在Java应用程序性能优化的领域,有多种策略可以帮助提升程序运行效率和响应速度。以下是一些实用的技巧,涵盖代码层面、JVM调优、以及设计模式等方面,旨在全面优化应用性能。1.代码层面优化避免不必要的对象创建频繁的对象创建和销毁会占用大量的CPU时间和内存资源。尽量重用对象,特别是在循环中。Java//优化前for(inti=0;i
《架构300讲》学习笔记(201-250)
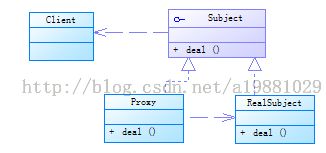
newProxyInstance
笔记架构
前言内容来自B站IT老齐架构300讲内容。201小心selectforupdate,有效规避索引选择性锁表202设计模式之建造者模式的用途20320分钟上手ELK日志监控系统分类:【ELK】204设计模式之门面模式Facade205设计模式之适配器模式Adapter206经典设计!如何让RabbitMQ支持消息延迟投递207Docker容器基于NFS实现跨容器文件共享208数据向上追溯场景该如何优
设计模式系列开篇:解锁软件设计的智慧密码
Ti笔记
设计模式java开发语言
在软件开发的世界里,我们常常会遇到这样一些问题:如何让代码更加优雅、可维护?如何在需求不断变化的情况下快速响应?如何让团队协作更加高效?这些问题看似复杂,但其实早已有人为我们提供了答案,那就是——设计模式。一、设计模式是什么?设计模式(DesignPattern)是软件设计中的一种通用解决方案,它是一种经过验证、可复用的代码设计模板,用于解决特定场景下的常见问题。设计模式并不是一段具体的代码,而是
(八五)HarmonyOS Design 在智能穿戴设备中的实践:应对设计限制与优化小屏幕体验
小_铁
HarmonyOSNext人工智能HarmonyOSNext
HarmonyOSDesign在智能穿戴设备中的实践:应对设计限制与优化小屏幕体验引言智能穿戴设备近年来发展迅猛,从智能手表到智能手环,它们已成为人们生活中不可或缺的一部分,提供健康监测、信息提醒、便捷交互等多种功能。HarmonyOSDesign以其创新的理念和技术,在智能穿戴设备领域不断探索实践,尤其在克服智能穿戴设备设计限制以及优化小屏幕用户体验方面取得了显著成果。智能穿戴设备的设计限制1.
【第8章】亿级电商平台订单系统-技术选型
cherry5230
架构系统架构架构java
1-1本章导学课程导学学习重点:订单系统技术选型实践200亿年交易规模BToB电商平台案例解析知识体系演进路径1.架构体系演变单体架构→大型云上架构体系互联网应用架构设计基本原则2.主流架构设计模式分层架构模式微服务架构模式基于事件的架构模式整洁架构模式六边形架构模式微内核模式基于空间的架构模式管道过滤器模式代理模式3.技术选型方法论3.1基本原则系统性能指标优先原则技术生态适配性原则团队技术栈延
C#中的设计模式:构建更加优雅的代码
Envyᥫᩣᩚ
c#开发语言
C#在面向对象编程(OOP)方面的强大支持,我们可以探讨“C#中的设计模式”。这不仅有助于理解如何更好地组织代码,还能提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。引言设计模式是软件工程中经过实践验证的解决方案模板,它们提供了一种标准化的方法来解决常见的开发问题。对于使用C#进行开发的程序员来说,理解和应用这些模式可以帮助创建结构良好、易于维护和扩展的应用程序。本文将介绍几种常用的设计模式,并展示如何用C#实现它
从底层到实践:深度解析 Vue Composition API 与 React Hooks 的异同
一、设计哲学与底层原理差异1.1响应式系统的基因差异Vue3的CompositionAPI建立在Proxy-based响应式系统之上,通过劫持对象的getter/setter实现依赖收集。当访问响应式对象时,Vue会自动建立组件与数据的依赖关系。//Vue响应式原理简版实现functionreactive(obj){returnnewProxy(obj,{get(target,key){track
