网卡驱动9-linux内核3.0.8的mdio_bus\phy_device\phy_driver
上次说了MII
还有RMII GMII RGMII、SGMII等,
GMII:
与MII接口相比,GMII的数据宽度由4位变为8位, 发送参考时钟GTX_CLK和接收参考时钟RX_CLK的频率均为125MHz(1000Mbps/8=125MHz)。支持MII模式。这个GMII可用于1000M网。
RGMII:
由于GMII线太多,RGMII把数据位宽变为4位,在时钟的上升沿和下降沿都采样数据。
本人现在用的1000M网卡用的急速RGMII接口。同时支持MII。
我当前用的SOC集成了MAC,有两个MAC,支持MII和RGMII,一个MDIO接口。
我的硬件是有两个网口,一个MAC对应一个PHY,一个MDIO总线上接两个PHY。一个PHY地址ID为1,另一个为2。内核驱动STMicroelectronics 公司的stmmac/,版本linux-3.0.8
看一下stmmac的源码,可以看出phy管理用的不是我们上篇说的mii.c。而是drivers/net/phy/下的东西。
我们关心的代码是phy.c phy_device.c mdio_bus.c 还有include /linux/phy.h
这些东西的使用和上次的mii.c使用比较的话,会给人一种总线、设备、驱动的概念。不是想上次的mii就是提供mdio读写去操作mii接口。
Bus:
struct mii_bus {
const char *name;
char id[MII_BUS_ID_SIZE];
void *priv;
int (*read)(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy_id, int regnum);
int (*write)(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy_id, int regnum, u16 val);
int (*reset)(struct mii_bus *bus);
/*
* A lock to ensure that only one thing can read/write
* the MDIO bus at a time
*/
struct mutex mdio_lock;
struct device *parent;
enum {
MDIOBUS_ALLOCATED = 1,
MDIOBUS_REGISTERED,
MDIOBUS_UNREGISTERED,
MDIOBUS_RELEASED,
} state;
struct device dev;
/* list of all PHYs on bus */
struct phy_device *phy_map[PHY_MAX_ADDR];
/* PHY addresses to be ignored when probing */
u32 phy_mask;
/*
* Pointer to an array of interrupts, each PHY's
* interrupt at the index matching its address
*/
int *irq;
};
在驱动中,我们要面对的接口。现在看看stmmac中对它的使用。在stmmac_mdio.c中,看一些关键代码:
stmmac_mii_bus = mdiobus_alloc();//动态分配
if (stmmac_mii_bus == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
irqlist = kzalloc(sizeof(int) * PHY_MAX_ADDR, GFP_KERNEL);//分配phy irq表
if (irqlist == NULL) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto irqlist_alloc_fail;
}
/* Assign IRQ to phy at address phy_addr */
if (priv->phy_addr != -1)//我当前的stmmac源码没有支持phy中断
irqlist[priv->phy_addr] = priv->phy_irq;
/*
可以到此去看看如何加一个phy,可能要代理
http://www.stlinux.com/kernel/network/phy-howto
*/
//下面检测时钟是否正常,主要是获取总线时钟,再计算toe时钟,是否合法。
tnkclk = mdio_clk_init();
priv->plat->clk_csr = get_clk_csr(tnkclk);
if (priv->plat->clk_csr == -1) {
pr_err("Can not get mdio clk.\n");
goto bus_register_fail;
}
stmmac_mii_bus->name = "STMMAC MII Bus";
stmmac_mii_bus->read = &stmmac_mdio_read;//读
stmmac_mii_bus->write = &stmmac_mdio_write;//写
stmmac_mii_bus->reset = &stmmac_mdio_reset;// 复位
snprintf(stmmac_mii_bus->id, MII_BUS_ID_SIZE, "%x",
