,
struct nameidata *nd)
{
return do_path_lookup(AT_FDCWD, name, flags, nd);
}
给定三个参数@name是文件路径名(可以是全路径,也可以是相对路径名);@flags路径查找标记;@nd此时不包含任何有用信息,用来返回查找结果。
do_path_lookup
1119 static int fastcall do_path_lookup(int dfd, const char *name,
1120 unsigned int flags, struct nameidata *nd)
1121 {
1122 int retval = 0;
1123 int fput_needed;
1124 struct file *file;
1125 struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
1126
1127 nd->last_type = LAST_ROOT; /* if there are only slashes... */
1128 nd->flags = flags;
1129 nd->depth = 0;
1130
1131 if (*name=='/') {
1132 read_lock(&fs->lock);
1133 if (fs->altroot && !(nd->flags & LOOKUP_NOALT)) {
1134 nd->mnt = mntget(fs->altrootmnt);
1135 nd->dentry = dget(fs->altroot);
1136 read_unlock(&fs->lock);
1137 if (__emul_lookup_dentry(name,nd))
1138 goto out; /* found in altroot */
1139 read_lock(&fs->lock);
1140 }
1141 nd->mnt = mntget(fs->rootmnt);
1142 nd->dentry = dget(fs->root);
1143 read_unlock(&fs->lock);
1144 } else if (dfd == AT_FDCWD) {
1145 read_lock(&fs->lock);
1146 nd->mnt = mntget(fs->pwdmnt);
1147 nd->dentry = dget(fs->pwd);
1148 read_unlock(&fs->lock);
1149 } else {
1150 struct dentry *dentry;
1151
1152 file = fget_light(dfd, &fput_needed);
1153 retval = -EBADF;
1154 if (!file)
1155 goto out_fail;
1157 dentry = file->f_path.dentry;
1158
1159 retval = -ENOTDIR;
1160 if (!S_ISDIR(dentry->d_inode->i_mode))
1161 goto fput_fail;
1162
1163 retval = file_permission(file, MAY_EXEC);
1164 if (retval)
1165 goto fput_fail;
1166
1167 nd->mnt = mntget(file->f_path.mnt);
1168 nd->dentry = dget(dentry);
1169
1170 fput_light(file, fput_needed);
1171 }
1172
1173 retval = path_walk(name, nd);
1174 out:
1175 if (unlikely(!retval && !audit_dummy_context() && nd->dentry &&
1176 nd->dentry->d_inode))
1177 audit_inode(name, nd->dentry);
1178 out_fail:
1179 return retval;
1180
1181 fput_fail:
1182 fput_light(file, fput_needed);
1183 goto out_fail;
1184 }
这个函数有一点长,但是逻辑很清楚,即为调用path_walk做准备,在进入do_path_lookup函数时,参数@nd不包含任何有用信息,而调用path_walk时,@nd则包含了查找起始点信息
因此从1127~1171行就是准备查找起始点的过程,这里分为三种情况:
1. 1131~1143 文件名包含绝对路径,因此我们优先使用文件系统的根目录作为查找起始点
2. 1144 ~ 1148 路径不是绝对路径,我们指定从当前目录开始开始查找
3. 1149 ~ 1171 函数第一个参数@dfd是一个目录文件描述符,我们就从这个目录开始查找。
1173 一切就绪,调用path_walk开始查找。
path_walk
1042 static int fastcall path_walk(const char * name, struct nameidata *nd)
1043 {
1044 current->total_link_count = 0;
1045 return link_path_walk(name, nd);
1046 }
符号链接是需要特殊处理的,一般情况下我们都会跟踪链接,如果没有符号链接,那么文件系统的必定是一个完美的树结构,符号链接使得这棵树不那么完美,有时可能会导致树内存在循环,所以路径查询时,会对跟进符号链接的数目有一个最大限制,2.6.24硬编码为40
1044 在开始一次新查找之前,我们初始化为0
link_path_walk
1018 static int fastcall link_path_walk(const char *name, struct nameidata *nd)
1019 {
1020 struct nameidata save = *nd;
1021 int result;
1022
1023 /* make sure the stuff we saved doesn't go away */
1024 dget(save.dentry);
1025 mntget(save.mnt);
1026
1027 result = __link_path_walk(name, nd);
1028 if (result == -ESTALE) {
1029 *nd = save;
1030 dget(nd->dentry);
