linux usb ehci controller driver
1 数据结构
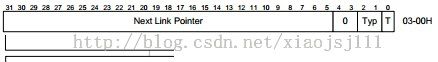
1.1 queue element transfer descriptor(qtd)
/*
* EHCI Specification 0.95 Section 3.5
* QTD: describe data transfer components (buffer, direction, ...)
* See Fig 3-6 "Queue Element Transfer Descriptor Block Diagram".
*
* These are associated only with "QH" (Queue Head) structures,
* used with control, bulk, and interrupt transfers.
*/
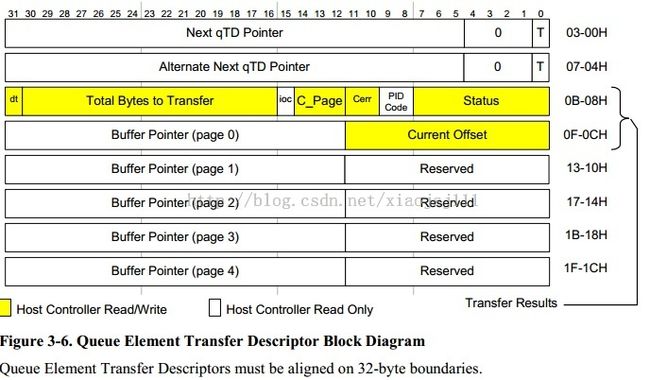
struct ehci_qtd {
/* first part defined by EHCI spec */
__hc32 hw_next; /* see EHCI 3.5.1 */
__hc32 hw_alt_next; /* see EHCI 3.5.2 */
__hc32 hw_token; /* see EHCI 3.5.3 */
#define QTD_TOGGLE (1 << 31) /* data toggle */
#define QTD_LENGTH(tok) (((tok)>>16) & 0x7fff)
#define QTD_IOC (1 << 15) /* interrupt on complete */
#define QTD_CERR(tok) (((tok)>>10) & 0x3)
#define QTD_PID(tok) (((tok)>>8) & 0x3)
#define QTD_STS_ACTIVE (1 << 7) /* HC may execute this */
#define QTD_STS_HALT (1 << 6) /* halted on error */
#define QTD_STS_DBE (1 << 5) /* data buffer error (in HC) */
#define QTD_STS_BABBLE (1 << 4) /* device was babbling (qtd halted) */
#define QTD_STS_XACT (1 << 3) /* device gave illegal response */
#define QTD_STS_MMF (1 << 2) /* incomplete split transaction */
#define QTD_STS_STS (1 << 1) /* split transaction state */
#define QTD_STS_PING (1 << 0) /* issue PING? */
#define ACTIVE_BIT(ehci) cpu_to_hc32(ehci, QTD_STS_ACTIVE)
#define HALT_BIT(ehci) cpu_to_hc32(ehci, QTD_STS_HALT)
#define STATUS_BIT(ehci) cpu_to_hc32(ehci, QTD_STS_STS)
__hc32 hw_buf [5]; /* see EHCI 3.5.4 */
__hc32 hw_buf_hi [5]; /* Appendix B */
/* the rest is HCD-private */
dma_addr_t qtd_dma; /* qtd address */
struct list_head qtd_list; /* sw qtd list */
struct urb *urb; /* qtd's urb */
size_t length; /* length of buffer */
} __attribute__ ((aligned (32)));该结构是数据传输组件,通过qtd->qtd_list成员挂在qh队列头下面。
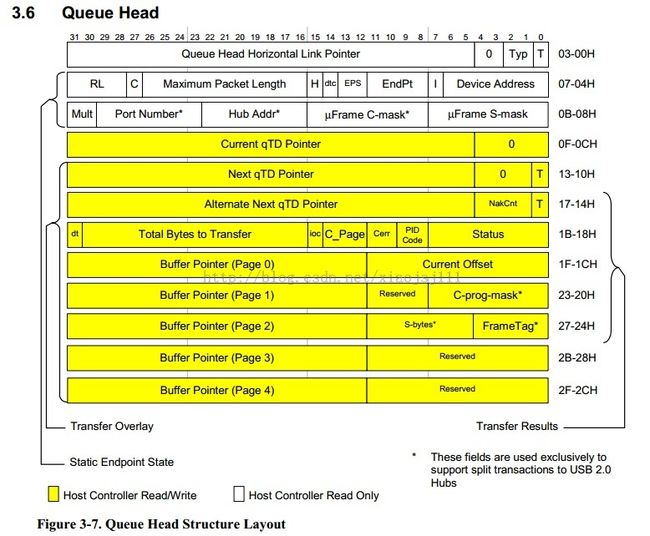
1.2 queue head 结构(qh)
/*
* EHCI Specification 0.95 Section 3.6
* QH: describes control/bulk/interrupt endpoints
* See Fig 3-7 "Queue Head Structure Layout".
*
* These appear in both the async and (for interrupt) periodic schedules.
*/
/* first part defined by EHCI spec */
struct ehci_qh_hw {
__hc32 hw_next; /* see EHCI 3.6.1 */
__hc32 hw_info1; /* see EHCI 3.6.2 */
#define QH_HEAD 0x00008000
__hc32 hw_info2; /* see EHCI 3.6.2 */
#define QH_SMASK 0x000000ff
#define QH_CMASK 0x0000ff00
#define QH_HUBADDR 0x007f0000
#define QH_HUBPORT 0x3f800000
#define QH_MULT 0xc0000000
__hc32 hw_current; /* qtd list - see EHCI 3.6.4 */
/* qtd overlay (hardware parts of a struct ehci_qtd) */
__hc32 hw_qtd_next;
__hc32 hw_alt_next;
__hc32 hw_token;
__hc32 hw_buf [5];
__hc32 hw_buf_hi [5];
} __attribute__ ((aligned(32)));
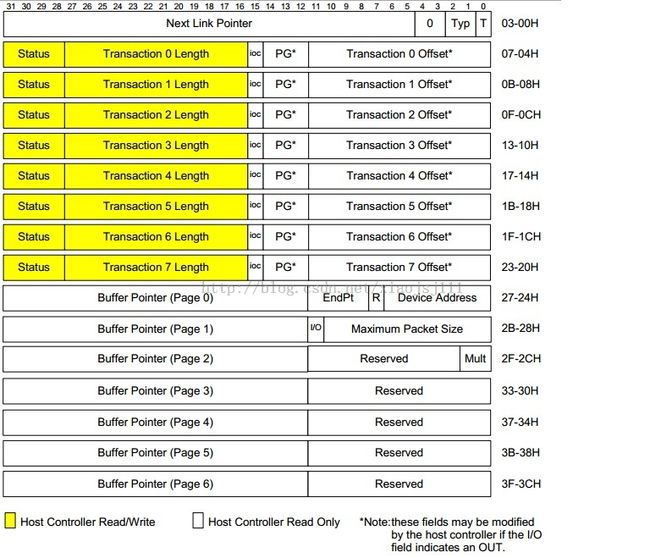
1.3 itd结构
- status 是由hc在transaction(事务)完成后,自动填充,表示传输的结果
- Transaction Length,表示该transaction的数据长度
- ioc表示该transaction完成后,是否产生中断
- PG用于选择下面的哪个buffer Pointer(指向一个虚拟页面,所以低12位都是0,所以低12位可用作其他用途)
- Transaction offset表示页内的偏移量
maxp = usb_maxpacket(dev, pipe, !is_input); unsigned multi = hb_mult(maxp); maxp = max_packet(maxp)*multi//计算一次同步传输,所包含的最大包的长度 stream->usecs = HS_USECS_ISO (maxp);//由包长换算成带宽时间 //bandwidth = stream->usecs * 8; //bandwidth /= interval;
/*
* EHCI Specification 0.95 Section 3.3
* Fig 3-4 "Isochronous Transaction Descriptor (iTD)"
*
* Schedule records for high speed iso xfers
*/
struct ehci_itd {
/* first part defined by EHCI spec */
__hc32 hw_next; /* see EHCI 3.3.1 */
__hc32 hw_transaction [8]; /* see EHCI 3.3.2 */
#define EHCI_ISOC_ACTIVE (1<<31) /* activate transfer this slot */
#define EHCI_ISOC_BUF_ERR (1<<30) /* Data buffer error */
#define EHCI_ISOC_BABBLE (1<<29) /* babble detected */
#define EHCI_ISOC_XACTERR (1<<28) /* XactErr - transaction error */
#define EHCI_ITD_LENGTH(tok) (((tok)>>16) & 0x0fff)
#define EHCI_ITD_IOC (1 << 15) /* interrupt on complete */
#define ITD_ACTIVE(ehci) cpu_to_hc32(ehci, EHCI_ISOC_ACTIVE)
__hc32 hw_bufp [7]; /* see EHCI 3.3.3 */
__hc32 hw_bufp_hi [7]; /* Appendix B */
/* the rest is HCD-private */
dma_addr_t itd_dma; /* for this itd */
union ehci_shadow itd_next; /* ptr to periodic q entry */
struct urb *urb;
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream; /* endpoint's queue */
struct list_head itd_list; /* list of stream's itds */
/* any/all hw_transactions here may be used by that urb */
unsigned frame; /* where scheduled */
unsigned pg;
unsigned index[8]; /* in urb->iso_frame_desc */
} __attribute__ ((aligned (32)));
该结构的前半部分用于hc,后半部分用于hcd来管理这个结构。
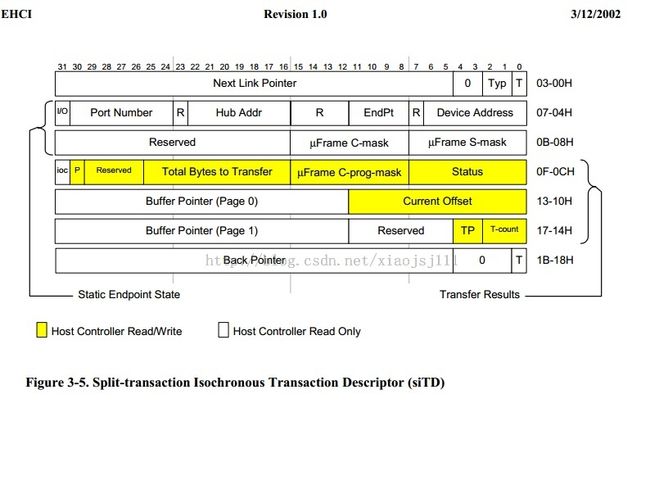
1.4 sitd结构
的基本结构。
/*
* EHCI Specification 0.95 Section 3.4
* siTD, aka split-transaction isochronous Transfer Descriptor
* ... describe full speed iso xfers through TT in hubs
* see Figure 3-5 "Split-transaction Isochronous Transaction Descriptor (siTD)
*/
struct ehci_sitd {
/* first part defined by EHCI spec */
__hc32 hw_next;
/* uses bit field macros above - see EHCI 0.95 Table 3-8 */
__hc32 hw_fullspeed_ep; /* EHCI table 3-9 */
__hc32 hw_uframe; /* EHCI table 3-10 */
__hc32 hw_results; /* EHCI table 3-11 */
#define SITD_IOC (1 << 31) /* interrupt on completion */