Java 和 Kotlin 实现 23 种设计模式:从理论到实践
tangweiguo03051987
androidKotlin语法androidkotlinjava
设计模式是软件开发中解决常见问题的经典解决方案模板。它们帮助开发者编写可维护、可扩展和可重用的代码。本文详细介绍了23种经典设计模式,包括创建型、结构型和行为型模式,并提供了Java和Kotlin的完整实现示例。无论你是初学者还是有经验的开发者,本文都能帮助你深入理解设计模式的核心思想,并将其应用到实际项目中。Java和Kotlin实现23种设计模式设计模式是软件开发中常见问题的解决方案模板。它们
Nginx、LVS、HAProxy 的区别和优缺点
青年夏日科技
nginx运维
Nginx、LVS、HAProxy是目前使用最广泛的三种负载均衡软件,本人都在多个项目中实施过,通常会结合Keepalive做健康检查,实现故障转移的高可用功能。1)在四层(tcp)实现负载均衡的软件:lvs------>重量级nginx------>轻量级,带缓存功能,正则表达式较灵活haproxy------>模拟四层转发,较灵活2)在七层(http)实现反向代理的软件:haproxy----
C++设计模式-观察者模式:从基本介绍,内部原理、应用场景、使用方法,常见问题和解决方案进行深度解析
牵牛老人
C++专栏c++设计模式观察者模式
一、基本介绍1.1模式定义与核心思想观察者模式(ObserverPattern)是一种行为型设计模式,它定义了对象间一对多的依赖关系。当被观察对象(Subject)状态改变时,所有依赖它的观察者(Observer)都会自动收到通知并更新。这种模式类似于报纸订阅机制——报社发布新刊时,所有订阅者都会收到最新报纸。1.2模式价值体现解耦利器:将事件发布者与订阅者解耦,提升系统扩展性动态响应:支持运行时
C++设计模式-工厂模式:从原理、适用场景、使用方法,常见问题和解决方案深度解析
牵牛老人
C++专栏c++设计模式开发语言
一、工厂模式的核心原理工厂模式是一种创建型设计模式,其核心思想是通过将对象创建的职责从客户端代码中剥离,交由专门的工厂类来管理。这种模式通过"封装对象创建过程"特性,实现了以下设计原则:开放封闭原则工厂模式允许系统在不修改已有代码的前提下扩展新的产品类型。如处理器内核的生产案例中,新增型号只需扩展新工厂而非修改原有逻辑。单一职责原则创建对象的逻辑集中在工厂类中,客户端只需关注接口调用,避免了对象构
OnionArch 项目教程
宁彦腾
OnionArch项目教程OnionArchA.NETCoredemoapplicationwhichusestheOnionArchitecture项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/on/OnionArch1.项目介绍OnionArch是一个基于.NETCore的演示应用程序,采用了洋葱架构(OnionArchitecture)。洋葱架构是一种软件设计模式,
LVS、Haproxy、Nginx区别
SHISHIZHIZHI
nginx负载均衡服务器
LVS、Haproxy、Nginx区别一、Haproxy调度算法1.常见的web集群调度器2.Haproxy应用分析3.Haproxy调度算法原理4.Haproxy的主要特性5.Haproxy的优点6、LVS.Haproxy、Nginx区别二、Haproxy优化三、Haproxy日志1.修改主配置文件2.修改rsyslog配置一、Haproxy调度算法1.常见的web集群调度器目前常见的web集群
lvs、nginx、haproxy区别和使用场景?