priv->plat->bus_id);//stmmac中是1
stmmac_mii_bus->priv = ndev;
stmmac_mii_bus->irq = irqlist;
stmmac_mii_bus->phy_mask = priv->phy_mask;//这里设为了0,没有地址被忽略
stmmac_mii_bus->parent = priv->device;
err = mdiobus_register(stmmac_mii_bus);//注册总线。
if (err != 0) {
pr_err("%s: Cannot register as MDIO bus\n",
stmmac_mii_bus->name);
goto bus_register_fail;
}
在mdiobus_register()中,有一段phy扫面程序
for (i = 0; i < PHY_MAX_ADDR; i++) {
if ((bus->phy_mask & (1 << i)) == 0) {
struct phy_device *phydev;
phydev = mdiobus_scan(bus, i);
if (IS_ERR(phydev)) {
err = PTR_ERR(phydev);
goto error;
}
}
}
Mdiobus_scan最终会去读:
MII_PHYSID1,MII_PHYSID2
这个在上一篇的MII寄存器上说过。
获得的id会存入structphy_device的phy_id。这个structphy_device会被存入bus的phy_map里面。
系统启动打印就是:
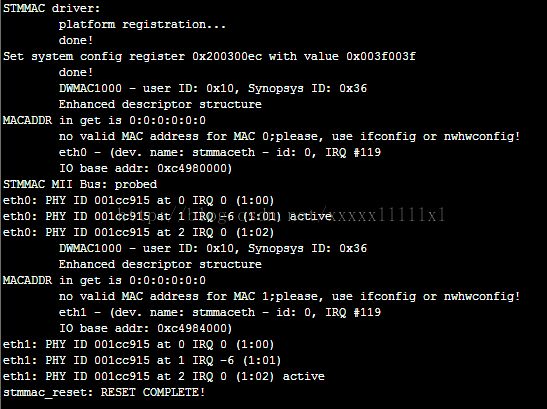
可以看到地址1和地址2的phy active.
还有IRQ -6其实是- ENXIO:No such device or address
我们在看看write read reset
Stmmac有一个GMII地址寄存器和数据寄存器
Read:
把要读的phy中的地址寄存器的值写入stmmac的GMII地址寄存器
等待地址寄存器第0位(busy)为0
读GMII数据寄存器,获得phy的相关设置值。
Write:
把要写的phy中的地址寄存器的值写入stmmac的GMII地址寄存器
把数据写入GMII数据寄存器
等待地址寄存器第0位(busy)为0
Reset:
当前就是把stmmac的GMII地址寄存器清零
现在我就当已经为内核提供bus完毕。
Device:
这个在mdiobus_scan时已经注册了,通过get_phy_device()获取phy的id,再把搜索到设备时会做phy_device_register动作。我们不具体看了。注册完之后,device_phy_id和driver_phy_id进程匹配,这就是device找到driver的过程。
从上面可以看出,device在驱动中是通过mii标准的寄存器去获取id,然后去匹配的。我们自己的驱动代码不需要太多的关心。也就是关心一下设备的address。
Driver:
在内核启动的时候已经注册了一个叫genphy_driver的驱动。
假设你的phy驱动需要一些特别的操作,你可以注册自己的driver,phy下有很多,如davicom.c/realtek.c等
你看一下realtek.c的驱动,对应的id是0x001cc912,我的板子用的是realtek的,id是0x001cc915,是rtl8211eg。所以我的板子没有RTL821x的phy_driver。用的就是genphy_driver。
不过genphy_driver的id和mask是
.phy_id =0xffffffff,
.phy_id_mask = 0xffffffff,
我们看一下mdio_bus中的match是
static int mdio_bus_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct phy_device *phydev = to_phy_device(dev);
struct phy_driver *phydrv = to_phy_driver(drv);
return ((phydrv->phy_id & phydrv->phy_id_mask) ==
(phydev->phy_id & phydrv->phy_id_mask));
}
这样不能与我的phy匹配。
不过我们不是靠这个机制。而是stmmac_main.c中stmmac_init_phy->phy_connect->phy_connect_direct->phy_attach_direct,看下面的代码;
/* Assume that if there is no driver, that it doesn't
* exist, and we should use the genphy driver. */
if (NULL == d->driver) {
d->driver = &genphy_driver.driver;//如果为空就赋值为genphy_driver。
err = d->driver->probe(d);
if (err >= 0)
err = device_bind_driver(d);
if (err)
return err;
}
如果你要写自己的驱动,你需要看看structphy_driver结构体,里面有很多的特别函数指针需要我们去实体化。我就不看了