#define SITD_PAGE (1 << 30) /* buffer 0/1 */
#define SITD_LENGTH(x) (0x3ff & ((x)>>16))
#define SITD_STS_ACTIVE (1 << 7) /* HC may execute this */
#define SITD_STS_ERR (1 << 6) /* error from TT */
#define SITD_STS_DBE (1 << 5) /* data buffer error (in HC) */
#define SITD_STS_BABBLE (1 << 4) /* device was babbling */
#define SITD_STS_XACT (1 << 3) /* illegal IN response */
#define SITD_STS_MMF (1 << 2) /* incomplete split transaction */
#define SITD_STS_STS (1 << 1) /* split transaction state */
#define SITD_ACTIVE(ehci) cpu_to_hc32(ehci, SITD_STS_ACTIVE)
__hc32 hw_buf [2]; /* EHCI table 3-12 */
__hc32 hw_backpointer; /* EHCI table 3-13 */
__hc32 hw_buf_hi [2]; /* Appendix B */
/* the rest is HCD-private */
dma_addr_t sitd_dma;
union ehci_shadow sitd_next; /* ptr to periodic q entry */
struct urb *urb;
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream; /* endpoint's queue */
struct list_head sitd_list; /* list of stream's sitds */
unsigned frame;
unsigned index;
} __attribute__ ((aligned (32)));
该结构的开始部分是用于host controller来访问的,后面是hcd使用的,其中sitd_list 成员将该sitd结构连入到列表中。这样便于hcd来遍历这个列表(我们称为软件列表)。而该结构的hw_next则是用于连接硬件列表,是专供host controller来访问的。
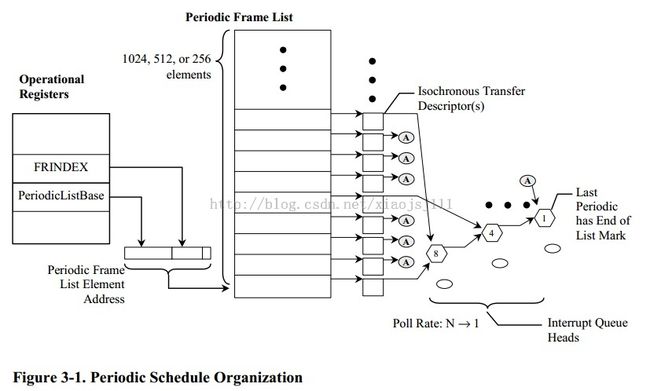
1.5 周期调度队列 vs 异步调度队列
该周期调度帧列表,是传输数据接口(指qtd,qh,itd,sitd等)在内存中的组织结构,这个组织结构将被host controller自动访问。但需要软件(hcd driver)来初始化好,并动态维护他(往这个结构中添加传输数据接口(对应enqueue操作),删除传输数据接口(dequeue操作))
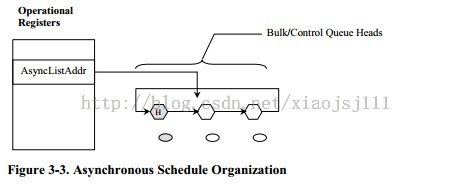
该结构用于管理和连接控制、块传输,该队列是单向循环队列,队列的节点就是qh,而每个qh描述一个端点的传输(可能是:高速/全速控制端点,高速/全速块端点),并且属于这个端点的所有待传数据都是通过qtd来描述,挂在qh节点对应的->qtd_list列表下。下图标有H的节点,则是这个循环调度队列的头节点。
2 操作模型
2.1 echi control对异步调度队列的处理过程
2.2 echi control对异步调度中的QH的删除算法(摘自ehci spec 4.8.2)
2.3 echi的ehci_urb_enqueue过程
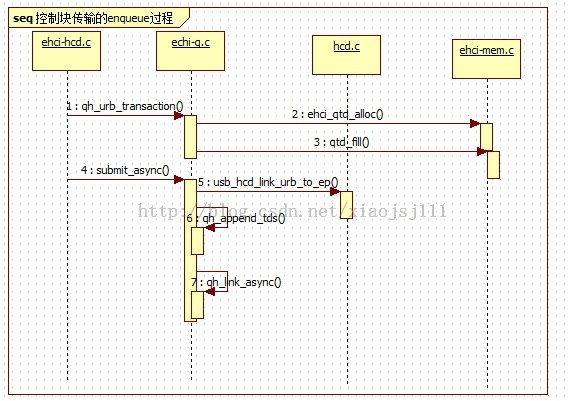
2.3.1 for usb bulk、control transfrer urb enqueue过程
* create a list of filled qtds for this URB; won't link into qh.
*/
static struct list_head *qh_urb_transaction (struct ehci_hcd*ehci,struct urb*urb,struct list_head*head,gfp_tflags)
- 该函数将一个urb传输映射成若干个qtd结构,并把他们关联起来。他们的关联分为两部分
- 一个是将这若干个qtd按他们被执行的顺序,通过qtd->qtd_list域连接到head列表头中,该列表主要用于软件来访问这些qtd
- 一个是通过qtd->hw_next指针,将这些qtd连接起来,这个连接是给host constroller使用的,所以->hw_next里存的是物理地址
- 一个是将这若干个qtd按他们被执行的顺序,通过qtd->qtd_list域连接到head列表头中,该列表主要用于软件来访问这些qtd
- 该函数根据urb->transfer_buffer_length的长度,来决定分配具体几个qtd,即一个qtd存不下所需传输的内容时,就调用ehci_qtd_alloc函数再分配一个qtd,然后再调用qtd_fill将剩余的数据的长度和buffer开始地址填充到qtd结构中。
- 该函数如果发现待传输的数据是控制传输,则为该控制传输,添加setup数据建立阶段所对应的qtd和状态阶段所对应的qtd
if (usb_pipecontrol (urb->pipe)) {//为控制的setup数据建立阶段,分配和填充qtd结构,并将它联入到head list列表头中
/* SETUP pid */
qtd_fill(ehci, qtd, urb->setup_dma,
sizeof (struct usb_ctrlrequest),
token | (2 /* "setup" */ << 8), 8);
/* ... and always at least one more pid */
token ^= QTD_TOGGLE;
qtd_prev = qtd;
qtd = ehci_qtd_alloc (ehci, flags);
if (unlikely (!qtd))
goto cleanup;
qtd->urb = urb;
qtd_prev->hw_next = QTD_NEXT(ehci, qtd->qtd_dma);
list_add_tail (&qtd->qtd_list, head);
/* for zero length DATA stages, STATUS is always IN */
if (len == 0)
token |= (1 /* "in" */ << 8);
}
如下代码为控制传输的状态阶段和以短包表示结束(URB_ZERO_PACKET)的bulk out传输分配和初始化qtd结构,并连入head list列表中
if (one_more) {
qtd_prev = qtd;
qtd = ehci_qtd_alloc (ehci, flags);
if (unlikely (!qtd))
goto cleanup;
qtd->urb = urb;
qtd_prev->hw_next = QTD_NEXT(ehci, qtd->qtd_dma);
list_add_tail (&qtd->qtd_list, head);
/* never any data in such packets */
qtd_fill(ehci, qtd, 0, 0, token, 0);
}
* For control/bulk/interrupt, return QH with these TDs appended.
* Allocates and initializes the QH if necessary.
* Returns null if it can't allocate a QH it needs to.
* If the QH has TDs (urbs) already, that's great.
*/
static struct ehci_qh *qh_append_tds (struct ehci_hcd*ehci,struct urb*urb,struct list_head*qtd_list,intepnum,void**ptr)
static struct ehci_qh *qh_append_tds (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct urb *urb,
struct list_head *qtd_list,
int epnum,
void **ptr
)
{
struct ehci_qh *qh = NULL;
__hc32 qh_addr_mask = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, 0x7f);
qh = (struct ehci_qh *) *ptr;
if (unlikely (qh == NULL)) { //如果该端点还没有对应的qh队列头,则就调用<span style="font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">qh_make函数</span>分配一个QH队列头
/* can't sleep here, we have ehci->lock... */
qh = qh_make (ehci, urb, GFP_ATOMIC);
*ptr = qh;
}
if (likely (qh != NULL)) {
struct ehci_qtd *qtd;
if (unlikely (list_empty (qtd_list)))
qtd = NULL;
else
qtd = list_entry (qtd_list->next, struct ehci_qtd,//获得列表节点所在的qtd结构
qtd_list);
/* control qh may need patching ... */
if (unlikely (epnum == 0)) {
/* usb_reset_device() briefly reverts to address 0 */
if (usb_pipedevice (urb->pipe) == 0)
qh->hw->hw_info1 &= ~qh_addr_mask;
}
/* just one way to queue requests: swap with the dummy qtd.
* only hc or qh_refresh() ever modify the overlay.
*/
if (likely (qtd != NULL)) {
struct ehci_qtd *dummy;
dma_addr_t dma;
__hc32 token;
/* to avoid racing the HC, use the dummy td instead of
* the first td of our list (becomes new dummy). both
* tds stay deactivated until we're done, when the
* HC is allowed to fetch the old dummy (4.10.2).
