解剖linux内核之文件系统
虚实结合
文件系统主要分为两个部分:vfs和ext2(以ext2为例),一虚一实,vfs是在机子启动的时候在内存中建立的,机子关掉便不存在了,是虚的;ext2是在磁盘介质上的,是磁盘在格式化的时候确定的,机子关机后仍然在磁盘上存在。
在磁盘上的ext2文件系统那个的格式如下:
Ext2中与superblock对应的结构体是
struct ext2_super_block {
__u32 s_inodes_count; /* Inodes count */ 12214272
__u32 s_blocks_count; /* Blocks count */ 48827904
…
__u32 s_blocks_per_group; /* # Blocks per group */32768
__u32 s_inodes_per_group; /* # Inodes per group */8192
….
};
与block group对应的结构体是:
struct ext2_group_desc
{
__u32 bg_block_bitmap; /* Blocks bitmap block*/
/*所表示的块组中的block bitmap所在块号 */
__u32 bg_inode_bitmap; /* Inodes bitmap block */
/*所表示的块组中的inode bitmap所在块号 */
__u32 bg_inode_table; /* Inodes table block */
/*所表示的块组中的inode table所在块号 */
__u16 bg_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */
__u16 bg_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */
__u16 bg_used_dirs_count; /* Directories count */
__u16 bg_flags;
__u32 bg_reserved[2];
__u16 bg_itable_unused; /* Unused inodes count */
__u16 bg_checksum; /* crc16(s_uuid+grouo_num+group_desc)*/
};
Block bimap与inode bitmap在ext2中没有对应的结构体,inodetable对应的结构体为:
truct ext2_inode {
__le16 i_mode; /* File mode ,描述的文件类型及其访问权限*/
…
__le32 i_size; /* Size in bytes ,描述的文件大小*/
….
__le32 i_blocks; /* Blocks count *,由下面推断为2^29? /
…
__le32 i_block[EXT3_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers toblocks ,指向文件数据所在block,使用12个直接索引,1个一级,1个2级,1个3级索引。Inode需要4byte记录一个block,所以可以记录的单文件最大为:12×4K+4096/4×4K+4096/4×4096/4×4K+4096/4×4096/4×4096/4×4K大约是4TB,但是由于上面i_blocks的限制,只能达到2TB*/
…
};
关于ext2文件系统的这些信息均可以通过dumpe2fs 了来获得,下面截取dumpe2fs
/dev/sda8:
…
Filesystem OS type: Linux
Inode count: 12214272
Block count: 48827904
Reserved block count: 2441395
Free blocks: 30065278
Free inodes: 12207259
First block: 0
Block size: 4096
…
Group 0: (Blocks 0-32767)
Primarysuperblock at 0, Group descriptors at 1-12
ReservedGDT blocks at 13-1024
Blockbitmap at 1025 (+1025), Inode bitmap at 1026 (+1026)
Inodetable at 1027-1538 (+1027)
31223free blocks, 8181 free inodes, 2 directories
Freeblocks: 1545-32767
Freeinodes: 12-8192
…
VFS层的数据结构与ext2文件系统对应的数据结构有structsuper_block,struct inode。另外在vfs层还增添了许多其他的数据结构,我们先来看在内存中的super block、inode与在磁盘上具体的ext2的super block、inode的对应关系。
