linux字符设备驱动程序的编写
在此涉及到两个重要的结构体cdev和file_operations,前者为描述字符设备,后者为设备驱动程序的入口点。
对与file_operations的成员描述请看 file_operations中各项解析
我用图表示下在内核2.6版本后新版本的字符设备注册
上图这是驱动程序应该做的,但是要真正地使用它,我们还必须还要创建设备节点(linux的设备操作都是标准的文件操作,就是当作文件来处理,所以必须生成相应的设备文件,在创建时,制定了主设备号和次设备号,就和设备联系了起来)和插入内核,不使用的时候从内核中卸载掉
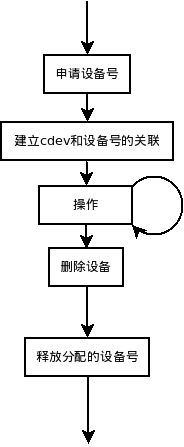
看这个图
整个的过程貌似这个,虚线框中的是字符驱动应该做的事。驱动与系统内核紧密联系的,所以这个程序都有规定好的格式,这也是必须的。
这两个函数是系统自动调用的
int init_module(void) 和void cleanup_module(void)
看函数名也知道这两个函数是在什么时候被调用,这两个相当于入口和出口,而对硬件的操作函数都在file_operations中被定义。结构体中除了一个数据成员外,其他的都是函数指针。在init的过程中我们需要填充这些指针,当应用程序使用open等系统调用对设备文件进行操作的时候,就会通过file_operations将此系统调用对应到驱动程序中的相应的函数来进行具体的操作。
1.设备号的分配
设备号是一个数字,用来标示设备。设备文件的创建要指明主设备号和次设备号。主设备号表明设备的类型,与一个确定的驱动程序对应,次设备号通常用来标明不同属性,例如不同的使用方法,不同的位置等,它标志某个具体的物理设备。
在2.6中,用dev_t类型来描述设备号,它是一个32位类型,高12为主设备号,后20为次设备号。使用MAJOR和MINOR取主次设备号,使用MKDEV来合并得到设备号。
设备号的分配分为两种:静态和动态。
静态分配知道主设备号,通过参数指定第一个设备号,通常次设备号为0,所以可以这么得到MKDEV(主设备号, 0)。
函数为int register_chrdev_region(dev_t first, unsigned int count, char* name)
count为设备号数目,name为设备名
动态分配通过参数仅需要第一个次设备号,通常为0,和分配的数目
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned int fristminor, char* name)
动态的时候需要注意,需要保存分配到的主设备号,不卸载设备的时候有麻烦。
释放已经分配的设备号使用unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t first, unsigned int count),不管动态还是静态。
2.字符设备的注册
在关联cdev和设备号之前,我们想来填充file_operations结构体,不然关联了也没有效果。
在linux中文件的基本操作是打开,释放和读写,在file_operations中肯定是有的。我们需要需要根据规定的定义(参数格式)来实现他们,我们实现的为
static int demo_open(struct inode *inodeP, struct file *fileP) static int demo_release(struct inode *inodeP, struct file *fileP) static ssize_t demo_read(struct file *fileP, char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos) static ssize_t demo_write(struct file *fileP, const char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
填充结构体
static struct file_operations demo_fops = {
owner:THIS_MODULE,
read:demo_read,
write:demo_write,
open:demo_open,
release:demo_release,
};
对cdev结构体的操作有下面几个函数
void cdev_init(struct cdev *, const struct file_operations *);//初始化,建立cdev和file_operation 之间的连接 struct cdev *cdev_alloc(void); //动态申请一个cdev内存 void cdev_put(struct cdev *p); //释放 int cdev_add(struct cdev *, dev_t, unsigned); //注册设备,通常发生在驱动模块的加载函数中 void cdev_del(struct cdev *);//注销设备,通常发生在驱动模块的卸载函数中
下面我贴出整个demo的源码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#define DEV_NAME "demo"
#define MAX_BUF_SIZE 1024
static struct cdev demo_cdev;
unsigned int major = 0;
static char *data = NULL;
/**
* [demo_open description]
* @param inodeP
* @param fileP
* @return
*/
static int demo_open(struct inode *inodeP, struct file *fileP)
{
printk("device open success!\n");
data = (char*)kmalloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_BUF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
memset(data, 0, MAX_BUF_SIZE);
return 0;
}
static int demo_release(struct inode *inodeP, struct file *fileP)
{
printk("release device\n");
if (data) {
kfree(data);
data = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
static ssize_t demo_read(struct file *fileP, char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
if (count < 0 ) {
/* code */
return -EINVAL;
}
if (count > MAX_BUF_SIZE) {
count = MAX_BUF_SIZE;
}
if (copy_to_user(buf, data, count) == EFAULT) {