*/
token = qtd->hw_token;
qtd->hw_token = HALT_BIT(ehci);
dummy = qh->dummy;
dma = dummy->qtd_dma;
*dummy = *qtd;
dummy->qtd_dma = dma;
list_del (&qtd->qtd_list);//将qtd_list列表中的第一个元素删除,将dummy添加到这个位置,此时dummy->hw_next是指向qtd->hw_next的
list_add (&dummy->qtd_list, qtd_list);
list_splice_tail(qtd_list, &qh->qtd_list);//将带dummy的qtd list列表添加到qh->qtd_list列表的末尾
ehci_qtd_init(ehci, qtd, qtd->qtd_dma);
qh->dummy = qtd; //将qh->dummy指向原qtd list列表的第一个元素(已从list删除下来)
/* hc must see the new dummy at list end */
dma = qtd->qtd_dma;
qtd = list_entry (qh->qtd_list.prev,
struct ehci_qtd, qtd_list);//
qtd->hw_next = QTD_NEXT(ehci, dma);//让qh->qtd_list列表的尾端链上这个新的dummy元素
/* let the hc process these next qtds */
wmb ();
dummy->hw_token = token;
urb->hcpriv = qh_get (qh);
}
}
return qh;
}
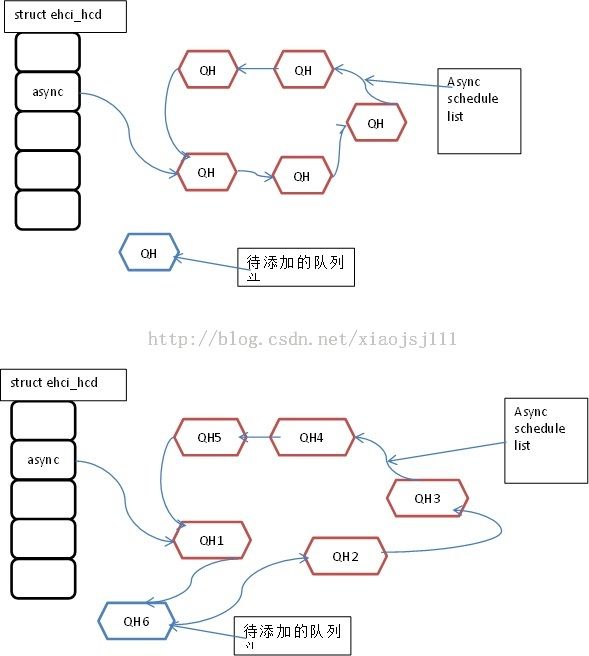
static void qh_link_async (struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh)
static void qh_link_async (struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh)
{
__hc32 dma = QH_NEXT(ehci, qh->qh_dma);
struct ehci_qh *head;
/* Don't link a QH if there's a Clear-TT-Buffer pending */
if (unlikely(qh->clearing_tt))
return;
WARN_ON(qh->qh_state != QH_STATE_IDLE);
/* (re)start the async schedule? */
head = ehci->async;//软件上的异步循环调度队列的头,并不是host controller所标识的队列头
timer_action_done (ehci, TIMER_ASYNC_OFF);
if (!head->qh_next.qh) {
u32 cmd = ehci_readl(ehci, &ehci->regs->command);
if (!(cmd & CMD_ASE)) {//对cmd寄存器中的cmd_ase位的控制,并不是立即使能的,需要结合status寄存器来最终确定。
/* in case a clear of CMD_ASE didn't take yet */
(void)handshake(ehci, &ehci->regs->status,
STS_ASS, 0, 150);
cmd |= CMD_ASE;
ehci_writel(ehci, cmd, &ehci->regs->command);
/* posted write need not be known to HC yet ... */
}
}
/* clear halt and/or toggle; and maybe recover from silicon quirk */
qh_refresh(ehci, qh);
/* splice right after start */
qh->qh_next = head->qh_next;
qh->hw->hw_next = head->hw->hw_next;
wmb ();
head->qh_next.qh = qh;
head->hw->hw_next = dma;
qh_get(qh);
qh->xacterrs = 0;
qh->qh_state = QH_STATE_LINKED;
/* qtd completions reported later by interrupt */
}
上述函数功能是将qh添加到异步循环调度队列中,必要时使能该异步调度使能位。上述操作见下面的示意图(注意每个QH对应一个端点的传输):
2.3.2 for PIPE_INTERRUPT urb enqueue过程(包括高速中断传输和分裂中断传输)
static int intr_submit (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct urb *urb,
struct list_head *qtd_list,
gfp_t mem_flags
) {
unsigned epnum;
unsigned long flags;
struct ehci_qh *qh;
int status;
struct list_head empty;
/* get endpoint and transfer/schedule data */
epnum = urb->ep->desc.bEndpointAddress;
spin_lock_irqsave (&ehci->lock, flags);
if (unlikely(!HCD_HW_ACCESSIBLE(ehci_to_hcd(ehci)))) {
status = -ESHUTDOWN;
goto done_not_linked;
}
status = usb_hcd_link_urb_to_ep(ehci_to_hcd(ehci), urb);
if (unlikely(status))
goto done_not_linked;
/* get qh and force any scheduling errors */
INIT_LIST_HEAD (&empty);
qh = qh_append_tds(ehci, urb, &empty, epnum, &urb->ep->hcpriv);
if (qh == NULL) {
status = -ENOMEM;
goto done;
}
if (qh->qh_state == QH_STATE_IDLE) {
if ((status = qh_schedule (ehci, qh)) != 0)
goto done;
}
/* then queue the urb's tds to the qh */
qh = qh_append_tds(ehci, urb, qtd_list, epnum, &urb->ep->hcpriv);
BUG_ON (qh == NULL);
/* ... update usbfs periodic stats */
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_int_reqs++;
done:
if (unlikely(status))
usb_hcd_unlink_urb_from_ep(ehci_to_hcd(ehci), urb);
done_not_linked:
spin_unlock_irqrestore (&ehci->lock, flags);
if (status)
qtd_list_free (ehci, urb, qtd_list);
return status;
}
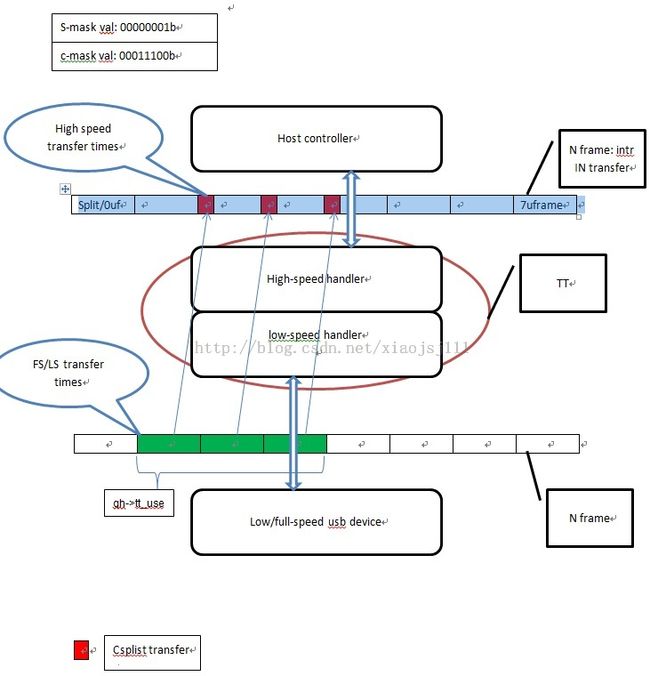
接下来的描述总线带宽,都是使用时间单位us(微秒)(总线带宽的描述,可以从时域和频域来描述),一个periodic frame list中的一frame的时间是1ms,而一个frame里包含了8个uframe,每个uframe对应一个总线的时隙(time slot),其带宽是固定的1000us/8=125us,并且usb2.0规定:周期传输的带宽不能超过总线带宽的80%,即不能超过125us*80%=100us。usb1.0中规定,同步传输的总线带宽不能够超过总线带宽的90%,但是low/full-speed设别,他们的总线时隙是1ms,即刚好对应一个frame帧的时间。
- qh->start:该成员仅对中断传输有意义,表示该QH被挂在周期微帧的什么位置,即在哪个周期微帧有中断传输,取值范围: 0..(qh->period - 1), or NO_FRAME(表示poll rate为1次/微帧)
- qh->usecs: 分裂传输分为split阶段和 csplit阶段,而该字段就是在split阶段所需要的总线带宽
- qh->c_usecs:表示在csplit阶段,所需要的总线带宽
- qh->tt_usecs:表示端点最大包长度在下行的全速总线上传输所需要占用的时间
- qh->gap_uf:表示该端点的最大包长度在下行的全速总线上传输完,该段时间对应多少个高速总线时隙
- qh->period:表示该中断传输的poll rate,表示每隔多少个uframe产生一次中断传输,单位为微帧
* Each QH holds a qtd list; a QH is used for everything except iso.
*
* For interrupt urbs, the scheduler must set the microframe scheduling
* mask(s) each time the QH gets scheduled. For highspeed, that's
* just one microframe in the s-mask. For split interrupt transactions
* there are additional complications: c-mask, maybe FSTNs.
*/
static struct ehci_qh *qh_make ( struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct urb *urb, gfp_t flags)
{
struct ehci_qh *qh = ehci_qh_alloc (ehci, flags);
u32 info1 = 0, info2 = 0;
int is_input, type;
int maxp = 0;
struct usb_tt *tt = urb->dev->tt;
struct ehci_qh_hw *hw;
if (!qh)
return qh;
/*
* init endpoint/device data for this QH
*/
info1 |= usb_pipeendpoint (urb->pipe) << 8;
info1 |= usb_pipedevice (urb->pipe) << 0;
is_input = usb_pipein (urb->pipe);
type = usb_pipetype (urb->pipe);
maxp = usb_maxpacket (urb->dev, urb->pipe, !is_input);
/* 1024 byte maxpacket is a hardware ceiling. High bandwidth
* acts like up to 3KB, but is built from smaller packets.
*/
if (max_packet(maxp) > 1024) {
ehci_dbg(ehci, "bogus qh maxpacket %d\n", max_packet(maxp));
goto done;
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//下面这段英文的注释,就是在初始化中断端点对应的QH时,需要考虑的问题,是难点!!!
/* Compute interrupt scheduling parameters just once, and save.
* - allowing for high bandwidth, how many nsec/uframe are used?
* - split transactions need a second CSPLIT uframe; same question
* - splits also need a schedule gap (for full/low speed I/O)
* - qh has a polling interval
*
* For control/bulk requests, the HC or TT handles these.
*/
if (type == PIPE_INTERRUPT) {//for 中断传输
qh->usecs = NS_TO_US(usb_calc_bus_time(USB_SPEED_HIGH,
is_input, 0,
hb_mult(maxp) * max_packet(maxp)));//计算该中断端点对应的最大包长度,在高速总线下需要的带宽()
qh->start = NO_FRAME;
qh->stamp = ehci->periodic_stamp;
if (urb->dev->speed == USB_SPEED_HIGH) {//高速中断传输
qh->c_usecs = 0;
qh->gap_uf = 0;
qh->period = urb->interval >> 3;
if (qh->period == 0 && urb->interval != 1) {//对于那些中断间隔为2,4个uframe的中断传输,直接都upscale到间隔为1个uframe的中断传输
/* NOTE interval 2 or 4 uframes could work.//这样更便于管理,带宽更高
* But interval 1 scheduling is simpler, and
* includes high bandwidth.
