R语言绘图篇
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/lilanfeng1991/article/details/34431865
1.散点图
- library(base)
- attach(mtcars)
- plot(mtcars$wt,mtcars$mpg,
- main="Basic Scatter plot of MPG vs.Weight",
- xlab="Car Weight(lbs/100)",
- ylab="Miles Per Gallon",
- pch=19)
- abline(lm(mtcars$mpg~mtcars$wt),col="red",lwd=2,lty=1)
- lines(lowess(mtcars$wt,mtcars$mpg),col="blue",lwd=2,lty=2)
- #lowess()函数用来添加一条平滑曲线,lowess()和loess(),loess是基于lowess()表达式版本的更新和更强大拟合函数

car中的scatterplot()函数可方便地绘制散点图,并添加拟合曲线、边界箱线图和置信椭圆,还可按子集绘图和交互式地识别点。
- library(car)
- scatterplot(mpg~wt|cyl,data=mtcars,lwd=2,
- main="Scatter Plot of MPG vs.Weight by # Cylinders",
- xlab="Weight of Car(lbs/1000)",
- ylab="Miles Per Gallon",
- legend.plot=TRUE,
- id.method="identify",
- labels=row.names(mtcars),
- boxplots="xy")

2.散点图矩阵
(1)pairs()函数可创建基础的散点图矩阵
- pairs(~mpg+disp+drat+wt,data=mtcars,main="Basic Scatter Plot Matrix")

- pairs(~mpg+disp+drat+wt,data=mtcars,main="Basic Scatter Plot Matrix",upper.panel=NULL)
(2)car包中的scatterplotMatrix()函数也可生成散点图矩阵
- library(car)
- scatterplotMatrix(~mpg+disp+drat+wt,data=mtcars,spread=FALSE,lty.smooth=2,main="Scatter Plot Matrix via car Packages")
- library(car)
- scatterplotMatrix(~mpg+disp+drat+wt|cyl,data=mtcars,spread=FALSE,diagonal="histogram",main="Scatter Plot Matrix via car Package")
(3)gclus包中的cpairs()函数
提供一个有趣的散点图矩阵变种,含有可能重排矩阵中变量位置的选项,可让相关性更高的变量更靠近主对角线,还可对各单元格进行颜色编码来展示变量间的相关性大小。
- install.packages("gclus")
- library(gclus)
- mydata<-mtcars[c(1,3,5,6)]
- mydata.corr<-abs
- mycolors<-dmat.color(mydata.corr)
- myorder<-order.single(mydata.corr)
- cpairs(mydata,myorder,panel.colors=mycolors,gap=5,main="Variable Ordered and Colored by Correlation")

由结果可知,相关性最高的变量是车重与排量,以及每加仑英里数与车重(标为红色,且离主对角线最近);
相关性最低的是后轴比与每加仑英里数(标注为黄色,且离主对角线很远)。
3.高密度散点图
- set.seed(1234)
- n<-10000
- c1<-matrix(rnorm(n,mean=0,sd=.5),ncol=2)
- c2<-matrix(rnorm(n,mean=3,sd=2),ncol=2)
- mydata<-rbind(c1,c2)
- mydata<-as.data.frame(mydata)
- names(mydata)<-c("x","y")
- with(mydata,plot(x,y,pch=19,main="Scatter Plot with 10,000 observation"))

- with(mydata,smoothScatter(x,y,main="Scatterplot Colored by Smoothed Densities"))
hexbin包中的hexbin()函数将二元变量的封箱放到六边形单元格中
- install.packages("hexbin")
- library(hexbin)
- with(mydata,{bin<-hexbin(x,y,xbins=50)
- plot(bin,main="Hexagonal Binning with 10,000 Observations")})

