C#多线程 - Mutex
互斥锁(Mutex)
互斥锁是一个互斥的同步对象,意味着同一时间有且仅有一个线程可以获取它。
互斥锁可适用于一个共享资源每次只能被一个线程访问的情况
函数:
//创建一个处于未获取状态的互斥锁
Public Mutex();
//如果owned为true,互斥锁的初始状态就是被主线程所获取,否则处于未获取状态
Public Mutex(bool owned);
如果要获取一个互斥锁。应调用互斥锁上的WaitOne()方法,该方法继承于Thread.WaitHandle类
它处于等到状态直至所调用互斥锁可以被获取,因此该方法将组织住主调线程直到指定的互斥锁可用,如果不需要拥有互斥锁,用ReleaseMutex方法释放,从而使互斥锁可以被另外一个线程所获取。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace MyTTCon
{
class shareRes
{
public static int count = 0;
public static Mutex mutex = new Mutex();
}
class IncThread
{
int number;
public Thread thrd;
public IncThread(string name, int n)
{
thrd = new Thread(this.run);
number = n;
thrd.Name = name;
thrd.Start();
}
void run()
{
Console.WriteLine(thrd.Name + "正在等待 the mutex");
//申请
shareRes.mutex.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine(thrd.Name + "申请到 the mutex");
do
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
shareRes.count++;
Console.WriteLine("In " + thrd.Name + "ShareRes.count is " + shareRes.count);
number--;
} while (number > 0);
Console.WriteLine(thrd.Name + "释放 the nmutex");
// 释放
shareRes.mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
class DecThread
{
int number;
public Thread thrd;
public DecThread(string name, int n)
{
thrd = new Thread(this.run);
number = n;
thrd.Name = name;
thrd.Start();
}
void run()
{
Console.WriteLine(thrd.Name + "正在等待 the mutex");
//申请
shareRes.mutex.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine(thrd.Name + "申请到 the mutex");
do
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
shareRes.count--;
Console.WriteLine("In " + thrd.Name + "ShareRes.count is " + shareRes.count);
number--;
} while (number > 0);
Console.WriteLine(thrd.Name + "释放 the nmutex");
// 释放
shareRes.mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IncThread mthrd1 = new IncThread("IncThread thread ", 5);
DecThread mthrd2 = new DecThread("DecThread thread ", 5);
mthrd1.thrd.Join();
mthrd2.thrd.Join();
}
}
}
System.Threading.Mutex在概念上和System.Threading.Monitor几乎完全一致,只是lock关键字用的不是它,而且它旨在进程间的同步。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace myConApp
{
class Test
{
/// <summary>
/// 应用程序的主入口点。
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool flag = false;
System.Threading.Mutex mutex = new System.Threading.Mutex(true, "Test", out flag);
//第一个参数:true--给调用线程赋予互斥体的初始所属权
//第一个参数:互斥体的名称
//第三个参数:返回值,如果调用线程已被授予互斥体的初始所属权,则返回true
if (flag)
{
Console.Write("Running");
}
else
{
Console.Write("Another is Running");
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(5000);//线程挂起5秒钟
Environment.Exit(1);//退出程序
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
运行以上代码生成的应用程序第一个实例,会得到结果
保持第一个运行状态,运行第二个实例,得到结果
以上代码中创建了一个mutex,从其参数的解释中得知,第一个调用线程将得到互斥体的初始所属权,如果不释放的话,其他的线程得不到互斥体所有权
下面看一段代码(出自 http://space.itpub.net/12639172/viewspace-448867 ),稍有改动
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace MonitorLockMutex
{
class Program
{
Thread thread1 = null;
Thread thread2 = null;
Mutex mutex = null;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
p.RunThread();
Console.ReadLine();
}
public Program()
{
mutex = new Mutex();
thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(thread1Func));
thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(thread2Func));
}
public void RunThread()
{
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
}
private void thread1Func()
{
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
TestFunc("Thread1 have run " + count.ToString() + " times");
//暂停500ms
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
private void thread2Func()
{
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
TestFunc("Thread2 have run " + count.ToString() + " times");
//暂停1500ms
Thread.Sleep(1500);
}
}
private void TestFunc(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", str, System.DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
}
}
}
两个线程基本上是按照各自的时间间隔+TestFunc的执行时间对TestFunc函数进行读取
将公共调用的函数加锁
private void TestFunc(string str)
{
lock (this)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", str, System.DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
}
}
再次运行查看结果,好像没什么区别?
加入mutex
private void thread1Func()
{
mutex.WaitOne();
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
TestFunc("Thread1 have run " + count.ToString() + " times");
//暂停500ms
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
private void thread2Func()
{
mutex.WaitOne();
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
TestFunc("Thread2 have run " + count.ToString() + " times");
//暂停1500ms
Thread.Sleep(1500);
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
再次运行查看结果。
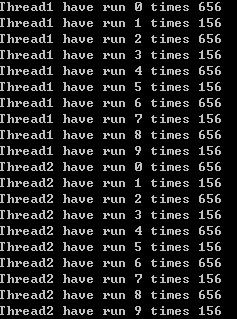
想到了什么?thread1Func() 或者thread2Func()中的全部执行完毕,之后释放互斥体,然后剩下的那个才可以访问。
再改动一次
private void thread1Func()
{
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
lock (this)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
TestFunc("Thread1 have run " + count.ToString() + " times");
//暂停500ms
Thread.Sleep(500);
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
private void thread2Func()
{
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
lock (this)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
TestFunc("Thread2 have run " + count.ToString() + " times");
//暂停1500ms
Thread.Sleep(1500);
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
看效果……
轮换执行……