20个JS优化代码技巧
原文网址链接为:http://www.jstips.co/ 。截取了一部分本人认为比较实用的技巧分享给大家。其中一小部分技巧为JS面向对象的写法,不宜一一列出。关于JS面向对象的写法可参考本人前几篇随笔:
JS面向对象(1) -- 简介,入门,系统常用类,自定义类,constructor,typeof,instanceof,对象在内存中的表现形式
JS面向对象(2) -- this的使用,对象之间的赋值,for...in语句,delete使用,成员方法,json对象的使用,prototype的使用,原型继承与原型链
JS面向对象(3) -- Object类,静态属性,闭包,私有属性, call和apply的使用,继承的三种实现方法
1.Insert item inside an Array(向数组中插入元素)
向一个数组中插入元素是平时很常见的一件事情。你可以使用push在数组尾部插入元素,可以用unshift在数组头部插入元素,也可以用splice在数组中间插入元素。
1 var arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
2 //old method
3 arr.push(6); 4 //new method 快43% 5 arr[arr.length] = 6; 6 7 var arr = [1,2,3,4,5]; 8 //old method 9 arr.unshift(0); 10 //new method 快98% 11 [0].concat(arr);
2.Improve Nested Conditionals(优化嵌套的条件语句)
面对大量的if-else语句
1 //method1
2 if (color) {
3 if (color === 'black') { 4 printBlackBackground(); 5 } else if (color === 'red') { 6 printRedBackground(); 7 } else if (color === 'blue') { 8 printBlueBackground(); 9 } else if (color === 'green') { 10 printGreenBackground(); 11 } else { 12 printYellowBackground(); 13 } 14 } 15 16 //method2 17 switch(color) { 18 case 'black': 19 printBlackBackground(); 20 break; 21 case 'red': 22 printRedBackground(); 23 break; 24 case 'blue': 25 printBlueBackground(); 26 break; 27 case 'green': 28 printGreenBackground(); 29 break; 30 default: 31 printYellowBackground(); 32 } 33 34 //method3 35 switch(true) { 36 case (typeof color === 'string' && color === 'black'): 37 printBlackBackground(); 38 break; 39 case (typeof color === 'string' && color === 'red'): 40 printRedBackground(); 41 break; 42 case (typeof color === 'string' && color === 'blue'): 43 printBlueBackground(); 44 break; 45 case (typeof color === 'string' && color === 'green'): 46 printGreenBackground(); 47 break; 48 case (typeof color === 'string' && color === 'yellow'): 49 printYellowBackground(); 50 break; 51 } 52 53 //method4 54 var colorObj = { 55 'black': printBlackBackground, 56 'red': printRedBackground, 57 'blue': printBlueBackground, 58 'green': printGreenBackground, 59 'yellow': printYellowBackground 60 }; 61 if (color in colorObj) { 62 colorObj[color](); 63 }
3.Sorting strings with accented characters(排列含音节字母的字符串)
Javascript有一个原生方法sort可以排列数组。一次简单的array.sort()将每一个数组元素视为字符串并按照字母表排列。但是当你试图整理一个非ASCII元素的数组时,你可能会得到一个奇怪的结果。
1 ['Shanghai', 'New York', 'Mumbai', 'Buenos Aires'].sort();
2 // ["Buenos Aires", "Mumbai", "New York", "Shanghai"]
3
4 //method1
5 // 西班牙语
6 ['único','árbol', 'cosas', 'fútbol'].sort(); 7 // ["cosas", "fútbol", "árbol", "único"] // bad order 8 // 德语 9 ['Woche', 'wöchentlich', 'wäre', 'Wann'].sort(); 10 // ["Wann", "Woche", "wäre", "wöchentlich"] // bad order 11 12 //method2 13 ['único','árbol', 'cosas', 'fútbol'].sort(Intl.Collator().compare); 14 // ["árbol", "cosas", "fútbol", "único"] 15 16 ['Woche', 'wöchentlich', 'wäre', 'Wann'].sort(Intl.Collator().compare); 17 // ["Wann", "wäre", "Woche", "wöchentlich"]
4.Differences between undefined and null(undefined与null的区别)
-
undefined表示一个变量没有被声明,或者被声明了但没有被赋值 -
null是一个表示“没有值”的值 -
Javascript将未赋值的变量默认值设为
undefined -
Javascript从来不会将变量设为
null。它是用来让程序员表明某个用var声明的变量时没有值的。 -
undefined不是一个有效的JSON,而null是 -
undefined的类型(typeof)是undefined -
null的类型(typeof)是object. -
它们都是基本类型
-
null === undefined // false
5.Check if a property is in a Object(检查某对象是否有某属性)
1 //method1
2 var myObject = {
3 name: '@tips_js'
4 }; 5 if (myObject.name) { } 6 7 //method2 8 var myObject = { 9 name: '@tips_js' 10 }; 11 12 myObject.hasOwnProperty('name'); // true 13 'name' in myObject; // true 14 15 myObject.hasOwnProperty('valueOf'); // false, valueOf 继承自原型链 16 'valueOf' in myObject; // true