*/
urb->interval = 1;
} else if (qh->period > ehci->periodic_size) {//对于那些周期超过1024*8的中断传输,则都直接upscale到间隔为1024*8个uframe的中断传输
qh->period = ehci->periodic_size;
urb->interval = qh->period << 3;
}
} else { //全速中断传输
int think_time;
/* gap is f(FS/LS transfer times) */
qh->gap_uf = 1 + usb_calc_bus_time (urb->dev->speed,//针对全速和低速设备的中断传输,首先计算出该中断端点的最大包长度在全速总线上所占的总线带宽
is_input, 0, maxp) / (125 * 1000); //并计算出该总线带宽对应几个高速总线时隙,即对应几个uframe
/* FIXME this just approximates SPLIT/CSPLIT times */
if (is_input) { // 分裂中断IN传输的操作模型:SPLIT(对应带宽:HS_USECS(1)), gap, CSPLIT+DATA(对应带宽:qh->c_usecs)<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">qh->c_usecs)</span>
qh->c_usecs = qh->usecs + HS_USECS (0);
qh->usecs = HS_USECS (1);
} else { //分裂中断OUT传输的操作模型: SPLIT+DATA, gap, CSPLIT
qh->usecs += HS_USECS (1);
qh->c_usecs = HS_USECS (0);
}
think_time = tt ? tt->think_time : 0;
qh->tt_usecs = NS_TO_US (think_time +
usb_calc_bus_time (urb->dev->speed,
is_input, 0, max_packet (maxp)));//即这个长度的包在全速总线上传输,所需要的时间
qh->period = urb->interval;
if (qh->period > ehci->periodic_size) {
qh->period = ehci->periodic_size;
urb->interval = qh->period;
}
}
}
/* support for tt scheduling, and access to toggles */
qh->dev = urb->dev;
/* using TT? */
switch (urb->dev->speed) {
case USB_SPEED_LOW:
info1 |= (1 << 12); /*更新QH结构中的 EPS域到 "low" */
/* FALL THROUGH */
case USB_SPEED_FULL:
/* EPS 0 means "full" */
if (type != PIPE_INTERRUPT)
info1 |= (EHCI_TUNE_RL_TT << 28);
if (type == PIPE_CONTROL) {
info1 |= (1 << 27); /*field:"C" for TT */
info1 |= 1 << 14; /*field:"dtc" toggle from qtd */
}
info1 |= maxp << 16; /*field:"Maximum package length"*/
info2 |= (EHCI_TUNE_MULT_TT << 30); /*field:"Mult"*/
/* Some Freescale processors have an erratum in which the
* port number in the queue head was 0..N-1 instead of 1..N.
*/
if (ehci_has_fsl_portno_bug(ehci))/*Port number*/
info2 |= (urb->dev->ttport-1) << 23;
else
info2 |= urb->dev->ttport << 23;
/* set the address of the TT; for TDI's integrated
* root hub tt, leave it zeroed.
*/
if (tt && tt->hub != ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.root_hub)/*Hub address*/
info2 |= tt->hub->devnum << 16;
/* NOTE: if (PIPE_INTERRUPT) { scheduler sets c-mask } */
break;
case USB_SPEED_HIGH: /* no TT involved */
info1 |= (2 << 12); /* EPS "high" */
if (type == PIPE_CONTROL) {
info1 |= (EHCI_TUNE_RL_HS << 28);
info1 |= 64 << 16; /* usb2 fixed maxpacket */
info1 |= 1 << 14; /* toggle from qtd */
info2 |= (EHCI_TUNE_MULT_HS << 30);
} else if (type == PIPE_BULK) {
info1 |= (EHCI_TUNE_RL_HS << 28);
/* The USB spec says that high speed bulk endpoints
* always use 512 byte maxpacket. But some device
* vendors decided to ignore that, and MSFT is happy
* to help them do so. So now people expect to use
* such nonconformant devices with Linux too; sigh.
*/
info1 |= max_packet(maxp) << 16;
info2 |= (EHCI_TUNE_MULT_HS << 30);
} else { /* PIPE_INTERRUPT */
info1 |= max_packet (maxp) << 16;
info2 |= hb_mult (maxp) << 30;
}
break;
default:
dbg ("bogus dev %p speed %d", urb->dev, urb->dev->speed);
done:
qh_put (qh);
return NULL;
}
/* NOTE: if (PIPE_INTERRUPT) { scheduler sets s-mask } */
/* init as live, toggle clear, advance to dummy */
qh->qh_state = QH_STATE_IDLE;
hw = qh->hw;
hw->hw_info1 = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, info1);
hw->hw_info2 = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, info2);
qh->is_out = !is_input;
usb_settoggle (urb->dev, usb_pipeendpoint (urb->pipe), !is_input, 1);
qh_refresh (ehci, qh);
return qh;
}
- 首先该值不为0,则说明是中断端点,然后再根据EPS域
- 如果是高速端点,则smask则表示在哪些对应的微帧发起中断传输
- 如果是低速、全速端点,则smask则表示在哪个微帧发起ssplit传输
- 如果该值为0,说明是在异步传输队列中,只能是控制、bulk传输
/* "first fit" scheduling policy used the first time through,
* or when the previous schedule slot can't be re-used.
*/
static int qh_schedule(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh)
{
int status;
unsigned uframe;
__hc32 c_mask;
unsigned frame; /* 0..(qh->period - 1), or NO_FRAME */
struct ehci_qh_hw *hw = qh->hw;
qh_refresh(ehci, qh);
hw->hw_next = EHCI_LIST_END(ehci);
frame = qh->start;
/* reuse the previous schedule slots, if we can */
if (frame < qh->period) {
uframe = ffs(hc32_to_cpup(ehci, &hw->hw_info2) & QH_SMASK);
status = check_intr_schedule (ehci, frame, --uframe,
qh, &c_mask);
} else {
uframe = 0;
c_mask = 0;
status = -ENOSPC;
}
/* else scan the schedule to find a group of slots such that all
* uframes have enough periodic bandwidth available.
*/
if (status) {
/* "normal" case, uframing flexible except with splits */
if (qh->period) {
int i;
for (i = qh->period; status && i > 0; --i) {
frame = ++ehci->random_frame % qh->period;
for (uframe = 0; uframe < 8; uframe++) {
status = check_intr_schedule (ehci,
frame, uframe, qh,
&c_mask);
if (status == 0)
break;
}
}
/* qh->period == 0 means every uframe */
} else {
frame = 0;
status = check_intr_schedule (ehci, 0, 0, qh, &c_mask);
}
if (status)
goto done;
qh->start = frame; //选定了该frame帧对应的uframe微帧,是符合条件的。
/* reset S-frame and (maybe) C-frame masks */
hw->hw_info2 &= cpu_to_hc32(ehci, ~(QH_CMASK | QH_SMASK));
hw->hw_info2 |= qh->period
? cpu_to_hc32(ehci, 1 << uframe) //qh->period == 0 means every uframe都有中断传输,
: cpu_to_hc32(ehci, QH_SMASK); //不为0,则意味着只有制定的那个微帧才有中断传输或start split传输
hw->hw_info2 |= c_mask;//制定csplit传输的位置,只有全速、低速中断才有意义,如果其他情况,应该都为0.
} else
ehci_dbg (ehci, "reused qh %p schedule\n", qh);
/* stuff into the periodic schedule */
status = qh_link_periodic (ehci, qh);
done:
return status;
}
- 如果EPS指示是高速中断端点,则qh->usecs表示该中断IN、OUT传输所需的最大带宽
- 如果EPS指示是全速、低速中断端点,且是OUT中断传输,则qh->usecs表示:ssplit+data所需最大的带宽
- 如果EPS指示是全速、低速中断端点,且是IN中断传输,则qh->usecs为0
static int check_intr_schedule (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
unsigned frame,
unsigned uframe,
const struct ehci_qh *qh,
__hc32 *c_maskp
)
{
int retval = -ENOSPC;
u8 mask = 0;
if (qh->c_usecs && uframe >= 6) /* FSTN territory? */目前usb驱动还不支持分裂传输跨H帧边界,所以需要这样一个判断
goto done;
if (!check_period (ehci, frame, uframe, qh->period, qh->usecs))//计算frame帧中的uframe微帧对应的时隙组,是否有足够多可用的同步带宽来容纳qh->usecs对应的带宽
goto done;
if (!qh->c_usecs) {//对于全速、低速设备而言,如果中断OUT传输,则qh->c_usecs为0,如果是中断IN传输,则不为0
retval = 0;
*c_maskp = 0;
goto done;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_EHCI_TT_NEWSCHED
if (tt_available (ehci, qh->period, qh->dev, frame, uframe,//该函数判断tt下行的fs、ls设备对应于frame帧的时隙组,是否有足够同步带宽来容纳qh->tt_usecs
qh->tt_usecs)) {
unsigned i;
/* TODO : this may need FSTN for SSPLIT in uframe 5. */
for (i=uframe+1; i<8 && i<uframe+4; i++)
if (!check_period (ehci, frame, i,
qh->period, qh->c_usecs))//判断对应的uframe微帧所对应的时隙组,是否有足够带宽发起csplit传输
goto done;
else
mask |= 1 << i;
retval = 0;
*c_maskp = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, mask << 8);//设定在哪些帧发起csplit传输,固定为3个csplit传输。
}
#else
/* Make sure this tt's buffer is also available for CSPLITs.
* We pessimize a bit; probably the typical full speed case
* doesn't need the second CSPLIT.
*
* NOTE: both SPLIT and CSPLIT could be checked in just
* one smart pass...