企鹅侠客
linux聊聊运维lvsnginx运维
0.运维干货分享软考系统架构设计师三科备考经验附学习资料信息安全管理体系(ISMS)制度模板分享免费文档翻译工具(支持word、pdf、ppt、excel)PuTTY中文版安装包MobaXterm中文版安装包pinginfoview网络诊断工具中文版LVS(LinuxVirtualServer)、Nginx和HAProxy都是常见的负载均衡工具,它们在不同的场景中各有优势。以下是它们的区别、特点及
23种设计模式详解
专吃僵尸的坚果
java设计模式
设计模式是代码开发人员总结归纳出的代码设计经验,使用合理的设计模式能够提高代码的可拓展性和可维护性。本文主要介绍了设计模式开山鼻祖经典书籍《DesignPatterns》描写的23种设计模式,不过正如GoF所说“Wedon’tconsiderthiscollectionofdesignpatternscompleteandstatic;it’smorearecordingofourcurrentt
java24种设计模式目录,为大家整理最全的24种设计模式详解,必收藏
高补
java24种设计模式目录
设计模式六大原则单一职责原则一个方法尽可能做一件事情,一般来说不应该让一个方法承担多个职责。单一职责原则的英文名称是SingleResponsibilityPrinciple,简称是SRP。单一职责原则的定义是:应该有且仅有一个原因引起类的变更。SRP的原话解释是:Thereshouldneverbemorethanonereasonforaclasstochange.单一职责原则提出了一个编写程
结构型模式之适配器模式:让不兼容的接口兼容
菜就多练少说
设计模式适配器模式
在软件开发中,经常会遇到这样一种情况:系统的不同部分需要进行交互,但由于接口不兼容,导致无法直接使用。这时,适配器模式(AdapterPattern)就能派上用场。适配器模式是设计模式中的结构型模式,它的目的是通过创建一个适配器类来“包装”一个不兼容的接口,使得两个接口能够兼容、协作。简单来说,适配器模式就是“转换接口”模式。本文将深入探讨适配器模式,讲解其概念、应用场景,并展示如何在Java中实
Python学习-----项目设计1.0(设计思维和ATM环境搭建)
Fitz&
Python学习学习python
目录前言:项目开发流程MVC设计模式什么是MVC设计模式?ATM项目要求ATM项目的环境搭建前言:我个人学习Python大概也有一个月了,在这一个月中我发布了许多关于Python的文章,建立了一个Python学习起步的专栏(https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73633088/category_12186491.html),在这里我非常感谢各位的一路陪伴,你们的支持是我创作的不竭动力
什么是 MVC 架构?它在后端开发中的作用是什么?
破碎的天堂鸟
学习教程mvc架构
MVC(Model-View-Controller)架构是一种广泛应用于软件开发的分层设计模式,尤其在后端开发和Web应用程序中占据重要地位。其核心思想是通过职责分离,将应用程序分为三个独立的组件——模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller),从而实现代码的高效管理和维护。以下从定义、组成部分及其在后端开发中的作用展开详细说明:一、MVC架构的定义与组成部分1.模型(Mo
Docker拉取镜像 - 代理
纳兰雨天
docker容器代理模式
docker配置代理创建或编辑Docker配置文件sudomkdir-p/etc/systemd/system/docker.service.dsudonano/etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf在文件中添加代理配置:[Service]Environment="HTTP_PROXY=127.0.0.1:7897"Environme
运行go mod tidy报错
Amber_37
golang开发语言后端
golang项目运行一些网上的项目或者陈旧的项目经常遇到gomodtidy执行失败分析1.包升级了,路径改了找到对应包进行升级,有的改版本号有的改路径2.gosum校验失败报错信息verifyingmodule:missingGOSUMDB使用国内镜像,gosumdb依然设置为空,是完全兼容的go国内镜像goenv-wGO111MODULE=ongoenv-wGOPROXY=https://gop
【设计模式】原型模式
浅慕Antonio
设计模式设计模式原型模式c++