两者检查属性的深度不同,换言之hasOwnProperty只在本身有此属性时返回true,而in操作符不区分属性来自于本身或继承自原型链。
6.Tip to measure performance of a javascript block(测量javascript代码块性能的小知识)
快速的测量javascript的性能,我们可以使用console的方法,例如
1 console.time("Array initialize");
2 var arr = new Array(100), 3 len = arr.length, 4 i; 5 6 for (i = 0; i < len; i++) { 7 arr[i] = new Object(); 8 }; 9 console.timeEnd("Array initialize"); // 0.711ms
7.Fat Arrow Functions(箭头函数)
语法: 更少的代码行; 不再需要一遍一遍的打function了
语义: 从上下文中捕获this关键字
1 // 使用functions
2 var arr = [5,3,2,9,1];
3 var arrFunc = arr.map(function(x) { 4 return x * x; 5 }); 6 console.log(arrFunc ) 7 8 // 使用箭头函数 9 var arr = [5,3,2,9,1]; 10 var arrFunc = arr.map((x) => x*x); 11 console.log(arrFunc )
箭头函数在这种情况下省去了写小括号,function以及return的时间。
8.Even simpler way of using indexOf as a contains clause(更简单的使用indexOf实现contains功能)
JavaScript并未提供contains方法。检测子字符串是否存在于字符串或者变量是否存在于数组你可能会这样做。
1 var someText = 'javascript rules';
2 if (someText.indexOf('javascript') !== -1) { 3 } 4 5 // or 6 if (someText.indexOf('javascript') >= 0) { 7 }
建议的方法:
1 var someText = 'text';
2 !!~someText.indexOf('tex'); // someText contains "tex" - true
3 !~someText.indexOf('tex'); // someText NOT contains "tex" - false
4 ~someText.indexOf('asd'); // someText doesn't contain "asd" - false
5 ~someText.indexOf('ext'); // someText contains "ext" - true
9.Rounding the fast way(更快的取整)
一个位操作符 ~ 将输入的32位的数字(input)转换为 -(input+1). 两个位操作符将输入(input)转变为 -(-(input + 1)+1) 是一个使结果趋向于0的取整好工具. 对于数字, 负数就像使用Math.ceil()方法而正数就像使用Math.floor()方法. 转换失败时,返回0,这在Math.floor()方法转换失败返回NaN时或许会派上用场。
1 // 单个 ~ 2 console.log(~1337) // -1338 3 4 // 数字输入 5 console.log(~~47.11) // -> 47 6 console.log(~~-12.88) // -> -12 7 console.log(~~1.9999) // -> 1 8 console.log(~~3) // -> 3 9 10 // 转换失败 11 console.log(~~[]) // -> 0 12 console.log(~~NaN) // -> 0 13 console.log(~~null) // -> 0 14 15 // 大于32位整数时转换失败 16 console.log(~~(2147483647 + 1) === (2147483647 + 1)) // -> 0
10.Safe string concatenation
1 //method 1
2 var one = 1;
3 var two = 2; 4 var three = '3'; 5 var result = ''.concat(one, two, three); //"123" 6 //method 2 7 var one = 1; 8 var two = 2; 9 var three = '3'; 10 var result = one + two + three; //"33" instead of "123"
拼接时使用加号,可能会导致意想不到的错误结果。
11.Return objects to enable chaining of functions(返回对象,使方法可以链式调用)
1 function Person(name) {
2 this.name = name; 3 4 this.sayName = function() { 5 console.log("Hello my name is: ", this.name); 6 return this; 7 }; 8 9 this.changeName = function(name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 return this; 12 }; 13 } 14 15 var person = new Person("John"); 16 person.sayName().changeName("Timmy").sayName();
在面向对象的Javascript中为对象建立一个方法时,返回当前对象可以让你在一条链上调用方法。
12.Converting to number fast way(转换为数字的更快方法)
将字符串转换为数字是极为常见的。最简单和快速的方法是使用+(加号) 来实现。
1 var one = '1';
2 var numberOne = +one; // Number 1
3 var one = '1'; 4 var negativeNumberOne = -one; // Number -1
13.Use === instead of ==(使用 === 而不是 ==)
== (或者 !=) 操作在需要的情况下自动进行了类型转换。=== (或 !==)操作不会执行任何转换。===在比较值和类型时,可以说比==更快。
1 [10] == 10 // 为 true 2 [10] === 10 // 为 false 3 4 '10' == 10 // 为 true 5 '10' === 10 // 为 false 6 7 [] == 0 // 为 true 8 [] === 0 // 为 false 9 10 '' == false // 为 true 但 true == "a" 为false 11 '' === false // 为 false
14.Filtering and Sorting a List of Strings(过滤并排序字符串列表)
你可能有一个很多名字组成的列表,需要过滤掉重复的名字并按字母表将其排序。