*/
mask = 0x03 << (uframe + qh->gap_uf);
*c_maskp = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, mask << 8);
mask |= 1 << uframe;
if (tt_no_collision (ehci, qh->period, qh->dev, frame, mask)) {
if (!check_period (ehci, frame, uframe + qh->gap_uf + 1,
qh->period, qh->c_usecs))
goto done;
if (!check_period (ehci, frame, uframe + qh->gap_uf,
qh->period, qh->c_usecs))
goto done;
retval = 0;
}
#endif
done:
return retval;
}
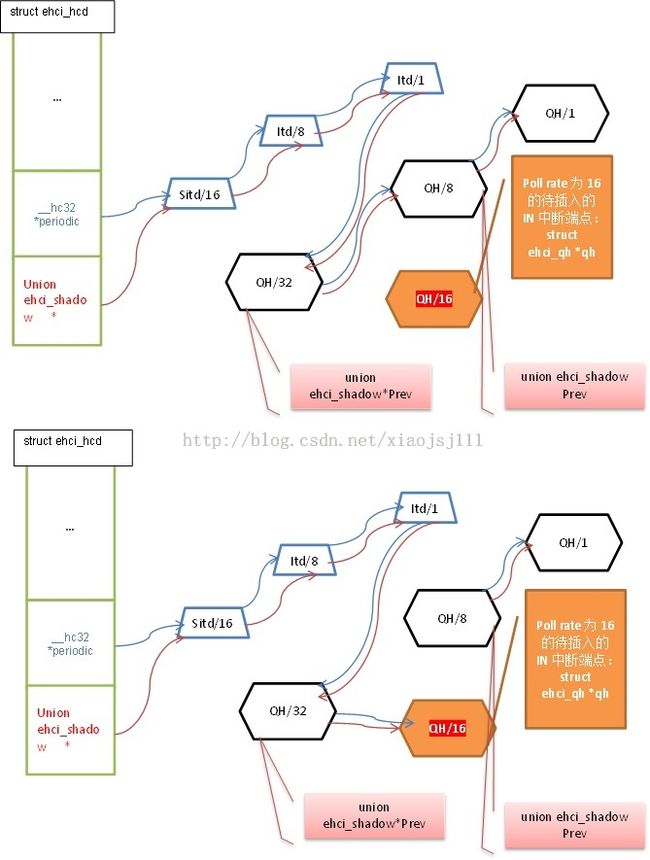
确定qh->start的值后,就可以通过qh_link_periodic函数,将qh以qh->period为间隔,链接到对应的时隙中。
- ehci->periodic[i]: 对应hc使用的periodic frame list,里面存储的是指向下一个接口数据的开始物理地址
- ehci->pshadow[i]:里面存储的是hc使用的接口数据对应的虚拟地址,与ehci->pshadow[i]的关系就是:
- 他们共相同的物理空间,ehci->periodic[i]是接口数据的ehci->pshadow[i]的开始部分,是hc在执行传输时需要的接口数据单元
- ehci->pshadow[i]中除去ehci->periodic[i]部分,还有剩余的私有部分,是用于软件来管理这些数据结构的。hc不会访问到。
-
ehci->periodic为硬件周期列表,共有1024项,供host constroller访问;ehci->pshadow是对应的软件结构列表,共hcd driver来访问。其实ehci->pshadow中前半部分,即为硬件表的内容,只是ehci->periodic种存的是物理地址,而ehci->pshadow使用的是物理地址对应的虚拟地址。
/* periodic schedule slots have iso tds (normal or split) first, then a
* sparse tree for active interrupt transfers.
*
* this just links in a qh; caller guarantees uframe masks are set right.
* no FSTN support (yet; ehci 0.96+)
*/
static int qh_link_periodic (struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh)
{
unsigned i;
unsigned period = qh->period;
dev_dbg (&qh->dev->dev,
"link qh%d-%04x/%p start %d [%d/%d us]\n",
period, hc32_to_cpup(ehci, &qh->hw->hw_info2)
& (QH_CMASK | QH_SMASK),
qh, qh->start, qh->usecs, qh->c_usecs);
/* high bandwidth, or otherwise every microframe */
if (period == 0)
period = 1;
for (i = qh->start; i < ehci->periodic_size; i += period) {
union ehci_shadow *prev = &ehci->pshadow[i];
__hc32 *hw_p = &ehci->periodic[i];
union ehci_shadow here = *prev;
__hc32 type = 0;
/* skip the iso nodes at list head */跳过前面的itd和sitd节点
while (here.ptr) {
type = Q_NEXT_TYPE(ehci, *hw_p);
if (type == cpu_to_hc32(ehci, Q_TYPE_QH))
break;
prev = periodic_next_shadow(ehci, prev, type);
hw_p = shadow_next_periodic(ehci, &here, type);
here = *prev;
}
/* sorting each branch by period (slow-->fast)//由于中断端点对应的qh在数据结构的组织上,根据poll rate从低到高连接在一起的。
* enables sharing interior tree nodes//所以要根据他们的qh->period来确定合适的插入位置
*/
while (here.ptr && qh != here.qh) {
if (qh->period > here.qh->period)
break;
prev = &here.qh->qh_next;
hw_p = &here.qh->hw->hw_next;
here = *prev; //在这里需要特别注意的是:here不是指针,而prev是指针,prev指向的是列表的前一个,而here指向的列表的当前节点
}
/* link in this qh, unless some earlier pass did that */
if (qh != here.qh) { // before insert: prev--->here ; after insert: prev-->qh--->here
qh->qh_next = here;
if (here.qh)
qh->hw->hw_next = *hw_p;
wmb ();
prev->qh = qh;
*hw_p = QH_NEXT (ehci, qh->qh_dma);
}
}
qh->qh_state = QH_STATE_LINKED;
qh->xacterrs = 0;
qh_get (qh);
/* update per-qh bandwidth for usbfs */
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_allocated += qh->period
? ((qh->usecs + qh->c_usecs) / qh->period)
: (qh->usecs * 8);
/* maybe enable periodic schedule processing */
return enable_periodic(ehci);
}
上面操作的示意图如下:
2.3.3 for PIPE_ISOCHRONOUS urb enqueue过程(包括高速同步和分裂同步传输)
- stream->usecs:表示传输该端口所允许的最大包所需要的带宽(用us单位计量,call HS_USECS_ISO())
- stream->c_usecs:对应同步分裂传输的csplit传输阶段所需的带宽
- stream->raw_mask:该成员存储了在哪些微帧需要发起ssplist和csplist传输,注意是相对于0uframe的,如果是从非0uframe开始,则整体左移。
- stream->next_uframe: 对应该端点的下次链入interface schedule data structure在periodic list列表的什么地方
- stream->splits:该成员是stream->raw_mask在左移uframe为后的值。(uframe为同步预算调度计算出来的对应的插入该同步传输的位置,0<=uframe<8)
- stream->interval:类似urb->interval的含义
1157 maximum_periodic_bytes_per_frame = 12 Mb/s * 1 ms / 8 bits_per_byte *6 data_bits / 7 bit-stuffed_data_bits * 90% maximum_periodic_data_per_frame
static void
iso_stream_init (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream,
struct usb_device *dev,
int pipe,
unsigned interval
)
{
static const u8 smask_out [] = { 0x01, 0x03, 0x07, 0x0f, 0x1f, 0x3f };//该数组表示以microframe的数目为index,相应的值为在哪些uframe slot需要发起start split传输
u32 buf1;
unsigned epnum, maxp;
int is_input;
long bandwidth;
/*
* this might be a "high bandwidth" highspeed endpoint,
* as encoded in the ep descriptor's wMaxPacket field
*/
epnum = usb_pipeendpoint (pipe);
is_input = usb_pipein (pipe) ? USB_DIR_IN : 0;
maxp = usb_maxpacket(dev, pipe, !is_input);
if (is_input) {
buf1 = (1 << 11);
} else {
buf1 = 0;
}
/* knows about ITD vs SITD */
if (dev->speed == USB_SPEED_HIGH) {//高速同步传输
unsigned multi = hb_mult(maxp);//陪乘数,表示在一个uframe中连续发起multi个IN/OUT传输
stream->highspeed = 1;
maxp = max_packet(maxp);
buf1 |= maxp;
maxp *= multi;
stream->buf0 = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, (epnum << 8) | dev->devnum);
stream->buf1 = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, buf1);
stream->buf2 = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, multi);
/* usbfs wants to report the average usecs per frame tied up
* when transfers on this endpoint are scheduled ...
*/
stream->usecs = HS_USECS_ISO (maxp);//同步带宽
bandwidth = stream->usecs * 8;
bandwidth /= interval;
} else {//全速同步分裂传输
u32 addr;
int think_time;
int hs_transfers;
addr = dev->ttport << 24;
if (!ehci_is_TDI(ehci)
|| (dev->tt->hub !=
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.root_hub))
addr |= dev->tt->hub->devnum << 16;
addr |= epnum << 8;
addr |= dev->devnum;
stream->usecs = HS_USECS_ISO (maxp);//同步带宽
think_time = dev->tt ? dev->tt->think_time : 0;
stream->tt_usecs = NS_TO_US (think_time + usb_calc_bus_time (//这个最大包长度在全速总线上,所占的总线带宽(以时间us计量)
dev->speed, is_input, 1, maxp));
hs_transfers = max (1u, (maxp + 187) / 188);//这个全速同步传输时间,跨越了几个uframe微帧,由于在一个微帧(125us)的时间里,全速同步传输最多可以传送188个字节。
if (is_input) {// 同步端点IN传输的操作模式:SSplit+IN , CSplit+IN+DATA
u32 tmp;
addr |= 1 << 31;
stream->c_usecs = stream->usecs;//同步IN传输csplist阶段所需的最大带宽
stream->usecs = HS_USECS_ISO (1);//同步In传输ssplit阶段所需的最大带宽
stream->raw_mask = 1;
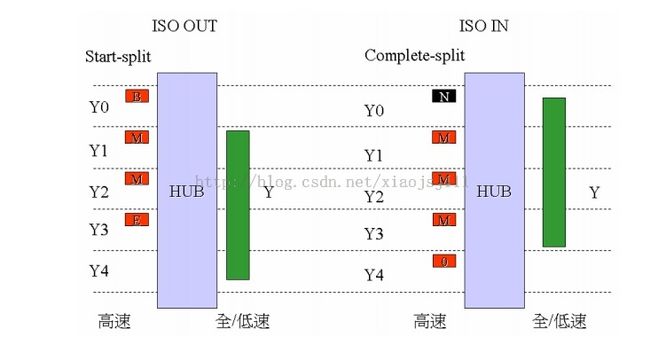
/* c-mask as specified in USB 2.0 11.18.4 3.c */该语句的含义,见下面的示意图
tmp = (1 << (hs_transfers + 2)) - 1;
stream->raw_mask |= tmp << (8 + 2);
} else //同步端点OUT传输的操作模式:SSplist+OUT+DATA,没有csplist阶段,因为同步传输是不不可靠传输,不需要响应
stream->raw_mask = smask_out [hs_transfers - 1];//对应那些位置需要发起ssplist out传输,如果数据包大于188byte,则需要多个ssplist
bandwidth = stream->usecs + stream->c_usecs;
bandwidth /= interval << 3;
/* stream->splits gets created from raw_mask later */
stream->address = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, addr);
}
stream->bandwidth = bandwidth;
stream->udev = dev;
stream->bEndpointAddress = is_input | epnum;
stream->interval = interval;
stream->maxp = maxp;
}
/* description of one iso transaction (up to 3 KB data if highspeed) */
struct ehci_iso_packet {
/* These will be copied to iTD when scheduling */
u64 bufp; /* itd->hw_bufp{,_hi}[pg] |= */
__hc32 transaction; /* itd->hw_transaction[i] |= */
u8 cross; /* buf crosses pages */
/* for full speed OUT splits */
u32 buf1;
};
/* temporary schedule data for packets from iso urbs (both speeds)
* each packet is one logical usb transaction to the device (not TT),
* beginning at stream->next_uframe
*/
struct ehci_iso_sched {
struct list_head td_list;
unsigned span;
struct ehci_iso_packet packet [0];
};
itd_urb_transaction 函数,就是根据urb的urb->number_of_packets和urb->interval来确定需要分配多少个itd结构体,并初始化他们,并挂在sched->td_list列表上。
static int
itd_urb_transaction (
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream,
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct urb *urb,
gfp_t mem_flags
)
{
struct ehci_itd *itd;
dma_addr_t itd_dma;
int i;
unsigned num_itds;
struct ehci_iso_sched *sched;
unsigned long flags;
sched = iso_sched_alloc (urb->number_of_packets, mem_flags);
if (unlikely (sched == NULL))
return -ENOMEM;
itd_sched_init(ehci, sched, stream, urb);
if (urb->interval < 8)
num_itds = 1 + (sched->span + 7) / 8;//计算一个urb需要多少个itd接口数据
else
num_itds = urb->number_of_packets;
/* allocate/init ITDs */
spin_lock_irqsave (&ehci->lock, flags);
for (i = 0; i < num_itds; i++) {
/* free_list.next might be cache-hot ... but maybe
* the HC caches it too. avoid that issue for now.
