mybatis核心组件详解——Executor(未完待续)
概述
Executor(org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor),执行器。
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
void clearLocalCache();
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
Transaction getTransaction();
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
它主要负责执行给定的MappedStatement对象和参数对象,以获取最终的结果List。在执行过程中,还涉及到缓存的操作和维护。
Executor对象随着SqlSession的创建而创建,被保存在SqlSession对象中,因此Executor的生命周期与SqlSession一致。
// DefaultSqlSessionFactory创建DefaultSqlSession的逻辑
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level,
boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 创建SqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call
// close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
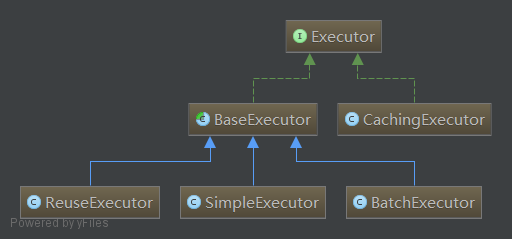
mybatis框架内部的执行器体系如下:
BaseExecutor是所有执行器实现类的基类,它只实现了基本的功能,其中包括对本地缓存(也就是我们所说的一级缓存)的操作和维护。子类需要实现具体的执行逻辑,包括:doUpdate更新逻辑、doQuery查询逻辑以及doFlushStatements批处理逻辑。
SimpleExecutor是Executor的最简单实现,它不支持批处理,且执行逻辑很简单:
创建StatemenHandler对象
调用StatemenHandler生成要执行的Statement(jdbc接口)对象
调用StatemenHandler执行Statement对象,并处理产生的结果,然后返回
ReuseExecutor额外在内部维护了一个Map,它可以实现复用还没有关闭连接的Statement对象。
// key为sql语句,value为Statement对象 private final Map<String, Statement> statementMap = new HashMap<String, Statement>();
BatchExecutor的doUpdate更新操作是批量执行,每一次更新操作保存在内部的statementList中,每调用一次flushStatements()进行一次批量执行。commit时会调用flushStatements(),查询操作时也会调用flushStatements()。
CachingExecutor,缓存执行器。可以把它理解为一个装饰器,主要负责二级缓存的操作和维护。