Preface
In this tutorial I will explain how to view your android internal files using Eclipse DDMS perspective.
I will shortly explain about the Linux file permissions and the basic use of adb tool with illustrated examples for Windows users; however other operating system users can benefit from this article as well, because the concept is the same.
Eclipse DDMS
In order to view android internal device files in Eclipse, you will need to open the DDMS perspective:
If you do not have already the DDMS tab near the Java and Debug tabs, do as follows:
(In Eclipse Main Menu Bar)
Window -> Open Perspective -> DDMS
File Explorer
In DDMS go to File Explorer tab, you should see the folder list as you click:
There is a directory called data that we are interested in.
If you cannot open the data folder in Eclipse that means that you do not have an appropriate permission for this file.
So what we need to do is to acquire this permission, in order to access it.
Using Android adb
What is android adb?
Android adb (Android Debug Bridge) is a part of ADT (Android Development Tools) which is a command line tool that lets you communicate with android connected devices; it can be an emulator or a real hardware device.
Opening adb
The adb tool is located in your SDK location under platform-tools directory:
[Your path to SDK directory]\ platform-tools
In my case:
C:\android_sdk\platform-tools
In order to start integration with adb you need to open a CMD (Windows Command Line) in this directory.
You can simply press [SHIFT + Right mouse button] and select the [Open command window here] Option from the menu or navigate to your path:
Basic Integration with adb
All the commands with adb will be performed through the adb shell prefix, which specifies that we are going to use the Linux shell ability.
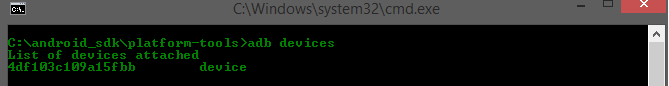
The very basic command is to see the list of connected devices.
Simply type in “adb devices”.
If you do not have any connected devices or launched emulators, you will get an empty response.
However, if you connected a device or launched an emulator you will get a similar response to mine.
The output is formatted like this:
[serial number] [state]
Other common adb commands:
adb kill-server - stops the integration port daemon process.
adb start-server - starts the integration port daemon process.
adb pull – gets specified file from android to your machine.
adb push – pushes specified file from your machine to the android
adb install – installs a package on your android device.
adb uninstall – uninstalls a package from your android device.
There are much more of adb commands and abilities, such as sqlite commands etc…
Understanding Linux file permissions
If you are looking at the File Explorer tab in Eclipse you will notice that for each file there is a permissions value:
Linux file permission convention
As you can see the permission value for each file is represented by 10 characters which are a 10 bit behind the scene.
The first character identifies the file type.
Linux File types Encoding
d – Directory file.
c – Character device.
b – Block device.
s – Local Domain Socket.
p – Named pipe.
l – Symbolic link.
- – Regular file.
These are the types of the Linux files; you don't need to understand them all. In this tutorial we will examine only the Regular file type (symbolized as ‘-‘ character) and the directory type (symbolized as ‘d’ character).
File permission overview
The first character in the permission value is the file type; the followed 9 characters represent the file permission.
For example, we have file with this permission value: -rwxrwxrwx
We can already say that it is a regular file, thus the first character (-).
The rest 9 symbols are separated by 3 parts:
User permission – This is the permission for the user who created the file, the file owner.
Group permission – In Linux each file or directory belongs to a group. Anyone who belongs to that group has these permissions for the file.
World permission – This permission is granted for everyone.
In our example, this particular file is accessible with rwx (Read/Write/Execute) permission for the owner, the group and the world, in other words, for every one.
File permission values
As we already said, the permission value is formed by 3 groups.
The value that you see in the DDMS is human readable format, but behind it there is a binary value.
--- : binary value: 000, octal value: 0
--x : binary value: 001, octal value: 1
-w- : binary value: 010, octal value: 2
-wx : binary value: 011, octal value: 3
r-- : binary value: 100, octal value: 4
r-x : binary value: 101, octal value: 5
rw- : binary value: 110, octal value: 6
rwx : binary value: 111, octal value: 7
In case you have rwx (Read/Write/Execute) permission on a file, the actual bits identifying that permission will be a binary value of 111, which in octal number system are 7 (as shown in the table bellow).
data/data directory
Directory named data holds the main data of your Android operating system.