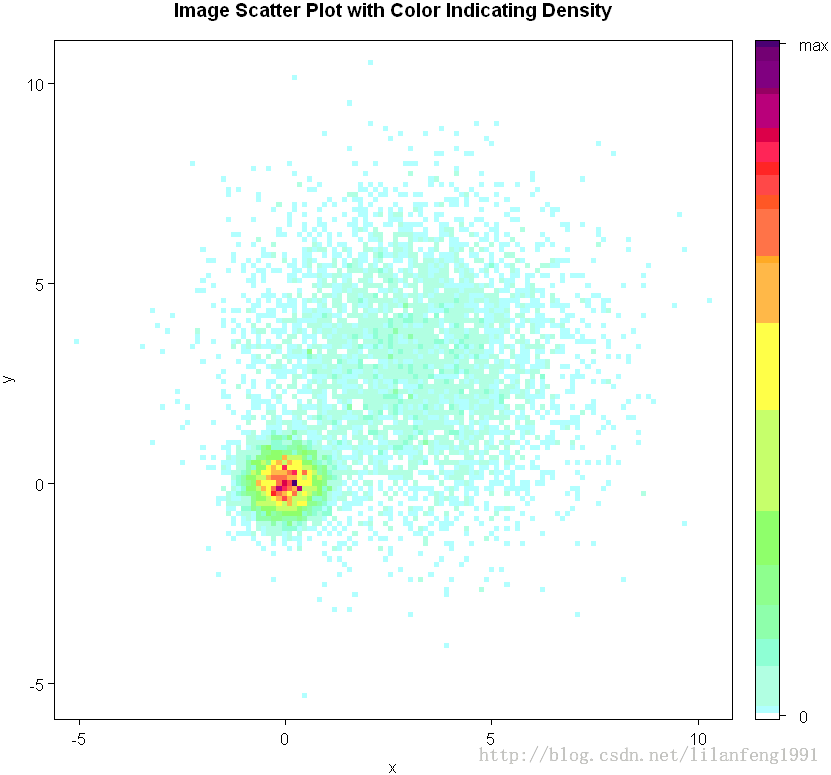
IDPmisc包中的iplot()函数可通过颜色来展示点的密度(在某特定点上数据点的数目)
- with(mydata,iplot(x,y,main="Image Scatter Plot with Color Indicating Density"))
4.三维散点图
对三个变量的交互关系进行可视化 可用scatterplot3d中的scatterplot3d()函数来绘制它们的关系
- install.packages("scatterplot3d")
- library(scatterplot3d)
- attach(mtcars)
- scatterplot3d(mtcars$wt,mtcars$disp,mtcars$mpg,
- main="Basic 3D Scatter Plot")

- library(scatterplot3d)
- attach(mtcars)
- scatterplot3d(mtcars$wt,mtcars$disp,mtcars$mpg,
- pch=16,
- highlight.3d=TRUE,
- type="h",
- main="Basic 3D Scatter Plot")

- s3d<-scatterplot3d(mtcars$wt,mtcars$disp,mtcars$mpg,
- pch=16,
- highlight.3d=TRUE,
- type="h",
- main="Basic 3D Scatter Plot")
- fit<-lm(mtcars$mpg~mtcars$wt+mtcars$disp)
- s3d$plane3d(fit)

旋转三维散点图
rgl包中的plot3d()函数创建可交互的三维散点图
- install.packages("rgl")
- library(rgl)
- attach(mtcars)
- plot3d(mtcars$wt,mtcars$disp,mtcars$mpg,col="red",size=5)

