使用VC++2010扩展python
使用VC++2010扩展python
简介:这里介绍使用VC2010编译C语言编写的python扩展模块,hdlc模块。Hdlc是高级数据链路控制(High-LevelData Link Control或简称HDLC),用于无界流数据上确保用户数据包的完整性。该模块接口应该是用hdlc_pkt = hdlc.pack(buf)把无界流数据buf打包成一个hdlc数据包hdlc_pkt,使用pkt,passlen = hdlc.unpack(buf)把hdlc_pkt数据包还原为pkt数据包,passlen是在buf上读取过的数据长度。
VC新建项目,选用win32的win32项目,输入python的模块名hdlc(源码文件见文档附录)
确定后在选择里选择dll,空项目
复制c文件到项目目录下,然后在VC添加文件。
完成源码文件的添加
配置项目属性:(release版本,不要debug版本)
1. 配置属性》常规,把目标文件扩展名改为.pyd
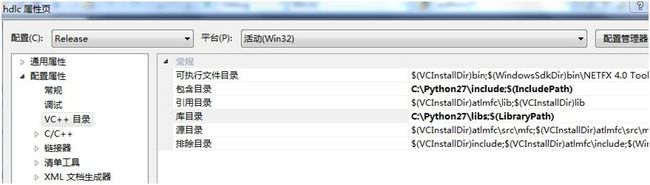
2. 添加python头文件目录与库目录
在项目属性的VC++目录页面,添加python的库目录和头文件目录
3. 去除预编译,在c/c++的预编译头,不适用预编译头
4. 选择release版本,然后编译,生成-》生成hdlc
完成python的C语言扩展模块的编译。
使用扩展模块
把Projects\hdlc\Release\hdlc.pyd这个pyd文件复制到python安装目录的dlls目录下,即可在python中import使用。
测试该模块
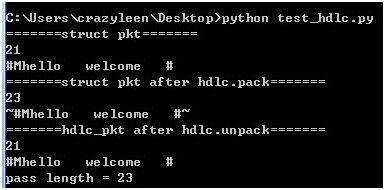
测试脚本
#!/usr/bin/python
import struct
import hdlc
#help(hdlc)
#help(struct)
pkt = struct.pack('cc8s10sc', '#', 'M', 'hello','welcome', '#')
print '=======struct pkt======='
print len(pkt)
print pkt
hdlc_pkt = hdlc.pack(pkt)
print '=======struct pkt after hdlc.pack======='
print len(hdlc_pkt)
print hdlc_pkt
rec_pkt,passlen = hdlc.unpack(hdlc_pkt)
print '=======hdlc_pkt after hdlc.unpack======='
print len(rec_pkt)
print rec_pkt
print 'pass length = %d' % passlen
结果输出
附录
头文件hdlc.h
/********************************************************
* HDLC(High level Data Link Control protocol) head
* 2012.07.28 -crazyleen
* Changeparameter type
*********************************************************/
#ifndef __HDLC_H__
#define __HDLC_H__
#ifndef __uint8_t
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
#endif
#ifndef __int32_t
typedef int __int32_t;
#endif
/* define HDLC control struct */
typedef struct _HDLC
{
__uint8_t state; /*HDLC process state */
__uint8_t *recv_buffer; /* receive destination buffer pointer */
__int32_t recv_buffer_length; /* receive destination buffer length in bytes*/
__int32_t recvd_length; /* the counter of received bytes */
}HDLC;
/**
*hdlc_init_recv - Init receive buffer for the HDLC object. The object save
* the buffer and the max lengthfor process control.
* @hdlc: HDLC control object pointer
* @buffer: The receive buffer pointer for this HDLCcontrol object
*@buffer_length: The max receive bufferlength
* @return: 0success, -1 failed
*/
int hdlc_init_recv(HDLC *hdlc, void *buffer, intbuffer_length);
/**
*hdlc_recv_char - Receiving one char and set it into data stream buffer.
* @hdlc: HDLC control object pointer
* @ch: A new byte of received data stream
* @return:
* > 0 --> the data queue length ofreceived packet.
* 0 --> the receiving is not complete.
* -1--> receive buffer overflow, failed.
*/
int hdlc_recv_char(HDLC *hdlc, unsigned char ch);
/**
*hdlc_send_buffer - Make data queue with HDLC, from src to dst.
* @dst HDLC destination buffer pointer
* @src source data stream buffer pointer
* @srclen source data stream length
* @return:Returns the HDLC data queue length of dst buffer.
