HDU 5269 ZYB loves Xor I——BestCoder Round #44(字典树)
ZYB loves Xor I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
Memphis loves xor very musch.Now he gets an array A.The length of A is n.Now he wants to know the sum of all (lowbit(
Ai xor
Aj ))
(i,j∈[1,n])
We define that lowbit(x)= 2k ,k is the smallest integer satisfied (( x and 2k )>0)
Specially,lowbit(0)=0
Because the ans may be too big.You just need to output ans mod 998244353
We define that lowbit(x)= 2k ,k is the smallest integer satisfied (( x and 2k )>0)
Specially,lowbit(0)=0
Because the ans may be too big.You just need to output ans mod 998244353
Input
Multiple test cases, the first line contains an integer T(no more than 10), indicating the number of cases. Each test case contains two lines
The first line has an integer n
The second line has n integers A1 , A2 .... An
n∈[1,5∗104] , Ai∈[0,229]
The first line has an integer n
The second line has n integers A1 , A2 .... An
n∈[1,5∗104] , Ai∈[0,229]
Output
For each case, the output should occupies exactly one line. The output format is Case #x: ans, here x is the data number begins at 1.
Sample Input
2 5 4 0 2 7 0 5 2 6 5 4 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 36 Case #2: 40
Source
BestCoder Round #44
附上该题对应的中文题
ZYB loves Xor I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others)
Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
问题描述
ZYB喜欢研究Xor,现在他得到了一个长度为n的数组A。于是他想知道:对于所有数对(i,j)(i∈[1,n],j∈[1,n]),lowbit(AixorAj)之和为多少.由于答案可能过大,你需要输出答案对998244353取模后的值 定义lowbit(x)=2k,其中k是最小的满足(x and 2k)>0的数 特别地:lowbit(0)=0
输入描述
一共T(T≤10)组数据,对于每组数据: 第一行一个正整数n,表示数组长度 第二行n个非负整数,第i个整数为Ai n∈[1,5∗104],Ai∈[0,229]
输出描述
每组数据输出一行Case #x: ans。x表示组数编号,从1开始。ans为所求值。
输入样例
2 5 4 0 2 7 0 5 2 6 5 4 0
输出样例
Case #1: 36 Case #2: 40
/****************************************************/
出题人的解题思路:
我们考虑,当 A xor B 的答案为 2p 时, A 和 B 表示成二进制数后末 p−1 位肯定相同 于是我们维护一颗字母树,将每个数表示成二进制数后翻转可以下,插入字母树 统计答案时,我们找出 Ai 的二进制数翻转后在字母树上的路径,对于路径上每个点 x ,设他走的边是 v ,且当前为第 k 位,则和他 xor 后lowbit为 2k 的数的个数为trans(x,v^1)的子树大小。 trans(x,v)表示字母树上在结点x,走连出去的字母为v的边到达的结点 时间复杂度: O(nlogA)其实lowbit(AixorAj)就是让你求一个数组中任意两个数异或之后所表示的二进制数的最低位1所表示的数
比如说lowbit(4 xor 2),首先4异或2的结果是6(100^010=110),然后lowbit取的是最低位1所表示的十进制大小,即110倒数第二位的1,表示十进制数2。其实就是找Ai和Aj代表的二进制数从末尾往前找最低的不相同的位
题目要我们求的就是所以lowbit值的和。首先
![]()
那必定保证A和B表示成的二进制数末尾k-1位是相同的,才能导致不相同的最低位是倒数第k位。
我们可以考虑用字典树的方法
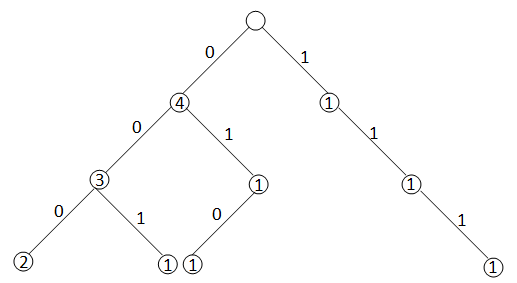
先按照输入的数组a建立一颗字典树,每个数表示成二进制数后反向建树
如样例1中,4 0 2 7 0 表示成二进制数
4:100 001
0:000 000
2:010 反转 010
7:111 111
0:000 000
每个结点记录的到该节点为止具有相同后缀的字符串的个数
比如标着4的节点表示的是具有相同后缀0的字符串有4个,即4 0 2 0
这样之后,我们只需遍历一遍输入的数组,求出与每个数组具有不同后缀的字符串个数及不同的位数高低,就是最终的结果
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<queue>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#define exp 1e-10
using namespace std;
const int N = 10005;
const int inf = 1000000000;
const int mod = 998244353;
struct tree
{
int t;
int a[2];
}s[500*N];
int p=0,x[5*N];
void init(int z)
{
s[z].t=0;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
s[z].a[i]=-1;
}
void buildtree(int c)
{
int i,k;
for(i=k=0;i<30;i++,c/=2)
{
if(s[k].a[c&1]==-1)
{
s[k].a[c&1]=++p;
init(k=p);
}
else
k=s[k].a[c&1];
s[k].t++;
}
}
__int64 find(int c)
{
int i,k,t=1;
__int64 result=0;
for(i=k=0;i<30;i++,c/=2,t*=2)
{
result=(result+s[s[k].a[c&1^1]].t*t%mod)%mod;
k=s[k].a[c&1];
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int t,n,i,k=1;
__int64 ans;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
ans=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
init(0);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x[i]);
buildtree(x[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
ans=(ans+find(x[i]))%mod;
printf("Case #%d: %I64d\n",k++,ans);
}
return 0;
}
菜鸟成长记