*/
/* prefer previously-allocated itds */
if (likely (!list_empty(&stream->free_list))) {
itd = list_entry (stream->free_list.prev,
struct ehci_itd, itd_list);
list_del (&itd->itd_list);
itd_dma = itd->itd_dma;
} else {
spin_unlock_irqrestore (&ehci->lock, flags);
itd = dma_pool_alloc (ehci->itd_pool, mem_flags,
&itd_dma);
spin_lock_irqsave (&ehci->lock, flags);
if (!itd) {
iso_sched_free(stream, sched);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ehci->lock, flags);
return -ENOMEM;
}
}
memset (itd, 0, sizeof *itd);
itd->itd_dma = itd_dma;
list_add (&itd->itd_list, &sched->td_list);
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore (&ehci->lock, flags);
/* temporarily store schedule info in hcpriv */
urb->hcpriv = sched;
urb->error_count = 0;
return 0;
}
/*
* This scheduler plans almost as far into the future as it has actual
* periodic schedule slots. (Affected by TUNE_FLS, which defaults to
* "as small as possible" to be cache-friendlier.) That limits the size
* transfers you can stream reliably; avoid more than 64 msec per urb.
* Also avoid queue depths of less than ehci's worst irq latency (affected
* by the per-urb URB_NO_INTERRUPT hint, the log2_irq_thresh module parameter,
* and other factors); or more than about 230 msec total (for portability,
* given EHCI_TUNE_FLS and the slop). Or, write a smarter scheduler!
*/
#define SCHEDULE_SLOP 80 /* microframes */
static int
iso_stream_schedule (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct urb *urb,
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream
)
{
u32 now, next, start, period, span;
int status;
unsigned mod = ehci->periodic_size << 3;
struct ehci_iso_sched *sched = urb->hcpriv;
period = urb->interval;
span = sched->span;
if (!stream->highspeed) {
period <<= 3;
span <<= 3;
}
if (span > mod - SCHEDULE_SLOP) {
ehci_dbg (ehci, "iso request %p too long\n", urb);
status = -EFBIG;
goto fail;
}
now = ehci_read_frame_index(ehci) & (mod - 1);//当前hc在哪个周期列表元素中执行
/* Typical case: reuse current schedule, stream is still active.
* Hopefully there are no gaps from the host falling behind
* (irq delays etc), but if there are we'll take the next
* slot in the schedule, implicitly assuming URB_ISO_ASAP.
*/
if (likely (!list_empty (&stream->td_list))) {//这个说明这个周期端点,之前已经被调度过了只要按对应的时隙间隔填充,不用再去判断对应的时隙组是否有足够可用的总线带宽,因为已经判断过了。
u32 excess;
/* For high speed devices, allow scheduling within the
* isochronous scheduling threshold. For full speed devices
* and Intel PCI-based controllers, don't (work around for
* Intel ICH9 bug).
*/
if (!stream->highspeed && ehci->fs_i_thresh)
next = now + ehci->i_thresh;
else
next = now;
/* Fell behind (by up to twice the slop amount)?
* We decide based on the time of the last currently-scheduled
* slot, not the time of the next available slot.
*/
excess = (stream->next_uframe - period - next) & (mod - 1);
if (excess >= mod - 2 * SCHEDULE_SLOP)
start = next + excess - mod + period *
DIV_ROUND_UP(mod - excess, period);//保证在对应的间隔为period的时隙slot中。
else
start = next + excess + period; //基于上次被调度的地方,而不是最近hc被访问的地方
if (start - now >= mod) {
ehci_dbg(ehci, "request %p would overflow (%d+%d >= %d)\n",
urb, start - now - period, period,
mod);
status = -EFBIG;
goto fail;
}
}
/* need to schedule; when's the next (u)frame we could start?
* this is bigger than ehci->i_thresh allows; scheduling itself
* isn't free, the slop should handle reasonably slow cpus. it
* can also help high bandwidth if the dma and irq loads don't
* jump until after the queue is primed.
*/
else {
int done = 0;
start = SCHEDULE_SLOP + (now & ~0x07);
/* NOTE: assumes URB_ISO_ASAP, to limit complexity/bugs */
/* find a uframe slot with enough bandwidth.
* Early uframes are more precious because full-speed
* iso IN transfers can't use late uframes,
* and therefore they should be allocated last.
*/
next = start;
start += period;
do {
start--;
/* check schedule: enough space? */
if (stream->highspeed) {
if (itd_slot_ok(ehci, mod, start,
stream->usecs, period))//详细见下面的解析
done = 1;
} else {
if ((start % 8) >= 6)
continue;
if (sitd_slot_ok(ehci, mod, stream,
start, sched, period))//详细见下面的解析
done = 1;
}
} while (start > next && !done);
/* no room in the schedule */
if (!done) {
ehci_dbg(ehci, "iso resched full %p (now %d max %d)\n",
urb, now, now + mod);
status = -ENOSPC;
goto fail;
}
}
/* Tried to schedule too far into the future? */
if (unlikely(start - now + span - period
>= mod - 2 * SCHEDULE_SLOP)) {
ehci_dbg(ehci, "request %p would overflow (%d+%d >= %d)\n",
urb, start - now, span - period,
mod - 2 * SCHEDULE_SLOP);
status = -EFBIG;
goto fail;
}
stream->next_uframe = start & (mod - 1);//该值在新的itd或sitd被连入到这个周期列表后,会被更新(详见itd_link_urb和sitd_link_urb函数)
/* report high speed start in uframes; full speed, in frames */
urb->start_frame = stream->next_uframe;
if (!stream->highspeed)
urb->start_frame >>= 3;
return 0;
fail:
iso_sched_free(stream, sched);
urb->hcpriv = NULL;
return status;
}
/* how many of the uframe's 125 usecs are allocated? */
static unsigned short
periodic_usecs (struct ehci_hcd *ehci, unsigned frame, unsigned uframe)
{
__hc32 *hw_p = &ehci->periodic [frame];
union ehci_shadow *q = &ehci->pshadow [frame];
unsigned usecs = 0;
struct ehci_qh_hw *hw;
while (q->ptr) {
switch (hc32_to_cpu(ehci, Q_NEXT_TYPE(ehci, *hw_p))) {
case Q_TYPE_QH: //该QH只能对应的就是中断端点,
hw = q->qh->hw;
/* is it in the S-mask? */
if (hw->hw_info2 & cpu_to_hc32(ehci, 1 << uframe))//对于高速中断设备,表示在S-mask对应的位置发起中断传输,对应的最大可能的带宽包存在qh->usecs变量中。
usecs += q->qh->usecs;
/* ... or C-mask? */
if (hw->hw_info2 & cpu_to_hc32(ehci,
1 << (8 + uframe)))//对于高速中断设备而言,该域为0,而对于全速设备而言,该域就是csplist传输,对应的带宽
usecs += q->qh->c_usecs;
hw_p = &hw->hw_next;
q = &q->qh->qh_next;
break;
// case Q_TYPE_FSTN:
default:
/* for "save place" FSTNs, count the relevant INTR
* bandwidth from the previous frame
*/
if (q->fstn->hw_prev != EHCI_LIST_END(ehci)) {
ehci_dbg (ehci, "ignoring FSTN cost ...\n");
}
hw_p = &q->fstn->hw_next;
q = &q->fstn->fstn_next;
break;
case Q_TYPE_ITD:
if (q->itd->hw_transaction[uframe])//高速同步端点,一个itd保存了8个微帧的传输,如果对应的微帧位置没有事务传输,则应该为0,如果有对应的传输,则最大可能的带宽保存在stream->usecs变量中
usecs += q->itd->stream->usecs;
hw_p = &q->itd->hw_next;
q = &q->itd->itd_next;
break;
case Q_TYPE_SITD:
/* is it in the S-mask? (count SPLIT, DATA) */
if (q->sitd->hw_uframe & cpu_to_hc32(ehci,
1 << uframe)) {
if (q->sitd->hw_fullspeed_ep &
cpu_to_hc32(ehci, 1<<31))
usecs += q->sitd->stream->usecs;// 全速设备的,In同步端点传输,对应的start split传输,最大可能的带宽保存在stream->usecs里
else /* worst case for OUT start-split */
usecs += HS_USECS_ISO (188);//全速设备的OUT同步端点传输,只有start-split+data传输,没有cspllist传输,out传输所允许最大的包大小就是188个字节
}
/* ... C-mask? (count CSPLIT, DATA) */
if (q->sitd->hw_uframe &
cpu_to_hc32(ehci, 1 << (8 + uframe))) {
/* worst case for IN complete-split */
usecs += q->sitd->stream->c_usecs;//全速设备的IN同步端点,他的csplit传输,包含了data阶段,所允许的最大带宽保存在stream->usecs里。
}
hw_p = &q->sitd->hw_next;
q = &q->sitd->sitd_next;
break;
}
}
#ifdef DEBUG
if (usecs > ehci->uframe_periodic_max)
ehci_err (ehci, "uframe %d sched overrun: %d usecs\n",
frame * 8 + uframe, usecs);
#endif
return usecs;
}
itd_slot_ok函数确定在uframe>>3的大帧中的第uframe&0x7个微帧位置,预算调度一个带宽为usecs时长的传输,是否符合同步带宽的约束条件(即总得周期带宽不能超过整个微帧总线带宽的80%)
static inline int
itd_slot_ok (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
u32 mod, //mod即为1024*8
u32 uframe,
u8 usecs,
u32 period //每隔多少个微帧发起一个同步传输
)
{
uframe %= period;//uframe的范围为0...(period-1)
do {
/* can't commit more than uframe_periodic_max usec */
if (periodic_usecs (ehci, uframe >> 3, uframe & 0x7)
> (ehci->uframe_periodic_max - usecs))
return 0;
/* we know urb->interval is 2^N uframes */
uframe += period;
} while (uframe < mod);//遍历整个周期帧列表,即有个1024个列表,而每个列表中的每项又包含了8个微帧的带宽分布情况
return 1;
}
- 分裂传输,涉及到TT,那也就是说,会同时涉及高速周期传输和低速周期传输,那要往这个frame大帧上预算分配一个调度(用stream来表述这个调度,类似qh的功能,一个同步端点对应一个stream),则这个调度要同时满足两个约束:
- 在高速总线带宽这边,要满足在对应的微帧中(125us),周期传输不能超过总线带宽的80%
- 同时在低速总线带宽这边,也要满足在对应的大帧中(1000us即1ms),周期传输不能超过总线带宽的90%
- 如果是OUT同步分裂传输,由于他只有start split+data阶段,没有csplit阶段,并且在data长度大于188字节时,会包含多个连续的start split+data阶段,就要保证每个split阶段对应的微帧的周期带宽都符合约束条件
- 如果是IN同步分裂传输,他是由:start split , csplit +IN + data阶段组成,所以主要是检查在发起csplist传输的微帧,它的周期带宽是否符合周期带宽的约束,由于会在多个微帧发起这个cplit传输,所以要根据cmask位检查多个对应的微帧
- stream->raw_mask是未移位的smask和cmask位掩码。在微帧uframe的位置确定后,就需要将stream->raw_mask集体向左移位uframe & 7位,即:stream->splits = stream->raw_mask << (uframe & 7)
static inline int
sitd_slot_ok (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
u32 mod,
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream,
u32 uframe,
struct ehci_iso_sched *sched,
u32 period_uframes
)
{
u32 mask, tmp;
u32 frame, uf;
mask = stream->raw_mask << (uframe & 7);
/* for IN, don't wrap CSPLIT into the next frame */
if (mask & ~0xffff) //目前尚不支持分裂传输跨H frame边界
return 0;
/* this multi-pass logic is simple, but performance may
* suffer when the schedule data isn't cached.