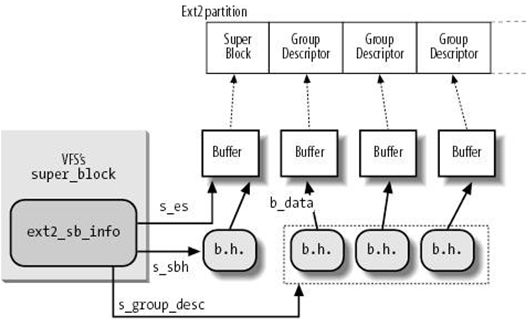
super block的对应是通过structext2_sb_info结构体建立起来的:
在vfs层没有与blockgroup descriptor对应的结构体,ext2的块组描述符直接在buffer head所指向的page中。
inode的对应关系是通过struct ext2_inode_info既然钩体建立起来的:
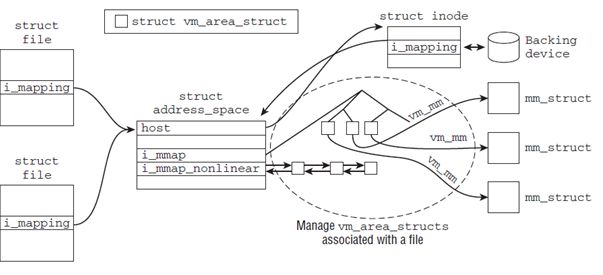
Memory pages是文件中的数据在内存中的存在形式,内核使用红黑树来组织;Data Blocks是数据在磁盘上的组织,ext2中的ext2_inode使用12个直接索引,1个一级索引,1个二级索引,1个三级索引来记录文件数据所在的数据块。
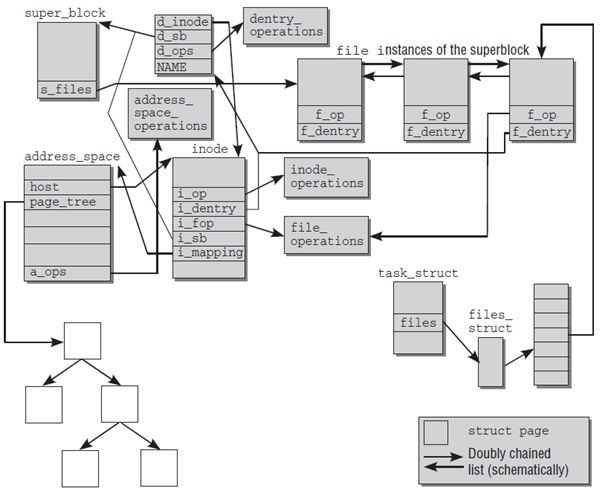
在磁盘上每一个ext2_inode对应一个文件,在VFS层的structinode对应于一个打开的文件,VFS层与打开文件相关的另外一个结果体是struct file。struct file主要针对的是对文件数据的操作(内嵌struct file_operations 结构体),structinode主要针对该文件属性的操作(内嵌struct inode_operations 结构体),前者的f_mapping与后者的i_mapping均指向的是文件的数据在内存中的page。另外struct file是从属于进程的,struct inode是属于文件,即不同的进程打开同一个文件的时候,会有多个struct file但是只有一个struct inode。
VFS中的structsuper_block结构体中的s_files记录了本文件系统中打开的所有文件;struct task_struct中的files记录了该进程打开的所有文件信息。
进程的task_struct中还记录了改进程的虚拟线性地址空间,那么该线性地址与具体的数据是怎么联系在一起的呢?
打印打开的所有文件信息
进程打开的所有文件均会在该进程的结构体中,那么每个进程到底打开了多少文件呢?
1 %{
2 #include <linux/list.h>
3 #include <linux/sched.h>
4 #include <linux/fdtable.h>
5 #include <linux/fs.h>
6 #include <linux/mm_types.h>
7 #include <linux/rcupdate.h>
8 #include <linux/gfp.h>
9 #include <linux/dcache.h>
10 %}
11 function process_list ()
12 %{
13 struct task_struct *p;
14 struct file *filp;
15 char *path=NULL;
16 char *page=NULL;
17 int fd;
18 for_each_process(p){
19 _stp_printf("%s %d openfiles:\n",p->comm,p->pid);
20 for(fd=0;fd<1024;fd++){
21 filp=fcheck_files(p->files,fd);
22 if(!filp)
23 continue;
24 page=(char*)__get_free_page(GFP_KERNEL);
25 path=d_path(&filp->f_path,page,PAGE_SIZE);
26 if(page)
27 free_page((unsigned long)page);
28 _stp_printf("\tfd:%d path:%s\n",fd,path);
29 }
30 }
31 %}
32
33 probe begin
34 {
35 process_list();
36 exit();
37 }
部分输出结果如下:
1 init 1 open files:
2 fd:0 path:/dev/null
3 fd:1 path:/dev/null
4 fd:2 path:/dev/null
5 fd:3 path:pipe:[6534]
6 fd:4 path:pipe:[6534]
7 fd:5 path:anon_inode:inotify
8 fd:6 path:anon_inode:inotify
9 fd:7 path:socket:[7376]
10 fd:8 path:socket:[6839]
11 fd:9 path:socket:[7403]
12 fd:10 path:socket:[8258]
13 fd:11 path:socket:[6863]
14 kthreadd 2 open files:
15 ksoftirqd/0 3 open files:
16 kworker/0:0 4 open files:
17 migration/0 6 open files:
18 migration/1 7 open files:
…