Android\OPhone自定义视图(View)
最经在Android上作游戏居多了,在Android平台做游戏和做应用少有少许的不同,做游戏就会更多的使用自定义视图了,有很多东西需要我们自己去实现,就不像做应用,用得最多的就是Android系统的一些组件,当然偶尔也会涉及到自定义一些界面,但是这些自定义界面都是使用系统的一些组件来组合完成了,而游戏不同了,游戏在图形的处理上要求会更多,这时,自定义视图就派上用场了。
说老实话,做了几个游戏出来之后,才发现,以前要实现某个功能会经过很多的步骤并且很复杂,在Android就可以很轻松的解决,比如最简单的一个渐变色的处理,要是在J2ME上计算就会多很多,在Android就需要定义一个shape的XML文件即可,同时还可以利用shape来绘制一些基本的图形(有机会右面会介绍这个shape),甚至代替很多图片内容,这样既节省了空间,又提高了效率,为什么不好呢?Android真的很强大,主要是很灵活,我们可以用很多方法去实现某个功能。
好了,又废话了这么多,下面进入正题。
我们都知道Android的UI,都是基于View和ViewGroup以及一些子类,比如layout等等,所以我们在自定义视图时就需要将自定义的类继承自这个类。
首先我们需要在values目录下建立一个attrs.xml文件,来定义我们在自定义视图中需要使用的一些资源,比如:背景、字体大小、字体等等。代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="TestView"> <attr name="textColor" format="color" /> <attr name="textSize" format="dimension" /> <attr name="backGround" format="integer" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
上面的代码很好理解,我们将自定义的试图名定位TestView,其中包括了字体颜色(textColor),字体尺寸(textSize)以及背景(backGround)。
接下来我们就需要建立一个类TestView,继承自View了。
代码如下(代码加入了注释,这里就不多说了):
package com.yarin.Android.Test;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class TestView extends View
{
private Paint mPaint = null;
private Context mContext = null;
/**
* mTestView = new TestView(this);
* setContentView(mTestView);
* 如果在Activity中这样写,那么就需要实现这个构造函数
*/
public TestView(Context context)
{
super(context);
mContext = context;
mPaint = new Paint();
}
/**
* setContentView(R.layout.main);
* mTestView = (TestView)findViewById(R.id.mTestView);
* 如果在Activity中这样写,那么就需要实现这个构造函数
*/
public TestView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
mContext = context;
mPaint = new Paint();
TypedArray params = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.TestView);
//取得xml布局文件中所定义的背景
int backgroudId = params.getResourceId(R.styleable.TestView_backGround,0);
if (backgroudId != 0)
{
setBackgroundResource(backgroudId);
}
//字体颜色
int textColor = params.getColor(R.styleable.TestView_textColor,0XFFFFFFFF);
mPaint.setColor(textColor);
//字体大小
float textSize = params.getDimension(R.styleable.TestView_textSize, 20);
mPaint.setTextSize(textSize);
}
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
super.onDraw(canvas);
//测试绘制一个矩形
canvas.drawRect(30, 50, 80, 90, mPaint);
//绘制一个字符串
canvas.drawText("测试字符串", 50, 150, mPaint);
}
}
接下来,我们需要在main.xml中来修改加入自定义视图了,修改如下:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:test="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.yarin.Android.Test"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<!-- 自定义视图
注意这里是如何来申明自定义视图中的字体颜色、字体大小、背景的,
在线性布局中不要忘记“xmlns:test="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.yarin.Android.Test”
-->
<com.yarin.Android.Test.TestView
android:id="@+id/mTestView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
test:textColor="#FFFFFFFF"
test:textSize="25dip"
test:backGround="@drawable/bg"
/>
</LinearLayout>
最后在Activity中,不管我们采用下面那一种方式来写都可以了://mTestView = new TestView(this);
//setContentView(mTestView);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mTestView = (TestView)findViewById(R.id.mTestView);
大家可以从代码看出,我们在屏幕上绘制了一个矩形和一个字符串做测试。效果如下(这个效果是在OPhone1.0上测试的):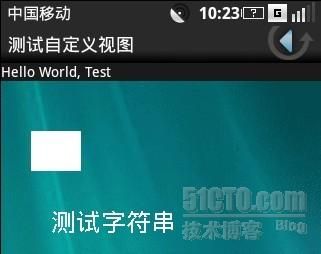
也没什么多说的,网络上已经早已有方法你来讲解了,就算自己作个记录吧,能帮助到某个朋友,当然很高兴,下面是Eclipse工程文件。
需要说明一下,3D的应用时不能这样的,3D需要使用SurfaceView来实现,后面有时间在介绍。最后总结一点经验,Android上开发应用,最主要的就是UI界面的布局,其他的都好解决,正在努力想UI的布局有没有更好的方式。
谢谢大家支持。