Spring IoC容器在Web环境中的启动源码阅读
注:本博客中的源码都是基于Spring3.1版本
由于功底尚浅,写出来的东西没什么营养,仅助自己的理解所学内容;虽名为博客,实则为自己的学习笔记而已...
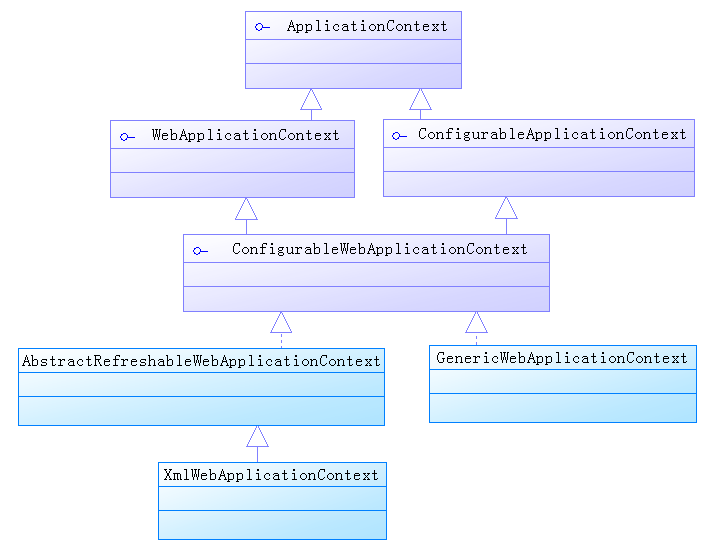
1、Spring中Web环境相关IoC容器类图
首先来看一下Spring中与Web环境相关的部分IoC容器类继承关系图:
在上图所示的类继承关系中,Spring在Web环境中的IoC容器通过ApplicationContext接口与BeanFactory基础IoC容器对接起来;而IoC的基本功能很多都是通过AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext抽象类来实现的,因为该类继承了AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext抽象类,从这里与非Web高级IoC容器对接起来。
2、Spring在Web环境中的使用
Web环境中使用Spring一般有两种方式:
1. 使用ContextLoaderListener监听器启动;
2. 使用配置为load-on-startup的ContextLoaderServlet启动(该类已不建议使用,在Spring3.x中已被移除).
在这两种使用方式中,使用监听器启动Spring应该更加常见,这种启动Spring的方式首先要在web.xml中配置如下代码:
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
这里的ContextLoaderListener很明显应该是一个符合Java Servlet规范的监听器,而且Spring要承载Web应用,那么其应该在Web应用启动时载入IoC容器,所以ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口。ServletContextListener是ServletContext的监听者,该接口定义了两个方法contextInitialized和contextDestroyed会结合Web容器的生命周期进行调用,前者在Web应用初始化时进行调用,而后者在Web应用销毁时进行调用。很明显,Spring应该会在contextInitialized方法实现中将IoC容器创建并启动,而在contextDestroyed方法实现中将IoC容器销毁。
本文就是以ContextLoaderListener监听器为入口来分析Spring在Web环境中的启动过程,详见下文。
3、Spring在Web环境中的启动
3.1、ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized
因为Web服务在启动时会通知所有的ServletContextListener监听器,调用其中的contextInitialized方法,ContextLoaderListener作为ServletContextListener接口的实现,当然也会被通知到。
下面来看看Web服务启动时,ContextLoaderListener监听器在contextInitialized方法实现中完成了什么内容:
/**
* Web应用启动时初始化根Web应用上下文
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
// 从Spring3.0起createContextLoader()方法被@Deprecated了,推荐使用ContextLoaderListener自身作为ContextLoader
// 从Spring3.0开始ContextLoaderListener继承了ContextLoader类
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}从上面代码可以看出,在contextInitialized方法中先是创建了ContextLoader,然后调用其initWebApplicationContext方法来完成具体的IoC容器初始化。但从Spring3.0开始创建ContextLoader的方法createContextLoader被标记为@Deprecated不建议使用了,而是让ContextLoaderListener直接继承自ContextLoader类,因此ContextLoaderListener本身就可以完成IoC容器的初始化(直接调用ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法)。
从此处开始具体的工作就交由ContextLoader类的initWebApplicationContext方法来完成,并将由ServletContextEvent 事件对象获取的ServletContext对象作为参数传了进去。
3.2、ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 如果在ServletContext中已经有了Spring根上下文(即IoC容器)存在,则抛异常
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
// 日志代码省略
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 标记启动开始时间
try {
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); // 开始创建Spring上下文
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext((ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context, servletContext); // 配置启动IoC容器
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); // 将IoC容器放到ServletContext中
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
} else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
// 部分日志代码省略,下面得到当前时间,与启动开始时间相减可得到IoC容器启动所耗费时间
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context; // 返回Spring上下文
} catch () {
// catch代码块省略
}
}在ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法中完成了Spring根上下文在Web容器中的创建。这个上下文是作为Web容器中唯一实例而存在的,如果在初始化过程中发现ServletContext中已经有上下文存在了,则抛出异常来中断创建。上下文的创建从Spring3.1开始被分为两步:创建和启动,而在之前版本是在一个方法createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, ApplicationContext parent)中实现了创建和启动。在上下文创建成功后会被存储到Web容器的ServletContext中,需要时可以直接从中获取。存储索引由Spring预先在WebApplicationContext接口中定义:
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
// 其它代码省略
}
3.3、IoC容器的创建
上下文对象的具体创建过程定义在ContextLoader的createWebApplicationContext方法中:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc); // 这里决定使用什么样的IoC容器(根上下文类型)
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
// 直接将取得的IoC容器的Class对象实例化并返回
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
return wac;
}
在createWebApplicationContext方法中首先调用determineContextClass方法来确定使用什么样的Spring IoC容器类,在确定了使用的IoC容器后determineContextClass方法会返回所使用IoC容器类的Class对象,程序会直接将其实例化并返回。需要注意的是程序在此仅仅是使用BeanUtils工具类将IoC容器类实例化,并没有加载BeanDefinition,所以此处的IoC容器只是个空对象。
我们在此先中断一下,进到determineContextClass方法中去看看程序是如何决定所使用IoC容器种类的:
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 从web.xml中获取配置的contextClass参数值(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM是一个常量,值为contextClass)
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) { // 如果不为null,则说明我们需要使用自定义的IoC容器
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
} else { // 如果没有配置自定义的IoC容器,则使用默认的IoC容器实现(默认使用XmlWebApplicationContext类)
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
程序显示我们可以在部署描述符(web.xml文件)中指定使用什么样的IoC容器,跟指定配置文件位置类似(参数名也为常量--contextClass);如果我们没有指定需要使用的IoC容器,则程序会使用Spring默认的IoC容器:XmlWebApplicationContext类。在else语句块中可以看到默认的IoC容器类是从defaultStrategies中取得的,defaultStrategies是java.util.Properties类型的常量,在ContextLoader类的声明部分可以找到这个常量的的定义及初始化代码:
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
try {
// 创建一个ClassPathResource指向DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH文件(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH是常量,值为ContextLoader.properties)
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
// 将ContextLoader.properties配置文件中的配置项加载到defaultStrategies成员变量中
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
这是一个静态初始化块,在类被加载时执行其中的代码,代码显示初始化块首选创建了一个ClassPathResource用于代表类路径下的某个资源,该资源文件名由一个常量DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH定义,常量值为ContextLoader.properties,也就是说在ContextLoader类被加载时静态初始化块会去类路径下寻找名为ContextLoader.properties的配置文件,并将其中的内容加载到defaultStrategies常量中。
我们并没有在类路径下提供ContextLoader.properties配置文件,那这个文件在哪儿呢?我们可以在Spring提供的org.springframework.web-3.1.2.RELEASE.jar包中可以找到这个配置文件,该文件除了注释外只有一行配置,如下所示:
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
由此可以看出,Spring在Web环境下默认的IoC容器确实就是XmlWebApplicationContext类。
3.4、IoC容器的加载与启动过程
源码分析到这里,Spring上下文对象(即IoC容器)已经创建出来,但此时的IoC容器还不具有Bean管理的功能,因为这仅仅是一个空的IoC容器,还没有载入Bean定义。为了载入Bean定义并启动IoC容器,ContextLoader又调用了另外一个方法:configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法实现如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM); // 取初始化ID参数
if (idParam != null) { 如果配置文件中指定了ID参数,则使用指定的ID为上下文的唯一标识
wac.setId(idParam);
} else { // 没有配置ID参数,则根据Servlet版本生成并设置Spring上下文的唯一标识
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getServletContextName()));
} else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
}
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(sc); // 加载双亲上下文
wac.setParent(parent); //设置双亲上下文
wac.setServletContext(sc); // 将ServletContext对象存储起来
String initParameter = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM); // 获取配置的Spring配置文件参数(contextConfigLocation参数)
if (initParameter != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(initParameter); // 设置Spring配置文件
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh(); // 启动初始化IoC容器
}
在configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法中首先为创建的IoC容器设置了唯一的ID标识,然后设置双亲上下文及Spring配置文件,最后调用refresh启动容器。
至此,Spring上下文已经在Web环境中建立并启动,而且还存储在了ServletContext中,Spring在Web环境启动完成。
4、Web环境中获取Spring上下文对象( IoC容器)
从上面的源码分析中我们可以了解到,ContextLoader在创建并启动了IoC容器(XmlWebApplicationContext实现)后将期存在了ServletContext对象中,如下所示:
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); // 将IoC容器放到ServletContext中
那么我们在程序中需要使用IoC容器时就可以这样获取到Spring上下文对象了:
ApplicationContext context = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
除此之外,Spring还为我们提供了WebApplicationContextUtils工具类,其中也定义了获取Spring上下文的方法getWebApplicationContext和getRequiredWebApplicationContext,二者的区别是如果当前ServletContext中没有相应的Spring Web容器,前者返回null而后者则抛出异常,源码如下:
public static WebApplicationContext getRequiredWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) throws IllegalStateException {
WebApplicationContext wac = getWebApplicationContext(sc);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: no ContextLoaderListener registered?");
}
return wac;
}
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
return getWebApplicationContext(sc, WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, String attrName) {
Object attr = sc.getAttribute(attrName);
if (attr == null) {
return null;
}
// 省略部分异常判断代码
return (WebApplicationContext) attr;
}
其实也没什么神奇的,同样是以WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE调用了servletContext.getAttribute方法来获取IoC容器对象,无非就是多了一些其它操作而已,两种方法都可以,用哪个方法就全凭个人爱好了。