可通过鼠标旋转坐标轴
- install.packages("Rcmdr")
- library(Rcmdr)
- attach(mtcars)
- scatter3d(mtcars$wt,mtcars$disp,mtcars$mpg)
5.气泡图
思想:创建一个二维散点图,然后用点的大小来代表第三个变量的值。
可用symbols()函数来创建气泡图
- attach(mtcars)
- r<-sqrt(disp/pi)
- symbols(mtcars$wt,mtcars$mpg,circler=r,inches=0.30,
- fg="white",bg="lightblue",
- main="Bubble Plot with point size proportional to displacement",
- xlab="Weigt of Car(lbs/1000)",ylab="Miles Per Gallon")
- text(wt,mpg,rownames(mtcars),cex=0.6)
- detach(mtcars)
6.折线图
- opar<-par(no.readonly=TRUE)
- par(mfrow=c(1,2))
- t1<-subset(Orange,Tree==1)
- plot(t1$age,t1$circumstance,
- xlab="Age(days)",
- ylab="Circmference(mm)",
- main="Orange Tree 1 Growth")
- plot(t1$age,t1$circumstance,
- xlab="Age(days)",
- ylab="Circmference(mm)",
- main="Orange Tree 1 Growth",
- type="b")

| 类型 | 图形外形 |
| p | 只有点 |
| l | 只有线 |
| o | 实心点和线(即线覆盖在点上) |
| b、c | 线连接点(c时不绘制点) |
| s、S | 阶梯线 |
| h | 直方图式的垂直线 |
| n | 不生成任何点和线(通常用来为后面的命令创建坐标) |
- Orange$Tree<-as.numeric(Orange$Tree)
- ntrees<-max(Orange$Tree)
- xrange<-range(Orange$age)
- yrange<-range(Orange$circumference)
- plot(xrange,yrange,
- type="n",
- xlab="Age(days)",
- ylab="Circumstance(mm)")
- colors<-rainbow(ntrees)
- linetype<-c(1:ntrees)
- plotchar<-seq(18,18+ntrees,1)
- for(i in 1:ntrees){
- tree<-subset(Orange,Tree==i)
- lines(tree$age,tree$circumference,
- type="b",
- lwd=2,
- lty=linetype[i],
- col=colors[i],
- pch=plotchar[i]
- )
- }
- title("Tree Growth","example of line plot")
- legend(xrange[1],yrange[2],
- 1:ntrees,
- cex=.8,
- col=colors,
- pch=plotchar,
- lty=linetype,
- title="Tree")
7.相关图
- install.packages("seriation")
- library(corrgram)
- corrgram(mtcars,ordr=TRUE,lower.panel=panel.shade,
- upper.panel=panel.pie,text.panel=panel.txt,
- main="Correlogram of mtcars intercorrelations")

默认地,蓝色和和从左下指向右上的斜杠表示单元格中的两个变量呈正相关;反过来,绝色和从左上指向右下的斜杠表示变量呈负相关。色彩越深,饱和度越高,说明变量相关性越大。
上三角单元格用饼图显示了相同的信息,颜色同上,但相关性大小由被填充的饼图块的大小来展示。正相关从12点钟处开始顺时针填充饼图,而负相关则是逆时针方向填充饼图。
corrgram()函数的panel选项
| 位置 | 面板选项 | 描述 |
| 非对角线 | panel.pie | 用饼图的填充比例来表示相关性大小 |
| panel.shade | 用阴影的深度来表示相关性的大小 | |
| panel.ellipse | 绘制置信椭圆和平滑拟合曲线 | |
| panel.pts | 绘制散点图 | |
| 主对角线 | panel.minmax | 输出变量的最大最小值 |
| panel.txt | 变量的名字 |
- corrgram(mtcars,ordr=TRUE,lower.panel=panel.shade,
- upper.panel=NULL,text.panel=panel.txt,
- main="Correlogram of mtcars intercorrelations")
8.马赛克图
·当变量是类别变量时,且数目多于三个的时候,可使用马赛克图。马赛克图中,嵌套矩阵面积正比于单元格频率,其中该频率即多维列联表中的频率。颜色和阴影可表示拟合模型的残差值。
vcd包中的mosaic()函数可以绘制马赛克图
base包中的mosaicplot()也可绘制马赛克图。
以 base中的Titanic数据集为例
- ftable(Titanic)
- library(vcd)
- mosaic(Titanic,shade=TRUE,legend=TRUE)