三、原型模式3.2原型模式同工厂模式一样,原型(Prototype)模式也是一种创建型模式。原型模式通过一个对象(原型对象)克隆出多个一模一样的对象。实际上,该模式与其说是一种设计模式,不如说是一种创建对象的方法(对象克隆),尤其是创建给定类的对象(实例)过程很复杂(例如,要设置许多成员变量的值)时,使用这种设计模式就比较合适。3.2.1通过工厂方法模式演变到原型模式回顾一下前面讲解工厂方法模式时
Android Dagger2 框架注入模块源码深度剖析(四)
&有梦想的咸鱼&
android
一、引言在Android开发中,依赖注入(DependencyInjection,简称DI)是一种重要的设计模式,它能够有效降低代码之间的耦合度,提高代码的可测试性和可维护性。Dagger2作为一款强大的依赖注入框架,在编译时生成依赖注入代码,避免了运行时反射带来的性能开销。注入模块是Dagger2的核心部分,负责将依赖对象注入到目标对象中。本文将深入分析Dagger2框架的注入模块,从源码级别详
白话设计模式之(53):迭代器模式——数据遍历的“百变魔方”
一杯年华@编程空间
白话设计模式设计模式迭代器模式
白话设计模式之(53):迭代器模式——数据遍历的“百变魔方”大家好!在软件开发的学习过程中,我们都在不断探索如何让代码更加高效、灵活且易于维护。设计模式作为编程领域的关键知识,为我们解决各种复杂问题提供了有力的工具。今天,咱们继续深入研究迭代器模式,它就像一个“百变魔方”,不仅能实现基本的数据遍历功能,还能通过各种扩展和变化,满足不同场景下的数据访问需求。希望通过这篇博客,能和大家一起更全面地理解
Java面向对象编程进阶:深入理解static、单例模式与继承
shy2005_5_31
Java全栈开发学习java单例模式开发语言
在面向对象编程(OOP)中,掌握高级特性是提升代码质量和设计能力的关键。本文基于Java语言,深入探讨static关键字、单例设计模式、继承等核心概念,并结合实际应用场景与深度思考,帮助读者构建系统化的知识体系。一、static关键字:共享与效率的基石1.静态变量vs实例变量静态变量:用static修饰,属于类,内存中仅一份,被所有对象共享。应用场景:全局计数器、配置参数。publicclassU
web前段跨域nginx代理配置
刘正强
nginxcmsWeb
nginx代理配置可参考server部分
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
spring学习笔记
caoyong
spring
一、概述
a>、核心技术 : IOC与AOP
b>、开发为什么需要面向接口而不是实现
接口降低一个组件与整个系统的藕合程度,当该组件不满足系统需求时,可以很容易的将该组件从系统中替换掉,而不会对整个系统产生大的影响
c>、面向接口编口编程的难点在于如何对接口进行初始化,(使用工厂设计模式)
Eclipse打开workspace提示工作空间不可用
0624chenhong
eclipse
做项目的时候,难免会用到整个团队的代码,或者上一任同事创建的workspace,
1.电脑切换账号后,Eclipse打开时,会提示Eclipse对应的目录锁定,无法访问,根据提示,找到对应目录,G:\eclipse\configuration\org.eclipse.osgi\.manager,其中文件.fileTableLock提示被锁定。
解决办法,删掉.fileTableLock文件,重
Javascript 面向对面写法的必要性?
一炮送你回车库
JavaScript
现在Javascript面向对象的方式来写页面很流行,什么纯javascript的mvc框架都出来了:ember
这是javascript层的mvc框架哦,不是j2ee的mvc框架
我想说的是,javascript本来就不是一门面向对象的语言,用它写出来的面向对象的程序,本身就有些别扭,很多人提到js的面向对象首先提的是:复用性。那么我请问你写的js里有多少是可以复用的,用fu
js array对象的迭代方法
换个号韩国红果果
array
1.forEach 该方法接受一个函数作为参数, 对数组中的每个元素
使用该函数 return 语句失效
function square(num) {
print(num, num * num);
}
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10];
nums.forEach(square);
2.every 该方法接受一个返回值为布尔类型
对Hibernate缓存机制的理解
归来朝歌
session一级缓存对象持久化
在hibernate中session一级缓存机制中,有这么一种情况:
问题描述:我需要new一个对象,对它的几个字段赋值,但是有一些属性并没有进行赋值,然后调用
session.save()方法,在提交事务后,会出现这样的情况:
1:在数据库中有默认属性的字段的值为空
2:既然是持久化对象,为什么在最后对象拿不到默认属性的值?