/* code */
return -EFAULT;
}
printk("user read data from device!\n");
return count;
}
static ssize_t demo_write(struct file *fileP, const char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
if (count < 0 ) {
/* code */
return -EINVAL;
}
if (count > MAX_BUF_SIZE) {
count = MAX_BUF_SIZE;
}
memset(data, 0, MAX_BUF_SIZE);
if (copy_from_user(data, buf, count) == EFAULT) {
return -EFAULT;
}
printk("user write data to device\n");
return count;
}
static void setup_cdev(struct cdev *dev, int minor, struct file_operations *fops)
{
int err;
int devno;
devno = MKDEV(major, minor);
cdev_init(dev, fops);
dev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
dev->ops = fops;
err = cdev_add(dev, devno, 1);
if (err) {
printk(KERN_NOTICE" Error %d adding dev %d", err, minor);
}
}
static struct file_operations demo_fops = {
owner:THIS_MODULE,
read:demo_read,
write:demo_write,
open:demo_open,
release:demo_release,
};
/**
* [init_module description] 加载驱动模块时调用
* @return [description]
*/
int init_module(void)
{
int re;
dev_t dev = MKDEV(major, 0);
if (major) {
re = register_chrdev_region(dev, 1, DEV_NAME);
} else {
re = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 1, DEV_NAME);
}
if (re < 0) {
printk(KERN_WARNING" Demo dev-->unable to get major %d\n", major);
return re;
}
/**
* 如果是动态分配的则要改变原来的major不然在调用setup_cdev时会不能关联设备和设备号,
*
* 在cleanup_module时也不能从/proc/devices中删除相应的设备号项目
*/
major = MAJOR(dev);
setup_cdev(&demo_cdev, 0, &demo_fops);
printk("The major of the demo device is %d\n", major);
return 0;
}
void cleanup_module(void)
{
cdev_del(&demo_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, 0), 1);
printk("Demo device uninstalled\n");
}
Makefile的编写
在编译这些内核模块时,建议使用你kbuild
详细情况见 http://www.mjmwired.net/kernel/Documentation/kbuild/modules.txt
obj-m := demo.o all: $(MAKE) -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules clean: $(MAKE) -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
上面是Makefile文件
写了加载和卸载的shell脚本
#!/bin/bash
module="demo"
device="demo"
rm -f /dev/${device}
/sbin/insmod -f ./$module.ko $* || exit 1
#查找/proc/devices文件中demo对应的设备号
major=`cat /proc/devices | awk -v var=${module} '{if($2==var)print $1}'`
echo $major
mknod /dev/${device} c $major 0
#!/bin/bash
module="demo"
device="demo"
/sbin/rmmod $module $* || exit 1
rm -f /dev/${device}
exit 0
测试的代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define DEV_NAME "/dev/demo"
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int fd;
char buffer[BUF_SIZE];
fd = open(DEV_NAME, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open dev fail!\n");
return -1;
}
do {
printf("Input some worlds to kernel(enter 'quit' to exit)\n");
memset(buffer, 0 ,BUF_SIZE);
if (fgets(buffer, BUF_SIZE, stdin) == NULL) {
perror("fgets error!\n");
break;
}
buffer[strlen(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
if (write(fd, buffer, strlen(buffer)) < 0) {
perror("write error\n");
break;
}
if (read(fd, buffer, BUF_SIZE) < 0) {
perror("read error\n");
break;
} else {
printf("The read string is from kernel : %s\n", buffer);
}
} while(strncmp(buffer, "quit" , 4));
close(fd);
return 0;
}
无图无真相
加载和卸载可以用lsmod命令察看,执行了load.sh后,也可以去看看/proc/devives文件
补充一下,当major,也就是主设备号为0时,说明是动态注册。