1 var keywords = ['do', 'if', 'in', 'for', 'new', 'try', 'var', 'case', 'else', 'enum', 'null', 'this', 'true', 'void', 'with', 'break', 'catch', 'class', 'const', 'false', 'super', 'throw', 'while', 'delete', 'export', 'import', 'return', 'switch', 'typeof', 'default', 'extends', 'finally', 'continue', 'debugger', 'function', 'do', 'if', 'in', 'for', 'int', 'new', 'try', 'var', 'byte', 'case', 'char', 'else', 'enum', 'goto', 'long', 'null', 'this', 'true', 'void', 'with', 'break', 'catch', 'class', 'const', 'false', 'final', 'float', 'short', 'super', 'throw', 'while', 'delete', 'double', 'export', 'import', 'native', 'public', 'return', 'static', 'switch', 'throws', 'typeof', 'boolean', 'default', 'extends', 'finally', 'package', 'private', 'abstract', 'continue', 'debugger', 'function', 'volatile', 'interface', 'protected', 'transient', 'implements', 'instanceof', 'synchronized', 'do', 'if', 'in', 'for', 'let', 'new', 'try', 'var', 'case', 'else', 'enum', 'eval', 'null', 'this', 'true', 'void', 'with', 'break', 'catch', 'class', 'const', 'false', 'super', 'throw', 'while', 'yield', 'delete', 'export', 'import', 'public', 'return', 'static', 'switch', 'typeof', 'default', 'extends', 'finally', 'package', 'private', 'continue', 'debugger', 'function', 'arguments', 'interface', 'protected', 'implements', 'instanceof', 'do', 'if', 'in', 'for', 'let', 'new', 'try', 'var', 'case', 'else', 'enum', 'eval', 'null', 'this', 'true', 'void', 'with', 'await', 'break', 'catch', 'class', 'const', 'false', 'super', 'throw', 'while', 'yield', 'delete', 'export', 'import', 'public', 'return', 'static', 'switch', 'typeof', 'default', 'extends', 'finally', 'package', 'private', 'continue', 'debugger', 'function', 'arguments', 'interface', 'protected', 'implements', 'instanceof'];
2 var filteredAndSortedKeywords = keywords 3 .filter(function (keyword, index) { 4 return keywords.lastIndexOf(keyword) === index; 5 }) 6 .sort(function (a, b) { 7 return a < b ? -1 : 1; 8 });
因为我们不想改变我们的原始列表,所以我们准备用高阶函数叫做filter,它将基于我们传递的回调方法返回一个新的过滤后的数组。回调方法将比较当前关键字在原始列表里的索引和新列表中的索引,仅当索引匹配时将当前关键字push到新数组。
最后我们准备使用sort方法排序过滤后的列表,sort只接受一个比较方法作为参数,并返回按字母表排序后的列表。
1 const filteredAndSortedKeywords = keywords
2 .filter((keyword, index) => keywords.lastIndexOf(keyword) === index) 3 .sort((a, b) => a < b ? -1 : 1); 4 console.log(filteredAndSortedKeywords); 5 // ['abstract', 'arguments', 'await', 'boolean', 'break', 'byte', 'case', 'catch', 'char', 'class', 'const', 'continue', 'debugger', 'default', 'delete', 'do', 'double', 'else', 'enum', 'eval', 'export', 'extends', 'false', 'final', 'finally', 'float', 'for', 'function', 'goto', 'if', 'implements', 'import', 'in', 'instanceof', 'int', 'interface', 'let', 'long', 'native', 'new', 'null', 'package', 'private', 'protected', 'public', 'return', 'short', 'static', 'super', 'switch', 'synchronized', 'this', 'throw', 'throws', 'transient', 'true', 'try', 'typeof', 'var', 'void', 'volatile', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
15.Short circuit evaluation in JS(JS中的短路求值)
短路求值是说, 只有当第一个运算数的值无法确定逻辑运算的结果时,才对第二个运算数进行求值:当AND(&&)的第一个运算数的值为false时,其结果必定为false;当OR(||)的第一个运算数为true时,最后结果必定为true。
逻辑或可以用来给参数设置默认值。
1 function theSameOldFoo(name){
2 name = name || 'Bar' ; 3 console.log("My best friend's name is " + name); 4 } 5 theSameOldFoo(); // My best friend's name is Bar 6 theSameOldFoo('Bhaskar'); // My best friend's name is Bhaskar
逻辑与可以用来避免调用undefined参数的属性时报错
1 var dog = {
2 bark: function(){ 3 console.log('Woof Woof'); 4 } 5 }; 6 // 调用 dog.bark(); 7 dog.bark(); // Woof Woof. 8 // 但是当dog未定义时,dog.bark() 将会抛出"Cannot read property 'bark' of undefined." 错误 9 // 防止这种情况,我们可以使用 &&. 10 dog&&dog.bark(); // This will only call dog.bark(), if dog is defined.