通过调试后解决方案如下:
对于问题一,如你在数据库里设置了
WebService调用错误合集
darkranger
webservice
Java.Lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Org/Apache/Commons/Discovery/Tools/DiscoverSingleton
调用接口出错,
一个简单的WebService
import org.apache.axis.client.Call;import org.apache.axis.client.Service;
首先必不可
JSP和Servlet的中文乱码处理
aijuans
Java Web
JSP和Servlet的中文乱码处理
前几天学习了JSP和Servlet中有关中文乱码的一些问题,写成了博客,今天进行更新一下。应该是可以解决日常的乱码问题了。现在作以下总结希望对需要的人有所帮助。我也是刚学,所以有不足之处希望谅解。
一、表单提交时出现乱码:
在进行表单提交的时候,经常提交一些中文,自然就避免不了出现中文乱码的情况,对于表单来说有两种提交方式:get和post提交方式。所以
面试经典六问
atongyeye
工作面试
题记:因为我不善沟通,所以在面试中经常碰壁,看了网上太多面试宝典,基本上不太靠谱。只好自己总结,并试着根据最近工作情况完成个人答案。以备不时之需。
以下是人事了解应聘者情况的最典型的六个问题:
1 简单自我介绍
关于这个问题,主要为了弄清两件事,一是了解应聘者的背景,二是应聘者将这些背景信息组织成合适语言的能力。
我的回答:(针对技术面试回答,如果是人事面试,可以就掌
contentResolver.query()参数详解
百合不是茶
androidquery()详解
收藏csdn的博客,介绍的比较详细,新手值得一看 1.获取联系人姓名
一个简单的例子,这个函数获取设备上所有的联系人ID和联系人NAME。
[java]
view plain
copy
public void fetchAllContacts() {
ora-00054:resource busy and acquire with nowait specified解决方法
bijian1013
oracle数据库killnowait
当某个数据库用户在数据库中插入、更新、删除一个表的数据,或者增加一个表的主键时或者表的索引时,常常会出现ora-00054:resource busy and acquire with nowait specified这样的错误。主要是因为有事务正在执行(或者事务已经被锁),所有导致执行不成功。
1.下面的语句
web 开发乱码
征客丶
springWeb
以下前端都是 utf-8 字符集编码
一、后台接收
1.1、 get 请求乱码
get 请求中,请求参数在请求头中;
乱码解决方法:
a、通过在web 服务器中配置编码格式:tomcat 中,在 Connector 中添加URIEncoding="UTF-8";
1.2、post 请求乱码
post 请求中,请求参数分两部份,
1.2.1、url?参数,
【Spark十六】: Spark SQL第二部分数据源和注册表的几种方式
bit1129
spark
Spark SQL数据源和表的Schema
case class
apply schema
parquet
json
JSON数据源 准备源数据
{"name":"Jack", "age": 12, "addr":{"city":"beijing&
JVM学习之:调优总结 -Xms -Xmx -Xmn -Xss
BlueSkator
-Xss-Xmn-Xms-Xmx
堆大小设置JVM 中最大堆大小有三方面限制:相关操作系统的数据模型(32-bt还是64-bit)限制;系统的可用虚拟内存限制;系统的可用物理内存限制。32位系统下,一般限制在1.5G~2G;64为操作系统对内存无限制。我在Windows Server 2003 系统,3.5G物理内存,JDK5.0下测试,最大可设置为1478m。典型设置:
java -Xmx355
jqGrid 各种参数 详解(转帖)
BreakingBad
jqGrid
jqGrid 各种参数 详解 分类:
源代码分享
个人随笔请勿参考
解决开发问题 2012-05-09 20:29 84282人阅读
评论(22)
收藏
举报
jquery
服务器
parameters
function
ajax
string
读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-代理模式-Proxy
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/*
* 下面
应用升级iOS8中遇到的一些问题
chenhbc
ios8升级iOS8
1、很奇怪的问题,登录界面,有一个判断,如果不存在某个值,则跳转到设置界面,ios8之前的系统都可以正常跳转,iOS8中代码已经执行到下一个界面了,但界面并没有跳转过去,而且这个值如果设置过的话,也是可以正常跳转过去的,这个问题纠结了两天多,之前的判断我是在
-(void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated
中写的,最终的解决办法是把判断写在
-(void
工作流与自组织的关系?
comsci
设计模式工作
目前的工作流系统中的节点及其相互之间的连接是事先根据管理的实际需要而绘制好的,这种固定的模式在实际的运用中会受到很多限制,特别是节点之间的依存关系是固定的,节点的处理不考虑到流程整体的运行情况,细节和整体间的关系是脱节的,那么我们提出一个新的观点,一个流程是否可以通过节点的自组织运动来自动生成呢?这种流程有什么实际意义呢?