*/
int hdlc_send_buffer(void *dst, const void *src, intsrclen);
#endif/* __HDLC_H__ */
源码文件hdlc.c
/********************************************************
* HDLC(Highlevel Data Link Control protocol)
* 2012.07.28-crazyleen
* Change parameter type
*********************************************************/
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "hdlc.h"
/****************************************************************
* HDLC is atype of Data_Link_Level protocols.
* It uses 0x7eand 0x7d as the keywords for data packet control.
*
* Every packetis defined by a pair of 0x7e
* 0x7e ...data... 0x7e
*
* If 0x7e or0x7d has been in the data queue, uses 0x7d to indicate
* it.
* When the datais 0x7e, it will be indicated by these 2 bytes
* 0x7e --> 0x7d, 0x5e
* When the datais 0x7d, it will be indicated by these 2 bytes
* 0x7d--> 0x7d, 0x5d
*
*****************************************************************/
/* define HDLC keywords */
#define HDLC_KEY_FLAG 0x7e
#define HDLC_KEY_ESC 0x7d
/* define portreceive state */
#define HDLC_ST_NOSYNC 0
#define HDLC_ST_SYNC 1
#define HDLC_ST_INFO 2
#define HDLC_ST_ESC 3
#define HDLC_ST_INACTIVE 4
/**
*hdlc_init_recv - Init receive buffer for the HDLC object. The object save
* the buffer and the max lengthfor process control.
* @hdlc HDLC control object pointer
* @buffer The receive buffer pointer for this HDLCcontrol object
*@buffer_length The max receive bufferlength
* @return: 0success, -1 failed
*/
int hdlc_init_recv(HDLC *hdlc, void *buffer, intbuffer_length) {
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_NOSYNC;
hdlc->recv_buffer= (__uint8_t *)buffer;
hdlc->recv_buffer_length= buffer_length;
hdlc->recvd_length= 0;
return 0;
}
/**
*hdlc_recv_char - Receiving one char and set it into data stream buffer.
* @hdlc: HDLC control object pointer
* @ch: A new byte of received data stream
* @return:
* > 0 --> the data queue length ofreceived packet.
* 0 --> the receiving is not complete.
* -1--> receive buffer overflow, failed.
*/
int hdlc_recv_char(HDLC *hdlc, unsigned char ch) {
int ret;
int i;
switch(hdlc->state) {
caseHDLC_ST_NOSYNC:
if (ch ==HDLC_KEY_FLAG) {
hdlc->recvd_length= 0;
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_SYNC;
}
break;
caseHDLC_ST_SYNC:
if (ch !=HDLC_KEY_FLAG) /* the next byte after 0x7e must not be 0x7e */
{
if(ch == HDLC_KEY_ESC) {
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_ESC;
}else {
if(hdlc->recvd_length == hdlc->recv_buffer_length) /* packet lengthoverflow */
{
printf(
"packetlength overflow at HDLC_ST_SYNC, recvd_length is \
%d,recv_buffer_length is %d\n",
hdlc->recvd_length,hdlc->recv_buffer_length);
for(i = 0; i < hdlc->recvd_length; i++)
printf("%.2x", hdlc->recv_buffer[i]);
printf("%.2x", ch);
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_INACTIVE;
return0;
//return-1;
}
hdlc->recv_buffer[hdlc->recvd_length]= ch; /* save the first byte */
hdlc->recvd_length++;
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_INFO;
}
}
break;
caseHDLC_ST_INFO:
if (ch ==HDLC_KEY_FLAG) {
//thisis not a user data -crazyleen
//hdlc->recvd_length++;
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_NOSYNC;
ret =hdlc->recvd_length;
hdlc->recvd_length= 0;
returnret; /* receive done */
} else if(ch == HDLC_KEY_ESC) {
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_ESC;
} else {
if(hdlc->recvd_length == hdlc->recv_buffer_length) /* packet lengthoverflow */
{
printf(
"packetlength overflow at HDLC_ST_INFO, recvd_length is \
%d,recv_buffer_length is %d\n",
hdlc->recvd_length,hdlc->recv_buffer_length);
for(i = 0; i < hdlc->recvd_length; i++)
printf("%.2x", hdlc->recv_buffer[i]);
printf("%.2x", ch);
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_INACTIVE;
return0;
//return-1;
}
hdlc->recv_buffer[hdlc->recvd_length]= ch;
hdlc->recvd_length++;
}
break;
case HDLC_ST_ESC:
if(hdlc->recvd_length == hdlc->recv_buffer_length) /* packet lengthoverflow */
{
printf(
"packetlength overflow at HDLC_ST_ESC, recvd_length is \
%d,recv_buffer_length is %d\n",
hdlc->recvd_length,hdlc->recv_buffer_length);
for(i = 0; i < hdlc->recvd_length; i++)
printf("%.2x", hdlc->recv_buffer[i]);
printf("%.2x", ch);
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_INACTIVE;
return0;
//return-1;
}
hdlc->recv_buffer[hdlc->recvd_length]= (ch ^ 0x20); /* get 0x7d or 0x7e */
hdlc->recvd_length++;
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_INFO;
break;
caseHDLC_ST_INACTIVE:
if (ch ==HDLC_KEY_FLAG) {
printf("\n");
hdlc->recvd_length= 0;
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_NOSYNC;
return0;
}
printf("%.2x", ch);
break;
default:
hdlc->state= HDLC_ST_NOSYNC;
break;
}/* endswtich */
return 0;
}
/**
*hdlc_send_buffer - Make data queue with HDLC, from src to dst.