*/
/* check bandwidth */
uframe %= period_uframes;// 范围:0<uframe<(period_uframes-1),单位是微帧
do {
u32 max_used;
frame = uframe >> 3;//计算对应的大帧
uf = uframe & 7; //计算对应的微帧
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_EHCI_TT_NEWSCHED
/* The tt's fullspeed bus bandwidth must be available.
* tt_available scheduling guarantees 10+% for control/bulk.
*/
if (!tt_available (ehci, period_uframes << 3,
stream->udev, frame, uf, stream->tt_usecs))//确定在对应的大帧是否有足够可用的低速周期带宽来发起这次分裂周期传输
return 0;
#else
/* tt must be idle for start(s), any gap, and csplit.
* assume scheduling slop leaves 10+% for control/bulk.
*/
if (!tt_no_collision (ehci, period_uframes << 3,
stream->udev, frame, mask))
return 0;
#endif
/* check starts (OUT uses more than one) */
max_used = ehci->uframe_periodic_max - stream->usecs;
for (tmp = stream->raw_mask & 0xff; tmp; tmp >>= 1, uf++) {//如果是OUT分裂传输,我们要确定在连续的这几个分裂OUT周期传输所对应的微帧是否有足够可用的周期带宽
if (periodic_usecs (ehci, frame, uf) > max_used)
return 0;
}
/* for IN, check CSPLIT */
if (stream->c_usecs) { //如果是IN分裂传输,我们要判断,在多个csplit传输对应的微帧是否都有足够可用的周期带宽
uf = uframe & 7;
max_used = ehci->uframe_periodic_max - stream->c_usecs;
do {
tmp = 1 << uf;
tmp <<= 8;
if ((stream->raw_mask & tmp) == 0)
continue;
if (periodic_usecs (ehci, frame, uf)
> max_used)
return 0;
} while (++uf < 8);
}
/* we know urb->interval is 2^N uframes */
uframe += period_uframes;
} while (uframe < mod);
stream->splits = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, stream->raw_mask << (uframe & 7));//保存移位后的smask和cmask
return 1;
}
/*
* Return true if the device's tt's downstream bus is available for a
* periodic transfer of the specified length (usecs), starting at the
* specified frame/uframe. Note that (as summarized in section 11.19
* of the usb 2.0 spec) TTs can buffer multiple transactions for each
* uframe.
*
* The uframe parameter is when the fullspeed/lowspeed transfer
* should be executed in "B-frame" terms, which is the same as the
* highspeed ssplit's uframe (which is in "H-frame" terms). For example
* a ssplit in "H-frame" 0 causes a transfer in "B-frame" 0.
* See the EHCI spec sec 4.5 and fig 4.7.
*
* This checks if the full/lowspeed bus, at the specified starting uframe,
* has the specified bandwidth available, according to rules listed
* in USB 2.0 spec section 11.18.1 fig 11-60.
*
* This does not check if the transfer would exceed the max ssplit
* limit of 16, specified in USB 2.0 spec section 11.18.4 requirement #4,
* since proper scheduling limits ssplits to less than 16 per uframe.
*/
static int tt_available (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
unsigned period,
struct usb_device *dev,
unsigned frame,
unsigned uframe,
u16 usecs
)
{
if ((period == 0) || (uframe >= 7)) /* error */
return 0;
for (; frame < ehci->periodic_size; frame += period) {
unsigned short tt_usecs[8];
periodic_tt_usecs (ehci, dev, frame, tt_usecs);//确定在frame大帧中(对应1000us),有多少带宽已经被全速周期传输占用了,并将他们记录在tt_usecs数组中。
ehci_vdbg(ehci, "tt frame %d check %d usecs start uframe %d in"
" schedule %d/%d/%d/%d/%d/%d/%d/%d\n",
frame, usecs, uframe,
tt_usecs[0], tt_usecs[1], tt_usecs[2], tt_usecs[3],
tt_usecs[4], tt_usecs[5], tt_usecs[6], tt_usecs[7]);
if (max_tt_usecs[uframe] <= tt_usecs[uframe]) {
ehci_vdbg(ehci, "frame %d uframe %d fully scheduled\n",
frame, uframe);
return 0;
}
/* special case for isoc transfers larger than 125us:
* the first and each subsequent fully used uframe
* must be empty, so as to not illegally delay
* already scheduled transactions
*/
if (125 < usecs) {//对于那些带宽大于125us的周期传输,我们要求第一个和随后的几个微帧都必须是空的,不然当前的周期传输就会被非法的延迟。
int ufs = (usecs / 125);
int i;
for (i = uframe; i < (uframe + ufs) && i < 8; i++)
if (0 < tt_usecs[i]) {
ehci_vdbg(ehci,
"multi-uframe xfer can't fit "
"in frame %d uframe %d\n",
frame, i);
return 0;
}
}
tt_usecs[uframe] += usecs;
carryover_tt_bandwidth(tt_usecs);
/* fail if the carryover pushed bw past the last uframe's limit */
if (max_tt_usecs[7] < tt_usecs[7]) {
ehci_vdbg(ehci,
"tt unavailable usecs %d frame %d uframe %d\n",
usecs, frame, uframe);
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
下面这个数组,是表示周期传输在全速总线带宽的约束下,在8个微帧中的最佳总线带宽分配时间。
static const unsigned char
max_tt_usecs[] = { 125, 125, 125, 125, 125, 125, 30, 0 };
/* How many of the tt's periodic downstream 1000 usecs are allocated?
*
* While this measures the bandwidth in terms of usecs/uframe,
* the low/fullspeed bus has no notion of uframes, so any particular
* low/fullspeed transfer can "carry over" from one uframe to the next,
* since the TT just performs downstream transfers in sequence.
*
* For example two separate 100 usec transfers can start in the same uframe,
* and the second one would "carry over" 75 usecs into the next uframe.