这里有篇论文,摘要是:“针对网格中的服务
Oracle11.2新特性之INSERT提示IGNORE_ROW_ON_DUPKEY_INDEX
daizj
oracle
insert提示IGNORE_ROW_ON_DUPKEY_INDEX
转自:http://space.itpub.net/18922393/viewspace-752123
在 insert into tablea ...select * from tableb中,如果存在唯一约束,会导致整个insert操作失败。使用IGNORE_ROW_ON_DUPKEY_INDEX提示,会忽略唯一
二叉树:堆
dieslrae
二叉树
这里说的堆其实是一个完全二叉树,每个节点都不小于自己的子节点,不要跟jvm的堆搞混了.由于是完全二叉树,可以用数组来构建.用数组构建树的规则很简单:
一个节点的父节点下标为: (当前下标 - 1)/2
一个节点的左节点下标为: 当前下标 * 2 + 1
&
C语言学习八结构体
dcj3sjt126com
c
为什么需要结构体,看代码
# include <stdio.h>
struct Student //定义一个学生类型,里面有age, score, sex, 然后可以定义这个类型的变量
{
int age;
float score;
char sex;
}
int main(void)
{
struct Student st = {80, 66.6,
centos安装golang
dcj3sjt126com
centos
#在国内镜像下载二进制包
wget -c http://www.golangtc.com/static/go/go1.4.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.4.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
#把golang的bin目录加入全局环境变量
cat >>/etc/profile<
10.性能优化-监控-MySQL慢查询
frank1234
性能优化MySQL慢查询
1.记录慢查询配置
show variables where variable_name like 'slow%' ; --查看默认日志路径
查询结果:--不用的机器可能不同
slow_query_log_file=/var/lib/mysql/centos-slow.log
修改mysqld配置文件:/usr /my.cnf[一般在/etc/my.cnf,本机在/user/my.cn
Java父类取得子类类名
happyqing
javathis父类子类类名
在继承关系中,不管父类还是子类,这些类里面的this都代表了最终new出来的那个类的实例对象,所以在父类中你可以用this获取到子类的信息!
package com.urthinker.module.test;
import org.junit.Test;
abstract class BaseDao<T> {
public void
Spring3.2新注解@ControllerAdvice
jinnianshilongnian
@Controller
@ControllerAdvice,是spring3.2提供的新注解,从名字上可以看出大体意思是控制器增强。让我们先看看@ControllerAdvice的实现:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Co
Java spring mvc多数据源配置
liuxihope
spring
转自:http://www.itpub.net/thread-1906608-1-1.html
1、首先配置两个数据库
<bean id="dataSourceA" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close&quo
第12章 Ajax(下)
onestopweb
Ajax
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
BW / Universe Mappings
blueoxygen
BO
BW Element
OLAP Universe Element
Cube Dimension
Class
Charateristic
A class with dimension and detail objects (Detail objects for key and desription)
Hi
Java开发熟手该当心的11个错误
tomcat_oracle
java多线程工作单元测试
#1、不在属性文件或XML文件中外化配置属性。比如,没有把批处理使用的线程数设置成可在属性文件中配置。你的批处理程序无论在DEV环境中,还是UAT(用户验收
测试)环境中,都可以顺畅无阻地运行,但是一旦部署在PROD 上,把它作为多线程程序处理更大的数据集时,就会抛出IOException,原因可能是JDBC驱动版本不同,也可能是#2中讨论的问题。如果线程数目 可以在属性文件中配置,那么使它成为
推行国产操作系统的优劣
yananay
windowslinux国产操作系统
最近刮起了一股风,就是去“国外货”。从应用程序开始,到基础的系统,数据库,现在已经刮到操作系统了。原因就是“棱镜计划”,使我们终于认识到了国外货的危害,开始重视起了信息安全。操作系统是计算机的灵魂。既然是灵魂,为了信息安全,那我们就自然要使用和推行国货。可是,一味地推行,是否就一定正确呢?
先说说信息安全。其实从很早以来大家就在讨论信息安全。很多年以前,就据传某世界级的网络设备制造商生产的交