One level bellow there is a directory called data/data which is where all of your installed applications are located, as well as their internal files, such as databases etc.
Using adb to change file permission
In my case, if you look at the snapshot that I took from my DDMS File Explorer, the permission for the data directory is: drwxrw—x
drwxrw—x means:
File type: d (Directory),
Owner permission : rwx (Read/Write/Execute),
Group permission : rwx (Read/Write/Execute),
World permission : --x (Only Execute), cannot read the internal data of the directory, or write into it.
When we use Eclipse DDMS we are considered as those with world permission. That’s why we need to acquire read and write permission for data directory, in order to access it or to make changes.
Using chmod command
chmod is a Linux command, it changes the specified file or directory mode (file permission) bits according to passed mode, which can be a symbolic or an octal value that represents the bit pattern of the new mode.
* In this tutorial we will use the octal value in our chmod command implementation, but you can simply change it to a symbolic representation if you wish.
Steps:
- Open the CMD in the [SDK location]\platform-tools directory as I described earlier.
- Type the chmod command:
adb shell su -c "chmod 777 /data"
If you get “Permission denied” from the adb, ensure that you allowed adb interaction with your device from Developer options menu.
If your device is rooted and connected, you will see now the permission of the data folder changed to –rwxrwxrwx.
Let’s examine what we just did:
The command we typed in: adb shell su -c "chmod 777 /data"
su - tells the adb shell that we are executing the command as the root user.
-c – is the su command option, which tells su to execute the command that directly follows it on the same line.
“chmod 777 /data” – tells to grand 777 permission to data directory, 777 is an octal number that stands for rwx (Read/Write/Execute) permission for all three parts (Owner, Group, World).
That’s it! Now we can access the data directory from the DDMS in Eclipse.
We need to access the data/data directory, so there is another level to grand permission to.
Notice that data/data permission is drwxrwx--x. So now we will grand the rwx for world permission to data/data directory:
Type in: adb shell su -c "chmod 777 /data/data"
Now we can see that data/data permission is changed to –rwxrwxrwx value and we can enter it:
Here (in data/data directory) you can see all the installed applications directories on your device showed as their packages names.
For Example:
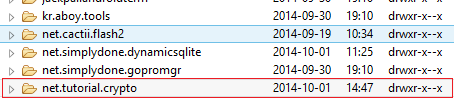
If you installed Mozilla Firefox on your device, you’ll have a directory named com.mozilla.firefox on the list.
If you launched your application named “net.tutorial.crypto” you will see this directory on the list as well.
Since the permission bellow is drwxr—x, you need to perform the same chmod command for each of the folders and their internal files.
Accessing specific Application internal files
Let’s say that I installed my application with package name net.tutorial.crypto, the default permission value will be drwxrwx—x.
In order to access it I will launch this command:
adb shell su -c "chmod 777 /data/data/net.tutorial.crypto"
Which will change the permission to drwxrwxrwx value.
To access the files folder, I will specify the desired directory name in my chmod command:
adb shell su -c "chmod 777 /data/data/net.tutorial.crypto/files".
Now you can see that there is a classified_file.txt file in the file directory with –rw------- permission. To acquire appropriate permission I will execute the chmod command as follows:
adb shell su -c "chmod 777 /data/data/net.tutorial.crypto/files/classified_file.txt".
Since classified_file.txt permission is changed to –rwxrwxrwx, I can pull it from the device and explore it on my PC.
Pull Command:
Convention: adb pull <remote path> <local path>
(Copies the file from android device to local machine)
I decided to pull it to my Download folder:
adb pull /data/data/net.tutorial.crypto/files/classified_file.txt C:\Users\Pavel\Downloads
You can use the eclipse GUI button called “Pull a file from the device” that have the same functionality, as well. Simply select the desired file and click on the button. Then select the destination and finally save.
Summery
Android is a Linux based operating system, that’s why in order to access its internal files you need to have appropriate permission for those files.
We used adb tool through which we granted the permission for our desired files, using the chmod Linux command, and explored them in Eclipse DDMS.
adb is one of the useful tools that I came across while developing for Android platform. Using its abilities can save you a lot of time and headaches. Please considerate further reading the android documentation:
http://developer.android.com/tools/help/adb.html
Hope it was helpful.
转载自: http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/825304/Accessing-internal-data-on-Android-device