1031 mntget(nd->mnt);
1032 nd->flags |= LOOKUP_REVAL;
1033 result = __link_path_walk(name, nd);
1034 }
1035
1036 dput(save.dentry);
1037 mntput(save.mnt);
1038
1039 return result;
1040 }
这个函数看起来也有点烦,主要是有的函数会返回ESTALE错误,此时需要重新执行路径查找,并且不要使用dcache。
我们这里不care这种特殊情况,因此只需要考虑__link_path_walk
__link_path_walk
这个函数接近200行,超出了我的大脑空间处理能力,因此分段阅读
826 static fastcall int __link_path_walk(const char * name, struct nameidata *nd)
827 {
828 struct path next;
829 struct inode *inode;
830 int err;
831 unsigned int lookup_flags = nd->flags;
832
833 while (*name=='/')
834 name++;
835 if (!*name)
836 goto return_reval;
837
838 inode = nd->dentry->d_inode;
839 if (nd->depth)
840 lookup_flags = LOOKUP_FOLLOW | (nd->flags & LOOKUP_CONTINUE);
833~836首先处理掉路径名前的/,
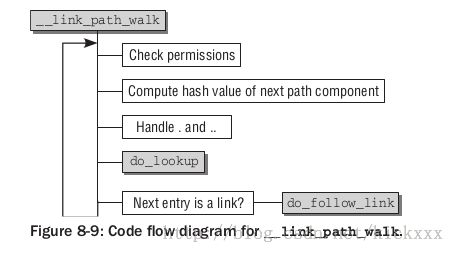
紧接着是一个大的循环,逐个路径分量进行处理。@name在循环内分解为各个路径分量。每个分量表示一个路径名。下图给出了代码流程图
权限检查
848 nd->flags |= LOOKUP_CONTINUE; 849 err = exec_permission_lite(inode, nd); 850 if (err == -EAGAIN) 851 err = vfs_permission(nd, MAY_EXEC); 852 if (err) 853 break;
计算路径分量hash
855 this.name = name;
856 c = *(const unsigned char *)name;
857
858 hash = init_name_hash();
859 do {
860 name++;
861 hash = partial_name_hash(c, hash);
862 c = *(const unsigned char *)name;
863 } while (c && (c != '/'));
864 this.len = name - (const char *) this.name;
865 this.hash = end_name_hash(hash);
处理.和..
874 /*
875 * "." and ".." are special - ".." especially so because it has
876 * to be able to know about the current root directory and
877 * parent relationships.
878 */
879 if (this.name[0] == '.') switch (this.len) {
880 default:
881 break;
882 case 2:
883 if (this.name[1] != '.')
884 break;
885 follow_dotdot(nd);
886 inode = nd->dentry->d_inode;
887 /* fallthrough */
888 case 1:
889 continue;
890 }
“.”表示当前路径,那么我们只需略过这个路径分量,开始处理下一个路径分量即可。
".."表示回到父目录,调用follow_dotdot即可,follow_dotdot并不像看起来那么简单,因为还要考虑安装点的存在
重新计算hash
891 /*
892 * See if the low-level filesystem might want
893 * to use its own hash..
894 */
895 if (nd->dentry->d_op && nd->dentry->d_op->d_hash) {
896 err = nd->dentry->d_op->d_hash(nd->dentry, &this);
897 if (err < 0)
898 break;
899 }
有些文件系统有他们自己的hash计算函数,比如fat文件系统并不区分大小写字母,因此hash函数需要做相应更改。
do_lookup
900 /* This does the actual lookups.. */ 901 err = do_lookup(nd, &this, &next); 902 if (err) 903 break;
这个函数后面会重点介绍
处理符号链接
913 if (inode->i_op->follow_link) {
914 err = do_follow_link(&next, nd);
915 if (err)
916 goto return_err;
917 err = -ENOENT;
918 inode = nd->dentry->d_inode;
919 if (!inode)
920 break;
921 err = -ENOTDIR;
922 if (!inode->i_op)
923 break;
924 } else
925 path_to_nameidata(&next, nd);
当inode->i_op->follow_link不为空时,说明这个inode对应的文件是一个符号链接文件,否则必定为空
do_follow_link用来处理符号链接的情况
924~925 不为符号链接,那么把next的结果赋给返回值@nd
do_lookup
779 /*
780 * It's more convoluted than I'd like it to be, but... it's still fairly
781 * small and for now I'd prefer to have fast path as straight as possible.
782 * It _is_ time-critical.