* @dst HDLC destination buffer pointer
* @src source data stream buffer pointer
* @srclen source data stream length
* @return:Returns the HDLC data queue length of dst buffer.
*/
int hdlc_send_buffer(void *dst, const void *src, intsrclen) {
int i, len =0;
__uint8_t*pdst = (__uint8_t *)dst;
const__uint8_t *psrc = (const __uint8_t *)src;
/* start flag*/
*pdst++ =HDLC_KEY_FLAG;
len++;
for (i = 0; i< srclen; i++, psrc++) {
if (*psrc== HDLC_KEY_FLAG) {
*pdst++= HDLC_KEY_ESC;
*pdst++= 0x5e;
len+= 2;
} else if(*psrc == HDLC_KEY_ESC) {
*pdst++= HDLC_KEY_ESC;
*pdst++= 0x5d;
len+= 2;
} else {
*pdst++= *psrc;
len++;
}
}/* end for*/
/* end flag;*/
*pdst =HDLC_KEY_FLAG;
len++;
return len;
}
模块扩展源文件hdlcmodule.c
#include <Python.h>
#include "hdlc.h"
static PyObject* hdlc_pack(PyObject* self, PyObject*args) {
int srclen;
int dstlen;
const char*src = NULL;
char *dst =NULL;
PyObject*result = NULL;
//TODO: getbinary stream from args
if(!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "s#", &src, &srclen)) {
returnNULL;
}
//max lengthaccording to hdlc protocol
dstlen =srclen * 2 + 3;
dst = (char*)PyMem_Malloc(dstlen);
if(dst ==NULL){
returnPyErr_NoMemory();
}
dstlen =hdlc_send_buffer(dst, src, srclen);
result =Py_BuildValue("s#", dst, dstlen);
PyMem_Free(dst);
returnresult;
}
static PyObject* hdlc_unpack(PyObject* self, PyObject*args) {
int srclen;
int dstlen;
int retlen;
const char*src = NULL;
const char*src_head = NULL;
char *dst =NULL;
HDLC hdlc;
PyObject*result = NULL;
//TODO: getbinary stream from args
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args,"s#", &src, &srclen)) {
returnNULL;
}
//max lengthaccording to hdlc protocol
dstlen =srclen;
dst = (char*)PyMem_Malloc(dstlen);
if(dst ==NULL){
returnPyErr_NoMemory();
}
hdlc_init_recv(&hdlc,dst, dstlen);
retlen = 0;
src_head =src;
while(srclen--> 0 && retlen == 0){
retlen =hdlc_recv_char(&hdlc, *src++);
}
//return atuple(data, readlen)
result =Py_BuildValue("s#,i", dst, retlen, (int)(src - src_head));
PyMem_Free(dst);
returnresult;
}
static PyMethodDef hdlcMethods[] = {
{"pack", hdlc_pack, METH_VARARGS, "pack data queue withHDLC." },
{"unpack", hdlc_unpack, METH_VARARGS,
"unpackdata queue with HDLC. Return a tuple containing unpacked data and length ofread data.(data, len)" },
{ NULL,NULL }
};
PyMODINIT_FUNC inithdlc() {
PyObject* m;
m =Py_InitModule("hdlc", hdlcMethods);
}
Linux系统下使用的Makefile
#compile so file for python
CC = gcc
CFLAG = -Wall -o2
INCLUDE = -I/usr/include/python2.6/
all: example.so
%.o:%.c
${CC} ${CFLAG}${INCLUDE} -fpic -c $< -o $@
example_obj=example.o wrap.o
example.so: ${example_obj}
${CC}${CFLAG} -shared $^ -o $@
.PYONY: clean
clean:
rm *.so *.o