*/
static void
periodic_tt_usecs (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct usb_device *dev,
unsigned frame,
unsigned short tt_usecs[8]
)
{
__hc32 *hw_p = &ehci->periodic [frame];
union ehci_shadow *q = &ehci->pshadow [frame];
unsigned char uf;
memset(tt_usecs, 0, 16);
while (q->ptr) {
switch (hc32_to_cpu(ehci, Q_NEXT_TYPE(ehci, *hw_p))) {
case Q_TYPE_ITD:
hw_p = &q->itd->hw_next;
q = &q->itd->itd_next;
continue;
case Q_TYPE_QH:
if (same_tt(dev, q->qh->dev)) {
uf = tt_start_uframe(ehci, q->qh->hw->hw_info2);//通过查看s-mask位,全速、低速中断传输将在哪个微帧被发起
tt_usecs[uf] += q->qh->tt_usecs;//对应的全速、低速中断传输的最大带宽
}
hw_p = &q->qh->hw->hw_next;
q = &q->qh->qh_next;
continue;
case Q_TYPE_SITD:
if (same_tt(dev, q->sitd->urb->dev)) {
uf = tt_start_uframe(ehci, q->sitd->hw_uframe);//通过查看s-mask位,全速、低速同步传输在哪个微帧被发起
tt_usecs[uf] += q->sitd->stream->tt_usecs;//低速同步带宽的最大带宽
}
hw_p = &q->sitd->hw_next;
q = &q->sitd->sitd_next;
continue;
// case Q_TYPE_FSTN:
default:
ehci_dbg(ehci, "ignoring periodic frame %d FSTN\n",
frame);
hw_p = &q->fstn->hw_next;
q = &q->fstn->fstn_next;
}
}
carryover_tt_bandwidth(tt_usecs);
if (max_tt_usecs[7] < tt_usecs[7])
ehci_err(ehci, "frame %d tt sched overrun: %d usecs\n",
frame, tt_usecs[7] - max_tt_usecs[7]);
}
itd_link_urb函数: 将urb对应的itd链接到硬件对应的周期列表中
/* fit urb's itds into the selected schedule slot; activate as needed */
static int
itd_link_urb (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct urb *urb,
unsigned mod,
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream
)
{
int packet;
unsigned next_uframe, uframe, frame;
struct ehci_iso_sched *iso_sched = urb->hcpriv;
struct ehci_itd *itd;
next_uframe = stream->next_uframe & (mod - 1);//itd被连入的位置
if (unlikely (list_empty(&stream->td_list))) {
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_allocated
+= stream->bandwidth;
ehci_vdbg (ehci,
"schedule devp %s ep%d%s-iso period %d start %d.%d\n",
urb->dev->devpath, stream->bEndpointAddress & 0x0f,
(stream->bEndpointAddress & USB_DIR_IN) ? "in" : "out",
urb->interval,
next_uframe >> 3, next_uframe & 0x7);
}
if (ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_isoc_reqs == 0) {
if (ehci->amd_pll_fix == 1)
usb_amd_quirk_pll_disable();
}
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_isoc_reqs++;
/* fill iTDs uframe by uframe */
for (packet = 0, itd = NULL; packet < urb->number_of_packets; ) {//注意一个itd可能包含多个struct ehci_iso_packet包,
if (itd == NULL) {
/* ASSERT: we have all necessary itds */
// BUG_ON (list_empty (&iso_sched->td_list));
/* ASSERT: no itds for this endpoint in this uframe */
itd = list_entry (iso_sched->td_list.next,
struct ehci_itd, itd_list); //iso_sched结构对应一个urb(是一一对应的),里面保存了用于填充itd的成员,iso_sched结构可以对应多个itd成员(1对多)。
list_move_tail (&itd->itd_list, &stream->td_list);//将这个itd连入到stream->td_list列表中
itd->stream = iso_stream_get (stream);
itd->urb = urb;
itd_init (ehci, stream, itd);//初始化itd,主要是包含一些同步端点的信息
}
uframe = next_uframe & 0x07;
frame = next_uframe >> 3;
itd_patch(ehci, itd, iso_sched, packet, uframe);//初始化同步端点在uframe微帧位置对应的传输描述,包括:itd->hw_transaction,pg,itd->hw_bufp
next_uframe += stream->interval;//跳到下一个填充微帧的位置
next_uframe &= mod - 1;
packet++;
/* link completed itds into the schedule */
if (((next_uframe >> 3) != frame)
|| packet == urb->number_of_packets) {//如果越过了itd结构对应的大帧frame,则这个itd连入到周期调度列表中
itd_link(ehci, frame & (ehci->periodic_size - 1), itd);//详细见下面的描述
itd = NULL;
}
}
stream->next_uframe = next_uframe;//用于下次调度的插入位置
/* don't need that schedule data any more */
iso_sched_free (stream, iso_sched);
urb->hcpriv = NULL;
timer_action (ehci, TIMER_IO_WATCHDOG);
return enable_periodic(ehci);
}
static inline void
itd_link (struct ehci_hcd *ehci, unsigned frame, struct ehci_itd *itd)
{
union ehci_shadow *prev = &ehci->pshadow[frame];//取得这个周期调度列表对应的软件部分
__hc32 *hw_p = &ehci->periodic[frame];//取得这个周期调度列表对应的硬件部分
union ehci_shadow here = *prev;
__hc32 type = 0;
/* skip any iso nodes which might belong to previous microframes */ //注意要跳过前面已经链入的所有同步节点。因为可以肯定的是,他们都是在当前要连入的微帧之前
while (here.ptr) {
type = Q_NEXT_TYPE(ehci, *hw_p);
if (type == cpu_to_hc32(ehci, Q_TYPE_QH))//已连入的同步节点之后,中断节点之前: itd--itd--itd(new added node)---qh---qh
break;
prev = periodic_next_shadow(ehci, prev, type);
hw_p = shadow_next_periodic(ehci, &here, type);
here = *prev;
}
itd->itd_next = here;//操作如下:itd--itd(prev)--itd(new added node)--qh(here)
itd->hw_next = *hw_p;
prev->itd = itd;
itd->frame = frame;
wmb ();
*hw_p = cpu_to_hc32(ehci, itd->itd_dma | Q_TYPE_ITD);
}
/* fit urb's sitds into the selected schedule slot; activate as needed */
static int
sitd_link_urb (
struct ehci_hcd *ehci,
struct urb *urb,
unsigned mod,
struct ehci_iso_stream *stream
)
{
int packet;
unsigned next_uframe;
struct ehci_iso_sched *sched = urb->hcpriv;
struct ehci_sitd *sitd;
next_uframe = stream->next_uframe; //该sitds列表插入的开始位置
if (list_empty(&stream->td_list)) {
/* usbfs ignores TT bandwidth */
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_allocated
+= stream->bandwidth;
ehci_vdbg (ehci,
"sched devp %s ep%d%s-iso [%d] %dms/%04x\n",
urb->dev->devpath, stream->bEndpointAddress & 0x0f,
(stream->bEndpointAddress & USB_DIR_IN) ? "in" : "out",
(next_uframe >> 3) & (ehci->periodic_size - 1),
stream->interval, hc32_to_cpu(ehci, stream->splits));
}
if (ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_isoc_reqs == 0) {
if (ehci->amd_pll_fix == 1)
usb_amd_quirk_pll_disable();
}
ehci_to_hcd(ehci)->self.bandwidth_isoc_reqs++;
/* fill sITDs frame by frame *///将urb中的数据填充到对应的sitd结构体中。
for (packet = 0, sitd = NULL;
packet < urb->number_of_packets;
packet++) {//需要注意的是:
/* ASSERT: we have all necessary sitds */
BUG_ON (list_empty (&sched->td_list));
/* ASSERT: no itds for this endpoint in this frame */
sitd = list_entry (sched->td_list.next,
struct ehci_sitd, sitd_list);
list_move_tail (&sitd->sitd_list, &stream->td_list);
sitd->stream = iso_stream_get (stream);
sitd->urb = urb;
sitd_patch(ehci, stream, sitd, sched, packet);//填充sitd结构
sitd_link(ehci, (next_uframe >> 3) & (ehci->periodic_size - 1),//将该sitd连入到周期帧列表中
sitd);
next_uframe += stream->interval << 3;//指向下次调度插入的地方
}
stream->next_uframe = next_uframe & (mod - 1);
/* don't need that schedule data any more */
iso_sched_free (stream, sched);
urb->hcpriv = NULL;
timer_action (ehci, TIMER_IO_WATCHDOG);
return enable_periodic(ehci);
2.4 分裂传输过程
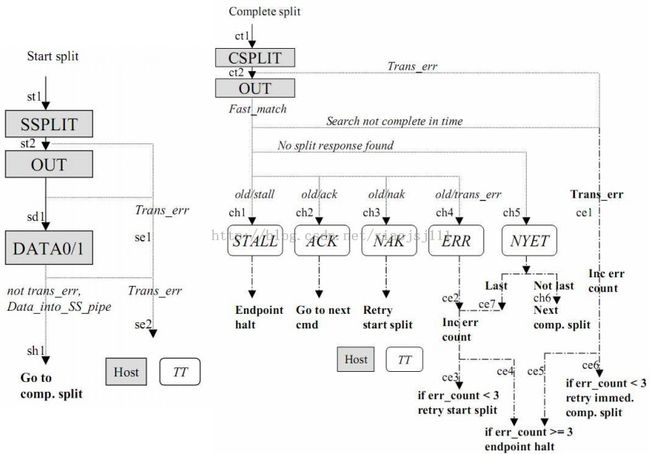
TT 采用流水的方式处理周期型的分离传输,一次周期型的分离传输在 TT 中共有四种状态:New、Pending、Ready 以及 Old。一次分离传输依次经历这四种状态。其中 New 态为这次分离传输在 TT 中建立的状态,是一个暂态、最长不能超过 1 个微帧的时间; Pending为等待传输完成的状态,最长不能超过 4 个微帧;Ready 为传输已经完成,等待 Host 取回结果的状态,最长不能超过 2 个微帧;Old 表示传输已经全部完成,TT 中该传输所占用的Buffer 可以重新利用。
由于速度不匹配,在一个微帧里,最多可以在全速总线上传输 188 字节的数据,在传输的数据量较大的情况下,例如同步传输的最大包长度为 1023 字节,如果等到整个包传完再响应 HOST 的 C-Split,不但要求 TT 有更多的 Buffer,并且会使 HOST 浪费较多的时间在等待数据传输完成。因此 TT 采用了如下的处理方式:
上行方向上,即 IN 型的传输:无论何时,只要 TT 收到超过 2 个字节的数据,就响应HOST 的 C-Split,向 HOST 发回数据,并在 PID 中以 MDATA,DATA1/0 表明还有没有未传完的数据。如果还有数据,则以 MDATA 发送,否则以 DATA1/0 发送。 HOST 在收到 MDATA后,应继续在下一个微帧里发起 C-Split 传输,向 HUB 请求数据,知道收到一个 DATA0/1
的数据包。
下行方向上,即 OUT 型的传输:HOST 把一个大的数据包拆成最大 188 字节的若干个小包,在连续的多个微帧里用 S-Split 向 TT 发送数据
针对iso的同步传输,如下图所示,B:表示begin;M:表示中间数据;E:表示最后的数据;N:表示nyet;0:表示data0,即最后一个数据包。
2.4.1 同步分裂传输的过程
2.4.2 控制/中断分裂传输的过程
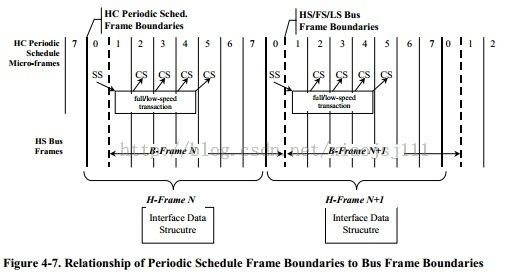
2.4.3 分裂传输时的H frame与B frame
2.5 urb的重要成员域
- urb->setup_dma/urb->setup_packet
- urb->transfer_buffer_length/urb->transfer_buffer
- urb->transfer_flags
- URB_SHORT_NOT_OK:report short reads as errors
- URB_ZERO_PACKET:Finish bulk OUT with short packet
- URB_NO_INTERRUPT:HINT: no non-error interrupt
- URB_NO_TRANSFER_DMA_MAP: urb->transfer_dma valid on submit
- URB_SHORT_NOT_OK:report short reads as errors
- urb->interval:针对周期传输由意义,表示每隔多少个uframe发起一次中断或同步传输
- urb->number_of_packets:该字段主要用来同个一个urb来提交多个同步传输,每个同步传输对应一个微帧,这些微帧之间的间隔为urb->interval
- urb->iso_frame_desc[i]:0<i<(urb->number_of_packets),每个usb_iso_packet_descriptor元素描述一个赌赢的同步传输所包含的数据buffer(开始地址和长度)