783 */
784 static int do_lookup(struct nameidata *nd, struct qstr *name,
785 struct path *path)
786 {
787 struct vfsmount *mnt = nd->mnt;
788 struct dentry *dentry = __d_lookup(nd->dentry, name);
789
790 if (!dentry)
791 goto need_lookup;
792 if (dentry->d_op && dentry->d_op->d_revalidate)
793 goto need_revalidate;
794 done:
795 path->mnt = mnt;
796 path->dentry = dentry;
797 __follow_mount(path);
798 return 0;
799
800 need_lookup:
801 dentry = real_lookup(nd->dentry, name, nd);
802 if (IS_ERR(dentry))
803 goto fail;
804 goto done;
805
806 need_revalidate:
807 dentry = do_revalidate(dentry, nd);
808 if (!dentry)
809 goto need_lookup;
810 if (IS_ERR(dentry))
811 goto fail;
812 goto done;
813
814 fail:
815 return PTR_ERR(dentry);
816 }
@nd 是输入参数,这个结构指定了查找的父目录项以及它所在的vfsmount
@name 输入参数,指定了路径分量名称。
@path 输出参数,保存查找结果。
788 在dentry cache中根据父dentry和路径分量名称查找,如果找到则在标号done中对path赋值,__follow_mount处理装载点的情况
790 如果没有在dentry cache中找到,那么就要调用底层文件系统的lookup进行查找了,real_lookup会调用底层lookup函数
792 如果存在dentry->d_op->d_revalidate,那么dentry cache中的目录项不一定是最新的,VFS并没有实现这个函数,但是为底层文件系统提供了这个接口,比如NFS文件系统,可能会导致本地dentry cache和远程文件内容不同步,我们不care这种情况。
__follow_mount
follow mount有两个版本,__follow_mount和follow_mount,差别不大。分析一个,另外一个其义自现
689 /* no need for dcache_lock, as serialization is taken care in
690 * namespace.c
691 */
692 static int __follow_mount(struct path *path)
693 {
694 int res = 0;
695 while (d_mountpoint(path->dentry)) {
696 struct vfsmount *mounted = lookup_mnt(path->mnt, path->dentry);
697 if (!mounted)
698 break;
699 dput(path->dentry);
700 if (res)
701 mntput(path->mnt);
702 path->mnt = mounted;
703 path->dentry = dget(mounted->mnt_root);
704 res = 1;
705 }
706 return res;
707 }
这个函数代码非常的简单,复杂在于其中隐含的概念。不过很难讲清楚,有点 只可意会,不可言传的意思。
我们知道,lookup的查找路径上可能存在着安装点,举个例子:
/mnt/sdcard/sd1是一个路径,有一个sd卡内部有文件file1 file2等,我们把一个sd卡mount到/mnt/sdcard/sd1/上。
此时我们的lookup查找/mnt/sdcard/sd1/file1,当我们查找到/mnt/sdcard/sd1时,我们得到的是根文件系统的vfsmount以及/mnt/sdcard/sd1的dentry,但是如果我们想要继续找到file1,那么我们一定要转为
sd1的vfsmount以及sd1的根dentry,才能继续查找file1.
ok, __follow_mount就是干的这个事情。循环是因为在sd1 mount到/mnt/sdcard/sd1之前,已经有其他设备也mount到/mnt/sdcard/sd1上了。
从这里,我们看到了 vfsmount的中要性了,因为dentry并不能唯一确定一个目录项,必须要由vfsmount和dentry二者共同确定,缺一不可。
do_follow_link
symlink和hardlink这小哥俩给文件系统引入了许多复杂性,hardlink对文件路径查找没有影响,symlink引入了一些麻烦
637 /*
638 * This limits recursive symlink follows to 8, while
639 * limiting consecutive symlinks to 40.
640 *
641 * Without that kind of total limit, nasty chains of consecutive
642 * symlinks can cause almost arbitrarily long lookups.
643 */
644 static inline int do_follow_link(struct path *path, struct nameidata *nd)
645 {
646 int err = -ELOOP;
647 if (current->link_count >= MAX_NESTED_LINKS)
648 goto loop;
649 if (current->total_link_count >= 40)
650 goto loop;
651 BUG_ON(nd->depth >= MAX_NESTED_LINKS);
652 cond_resched();
653 err = security_inode_follow_link(path->dentry, nd);
654 if (err)
655 goto loop;
656 current->link_count++;
657 current->total_link_count++;
658 nd->depth++;
659 err = __do_follow_link(path, nd);
660 current->link_count--;
661 nd->depth--;
662 return err;
663 loop:
664 dput_path(path, nd);
665 path_release(nd);
666 return err;
667 }
在路径查找中,symlink文件本身,并不是查找的目录,查找目标是它所表示的文件路径。
为了防止路径死循环,以及那些很nasty的情况(nasty这个词只可意会,不可言传啊),linux允许最大递归次数是8次,最大连接数是40个
发生递归是656行还有可能调用到do_follow_link,因此如果递归次数超过8次,647就会返回ELOOP