16.!!(!!)
1 !!"" // false
2 !!0 // false
3 !!null // false
4 !!undefined // false
5 !!NaN // false
6
7 !!"hello" // true
8 !!1 // true
9 !!{} // true
10 !![] // true
17.Avoid modifying or passing arguments into other functions — it kills optimization(避免修改和传递arguments给其他方法 — 影响优化)
在JavaScript的方法里,arguments参数可以让你访问传递给该方法的所有参数。arguments是一个类数组对象;arguments可是使用数组标记访问,而且它有length参数,但是它没有filter, map, forEach这样内建到数组内的方法。因此,如下代码是一个非常常见的将arguments转换为数组的办法:
1 var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
2 //或者
3 var args = [].slice.call(arguments);
不幸的是,传递arguments给任何参数,将导致Chrome和Node中使用的V8引擎跳过对其的优化,这也将使性能相当慢。所以,正确的做法只有:
1 var args = new Array(arguments.length);
2 for(var i = 0; i < args.length; ++i) { 3 args[i] = arguments[i]; 4 }
18.Implementing asynchronous loop(实现异步循环)
试着写一个异步方法,每秒打印一次循环的索引值。
1 for (var i=0; i<5; i++) {
2 setTimeout(function(){ 3 console.log(i); 4 }, 1000); 5 }
但输出的结果会是5,5,5,5,5。这明显是有问题的,原因是:每次时间结束(timeout)都指向原始的i,而并非它的拷贝。所以,for循环使i增长到5,之后timeout运行并调用了当前i的值(也就是5)。
解决的办法是:有几个不同的方式可以拷贝i。最普通且常用方法是通过声明函数来建立一个闭包,并将i传给此函数。我们这里使用了自调用函数。
1 for (var i=0; i<5; i++) {
2 (function(num){ 3 setTimeout(function(){ 4 console.log(num); 5 }, 1000); 6 })(i); 7 }
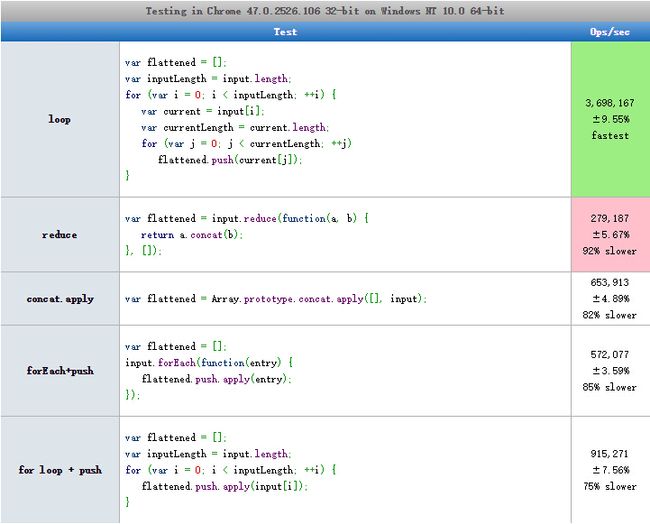
19.Flattening multidimensional Arrays in JavaScript(Javascript多维数组扁平化)
测试地址:http://jsperf.com/flatten-an-array-loop-vs-reduce/6
20.Using JSON.Stringify(使用JSON.Stringify)
加入有一个对象具有参数"prop1", "prop2", "prop3"。 我们可以通过传递 附加参数 给 JSON.stringify 来选择性将参数生成字符串,像这样:
1 var obj = {
2 'prop1': 'value1', 3 'prop2': 'value2', 4 'prop3': 'value3' 5 }; 6 7 var selectedProperties = ['prop1', 'prop2']; 8 9 var str = JSON.stringify(obj, selectedProperties); 10 11 // str 12 // {"prop1":"value1","prop2":"value2"}